Building Dynamic Forms in Angular for Enterprise Applications
Introduction
Dynamic forms are useful for enterprise applications where form structures need to be flexible, configurable, and generated at runtime based on business requirements. This approach allows developers to create forms from configuration objects rather than hardcoding them, enabling greater flexibility and maintainability.
Benefits
- Flexibility: Forms can be easily modified without changing the code.
- Reusability: Form components can be shared across components.
- Maintainability: Changes to form structures can be managed through configuration files or databases.
- Scalability: New form fields and types can be added without significant code changes.
- User Experience: Dynamic forms can adapt to user roles and permissions, providing a tailored experience.
Architecture
1. Defining Form Configuration Models
We will define form configuration model as a first step. This models stores field types, labels, validation rules, and other metadata.
1.1. Form Field Configuration
Form field configuration interface represents individual form fields and contains properties like type, label, validation rules and conditional logic.
export interface FormFieldConfig {
key: string;
value?: any;
type: 'text' | 'email' | 'number' | 'select' | 'checkbox' | 'date' | 'textarea';
label: string;
placeholder?: string;
required?: boolean;
disabled?: boolean;
options?: { key: string; value: any }[];
validators?: ValidatorConfig[]; // Custom validators
conditionalLogic?: ConditionalRule[]; // For showing/hiding fields based on other field values
order?: number; // For ordering fields in the form
gridSize?: number; // For layout purposes, e.g., Bootstrap grid size (1-12)
}
1.2. Validator Configuration
Validator configuration interface defines validation rules for form fields.
export interface ValidatorConfig {
type: 'required' | 'email' | 'minLength' | 'maxLength' | 'pattern' | 'custom';
value?: any;
message: string;
}
1.3. Conditional Logic
Conditional logic interface defines rules for showing/hiding or enabling/disabling fields based on other field values.
export interface ConditionalRule {
dependsOn: string;
condition: 'equals' | 'notEquals' | 'contains' | 'greaterThan' | 'lessThan';
value: any;
action: 'show' | 'hide' | 'enable' | 'disable';
}
2. Dynamic Form Service
We will create dynamic form service to handle form creation and validation processes.
@Injectable({
providedIn: 'root'
})
export class DynamicFormService {
// Create form group based on fields
createFormGroup(fields: FormFieldConfig[]): FormGroup {
const group: any = {};
fields.forEach(field => {
const validators = this.buildValidators(field.validators || []);
const initialValue = this.getInitialValue(field);
group[field.key] = new FormControl({
value: initialValue,
disabled: field.disabled || false
}, validators);
});
return new FormGroup(group);
}
// Returns an array of form field validators based on the validator configurations
private buildValidators(validatorConfigs: ValidatorConfig[]): ValidatorFn[] {
return validatorConfigs.map(config => {
switch (config.type) {
case 'required':
return Validators.required;
case 'email':
return Validators.email;
case 'minLength':
return Validators.minLength(config.value);
case 'maxLength':
return Validators.maxLength(config.value);
case 'pattern':
return Validators.pattern(config.value);
default:
return Validators.nullValidator;
}
});
}
private getInitialValue(field: FormFieldConfig): any {
switch (field.type) {
case 'checkbox':
return false;
case 'number':
return 0;
default:
return '';
}
}
}
3. Dynamic Form Component
The main component that renders the form based on the configuration it receives as input.
@Component({
selector: 'app-dynamic-form',
template: `
<form [formGroup]="dynamicForm" (ngSubmit)="onSubmit()" class="dynamic-form">
@for (field of sortedFields; track field.key) {
<div class="row">
<div [ngClass]="'col-md-' + (field.gridSize || 12)">
<app-dynamic-form-field
[field]="field"
[form]="dynamicForm"
[isVisible]="isFieldVisible(field)"
(fieldChange)="onFieldChange($event)">
</app-dynamic-form-field>
</div>
</div>
}
<div class="form-actions">
<button
type="button"
class="btn btn-secondary"
(click)="onCancel()">
Cancel
</button>
<button
type="submit"
class="btn btn-primary"
[disabled]="!dynamicForm.valid || isSubmitting">
{{ submitButtonText() }}
</button>
</div>
</form>
`,
styles: [`
.dynamic-form {
display: flex;
gap: 0.5rem;
flex-direction: column;
}
.form-actions {
display: flex;
justify-content: flex-end;
gap: 0.5rem;
}
`],
imports: [ReactiveFormsModule, CommonModule, DynamicFormFieldComponent],
})
export class DynamicFormComponent implements OnInit {
fields = input<FormFieldConfig[]>([]);
submitButtonText = input<string>('Submit');
formSubmit = output<any>();
formCancel = output<void>();
private dynamicFormService = inject(DynamicFormService);
dynamicForm!: FormGroup;
isSubmitting = false;
fieldVisibility: { [key: string]: boolean } = {};
ngOnInit() {
this.dynamicForm = this.dynamicFormService.createFormGroup(this.fields());
this.initializeFieldVisibility();
this.setupConditionalLogic();
}
get sortedFields(): FormFieldConfig[] {
return this.fields().sort((a, b) => (a.order || 0) - (b.order || 0));
}
onSubmit() {
if (this.dynamicForm.valid) {
this.isSubmitting = true;
this.formSubmit.emit(this.dynamicForm.value);
} else {
this.markAllFieldsAsTouched();
}
}
onCancel() {
this.formCancel.emit();
}
onFieldChange(event: { fieldKey: string; value: any }) {
this.evaluateConditionalLogic(event.fieldKey);
}
isFieldVisible(field: FormFieldConfig): boolean {
return this.fieldVisibility[field.key] !== false;
}
private initializeFieldVisibility() {
this.fields().forEach(field => {
this.fieldVisibility[field.key] = !field.conditionalLogic?.length;
});
}
private setupConditionalLogic() {
this.fields().forEach(field => {
if (field.conditionalLogic) {
field.conditionalLogic.forEach(rule => {
const dependentControl = this.dynamicForm.get(rule.dependsOn);
if (dependentControl) {
dependentControl.valueChanges.subscribe(() => {
this.evaluateConditionalLogic(field.key);
});
}
});
}
});
}
private evaluateConditionalLogic(fieldKey: string) {
const field = this.fields().find(f => f.key === fieldKey);
if (!field?.conditionalLogic) return;
field.conditionalLogic.forEach(rule => {
const dependentValue = this.dynamicForm.get(rule.dependsOn)?.value;
const conditionMet = this.evaluateCondition(dependentValue, rule.condition, rule.value);
this.applyConditionalAction(fieldKey, rule.action, conditionMet);
});
}
private evaluateCondition(fieldValue: any, condition: string, ruleValue: any): boolean {
switch (condition) {
case 'equals':
return fieldValue === ruleValue;
case 'notEquals':
return fieldValue !== ruleValue;
case 'contains':
return fieldValue && fieldValue.includes && fieldValue.includes(ruleValue);
case 'greaterThan':
return Number(fieldValue) > Number(ruleValue);
case 'lessThan':
return Number(fieldValue) < Number(ruleValue);
default:
return false;
}
}
private applyConditionalAction(fieldKey: string, action: string, shouldApply: boolean) {
const control = this.dynamicForm.get(fieldKey);
switch (action) {
case 'show':
this.fieldVisibility[fieldKey] = shouldApply;
break;
case 'hide':
this.fieldVisibility[fieldKey] = !shouldApply;
break;
case 'enable':
if (control) {
shouldApply ? control.enable() : control.disable();
}
break;
case 'disable':
if (control) {
shouldApply ? control.disable() : control.enable();
}
break;
}
}
private markAllFieldsAsTouched() {
Object.keys(this.dynamicForm.controls).forEach(key => {
this.dynamicForm.get(key)?.markAsTouched();
});
}
}
4. Dynamic Form Field Component
This component renders individual form fields, handling different types and validation messages based on the configuration.
@Component({
selector: 'app-dynamic-form-field',
template: `
@if (isVisible) {
<div class="field-container" [formGroup]="form">
@if (field.type === 'text') {
<!-- Text Input -->
<div class="form-group">
<label [for]="field.key">{{ field.label }}</label>
<input
[id]="field.key"
[formControlName]="field.key"
[placeholder]="field.placeholder || ''"
class="form-control"
[class.is-invalid]="isFieldInvalid()">
@if (isFieldInvalid()) {
<div class="invalid-feedback">
{{ getErrorMessage() }}
</div>
}
</div>
} @else if (field.type === 'select') {
<!-- Select Dropdown -->
<div class="form-group">
<label [for]="field.key">{{ field.label }}</label>
<select
[id]="field.key"
[formControlName]="field.key"
class="form-control"
[class.is-invalid]="isFieldInvalid()">
<option value="">Please select...</option>
@for (option of field.options; track option.key) {
<option
[value]="option.key">
{{ option.value }}
</option>
}
</select>
@if (isFieldInvalid()) {
<div class="invalid-feedback">
{{ getErrorMessage() }}
</div>
}
</div>
} @else if (field.type === 'checkbox') {
<!-- Checkbox -->
<div class="form-group form-check">
<input
type="checkbox"
[id]="field.key"
[formControlName]="field.key"
class="form-check-input"
[class.is-invalid]="isFieldInvalid()">
<label class="form-check-label" [for]="field.key">
{{ field.label }}
</label>
@if (isFieldInvalid()) {
<div class="invalid-feedback">
{{ getErrorMessage() }}
</div>
}
</div>
} @else if (field.type === 'email') {
<!-- Email Input -->
<div class="form-group">
<label [for]="field.key">{{ field.label }}</label>
<input
type="email"
[id]="field.key"
[formControlName]="field.key"
[placeholder]="field.placeholder || ''"
class="form-control"
[class.is-invalid]="isFieldInvalid()">
@if (isFieldInvalid()) {
<div class="invalid-feedback">
{{ getErrorMessage() }}
</div>
}
</div>
} @else if (field.type === 'textarea') {
<!-- Textarea -->
<div class="form-group">
<label [for]="field.key">{{ field.label }}</label>
<textarea
[id]="field.key"
[formControlName]="field.key"
[placeholder]="field.placeholder || ''"
rows="4"
class="form-control"
[class.is-invalid]="isFieldInvalid()">
</textarea>
@if (isFieldInvalid()) {
<div class="invalid-feedback">
{{ getErrorMessage() }}
</div>
}
</div>
}
</div>
<!-- Add more field types as needed-->
}
`,
imports: [ReactiveFormsModule],
})
export class DynamicFormFieldComponent implements OnInit {
@Input() field!: FormFieldConfig;
@Input() form!: FormGroup;
@Input() isVisible: boolean = true;
@Output() fieldChange = new EventEmitter<{ fieldKey: string; value: any }>();
ngOnInit() {
const control = this.form.get(this.field.key);
if (control) {
control.valueChanges.subscribe(value => {
this.fieldChange.emit({ fieldKey: this.field.key, value });
});
}
}
isFieldInvalid(): boolean {
const control = this.form.get(this.field.key);
return !!(control && control.invalid && (control.dirty || control.touched));
}
getErrorMessage(): string {
const control = this.form.get(this.field.key);
if (!control || !control.errors) return '';
const validators = this.field.validators || [];
for (const validator of validators) {
if (control.errors[validator.type]) {
return validator.message;
}
}
// Fallback error messages
if (control.errors['required']) return `${this.field.label} is required`;
if (control.errors['email']) return 'Please enter a valid email address';
if (control.errors['minlength']) return `Minimum length is ${control.errors['minlength'].requiredLength}`;
if (control.errors['maxlength']) return `Maximum length is ${control.errors['maxlength'].requiredLength}`;
return 'Invalid input';
}
}
5. Usage Example
@Component({
selector: 'app-home',
template: `
<div class="row">
<div class="col-4 offset-4">
<app-dynamic-form
[fields]="formFields"
submitButtonText="Save User"
(formSubmit)="onSubmit($event)"
(formCancel)="onCancel()">
</app-dynamic-form>
</div>
</div>
`,
imports: [DynamicFormComponent]
})
export class HomeComponent {
@Input() title: string = 'Home Component';
formFields: FormFieldConfig[] = [
{
key: 'firstName',
type: 'text',
label: 'First Name',
placeholder: 'Enter first name',
required: true,
validators: [
{ type: 'required', message: 'First name is required' },
{ type: 'minLength', value: 2, message: 'Minimum 2 characters required' }
],
gridSize: 12,
order: 1
},
{
key: 'lastName',
type: 'text',
label: 'Last Name',
placeholder: 'Enter last name',
required: true,
validators: [
{ type: 'required', message: 'Last name is required' }
],
gridSize: 12,
order: 2
},
{
key: 'email',
type: 'email',
label: 'Email Address',
placeholder: 'Enter email',
required: true,
validators: [
{ type: 'required', message: 'Email is required' },
{ type: 'email', message: 'Please enter a valid email' }
],
order: 3
},
{
key: 'userType',
type: 'select',
label: 'User Type',
required: true,
options: [
{ key: 'admin', value: 'Administrator' },
{ key: 'user', value: 'Regular User' },
{ key: 'guest', value: 'Guest User' }
],
validators: [
{ type: 'required', message: 'Please select user type' }
],
order: 4
},
{
key: 'adminNotes',
type: 'textarea',
label: 'Admin Notes',
placeholder: 'Enter admin-specific notes',
conditionalLogic: [
{
dependsOn: 'userType',
condition: 'equals',
value: 'admin',
action: 'show'
}
],
order: 5
}
];
onSubmit(formData: any) {
console.log('Form submitted:', formData);
// Handle form submission
}
onCancel() {
console.log('Form cancelled');
// Handle form cancellation
}
}
Result
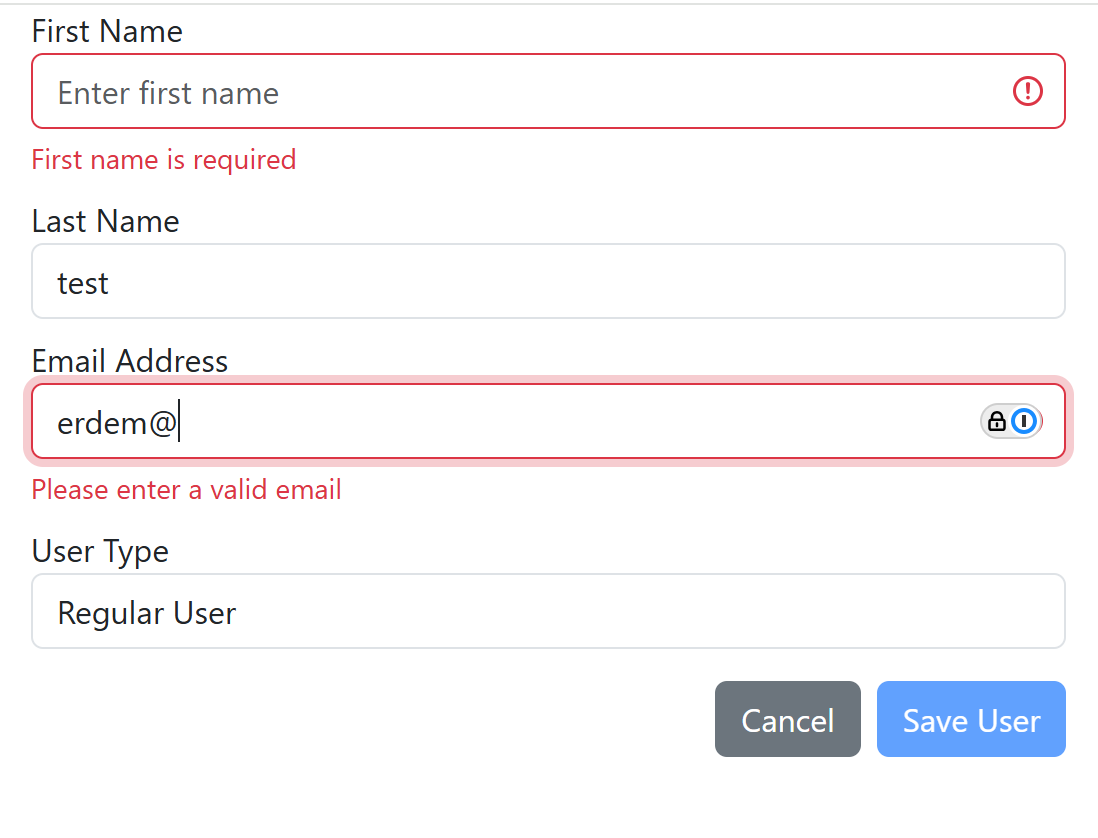
Conclusion
These kinds of components are essential for large applications because they allow for rapid development and easy maintenance. By defining forms through configuration, developers can quickly adapt to changing requirements without extensive code changes. This approach also promotes consistency across the application, as the same form components can be reused in different contexts.
































































Comments
Enis Necipoğlu 20 weeks ago
This is config-driven form wizardry at its finest