Consuming gRPC Services from Blazor WebAssembly Application Using gRPC-Web
WARNING: I've demonstrated Using gRPC with the ABP Framework in my latest post. If you haven't seen it, you should read it before this article, since this is a continuation of that article.
In this second part, I will show how to consume the gRPC service from the Blazor WebAssembly application, using the gRPC-Web technology.
This will be a short article, based on Microsoft's gRPC-Web in ASP.NET Core gRPC apps and Code-first gRPC services and clients with .NET documents. For more information, I suggest to check these documents. Let's get started...
Configuring the Server Side
First of all, the server-side should support gRPC-Web. Follow the steps below to enable it:
Add Grpc.AspNetCore.Web Package
Add Grpc.AspNetCore.Web NuGet package to the ProductManagement.HttpApi.Host project.
Add GrpcWeb Middleware
Add the following line just before the app.UseConfiguredEndpoints(...) line to add the GrpcWeb middleware to your ASP.NET Core request pipeline:
app.UseGrpcWeb(new GrpcWebOptions { DefaultEnabled = true });
Configure Cors
ABP's startup template already configures Cors when you create a new solution. However, we need to allow some extra headers in our Cors configuration.
Add the following line just after the .WithAbpExposedHeaders() line in the OnApplicationInitialization method of the ProductManagementHttpApiHostModule class:
.WithExposedHeaders("Grpc-Status", "Grpc-Message", "Grpc-Encoding", "Grpc-Accept-Encoding")
Finally, call RequireCors extension method just after the MapGrpcService calls:
app.UseConfiguredEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints
.MapGrpcService<IProductAppService>()
.RequireCors("__DefaultCorsPolicy"); // Configure Cors for the product service
});
__DefaultCorsPolicy may seem a magic string here. Let me explain it: ABP startup template configures the default Cors policy with the context.Services.AddCors(...) method (you can see it in the source code). If we define a named policy, we should use the same name here. However, when we don't specify, ASP.NET Core uses __DefaultCorsPolicy as the policy name by default. If you don't want to use the magic string, you can resolve the IOptions<CorsOptions> service and get the DefaultPolicyName from the CorsOption object.
Anyway, that's all on the server-side. We can work on he client now.
Configuring the Client Side
ProductManagement.Blazor is the Blazor WebAssembly application in the solution I'd created in the first article. We will configure that project to be able to consume the server-side gRPC services from our Blazor application.
Add Client-side Nuget Packages
Add Grpc.Net.Client, Grpc.Net.Client.Web and protobuf-net.Grpc NuGet packages to the ProductManagement.Blazor project. We are ready to consume the gRPC services.
Consume the Product Service
Change the Pages/Index.razor.cs file's content with the following code block:
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Net.Http;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Grpc.Net.Client;
using Grpc.Net.Client.Web;
using ProductManagement.Products;
using ProtoBuf.Grpc.Client;
namespace ProductManagement.Blazor.Pages;
public partial class Index
{
private List<ProductDto> Products { get; set; } = new();
protected override async Task OnInitializedAsync()
{
var channel = GrpcChannel.ForAddress("https://localhost:10042", new GrpcChannelOptions
{
HttpHandler = new GrpcWebHandler(new HttpClientHandler())
});
var productAppService = channel.CreateGrpcService<IProductAppService>();
Products = await productAppService.GetListAsync();
}
}
- We've created a gRPC channel for the server-side endpoint (surely, you get the address from a configuration) with channel options by specifying that we will use the
GrpcWebHandler. - We've created a service proxy object using the
CreateGrpcServiceextension method that is defined by the protobuf-net.Grpc NuGet package. - We've used the service proxy object,
productAppService, to consume remote endpoint just like a local service.
That's all. If we want to show the products on the page, we can add the following markup into the Pages/Index.razor view:
<h2>A list of products:</h2>
<ul class="list-group">
@foreach(var product in Products)
{
<li class="list-group-item">
@product.Name <br/>
<small>@product.Id.ToString()</small>
</li>
}
</ul>
Run the applications (first run the ProductManagement.HttpApi.Host project, then run the ProductManagement.Blazor project in the solution) to see it in action:
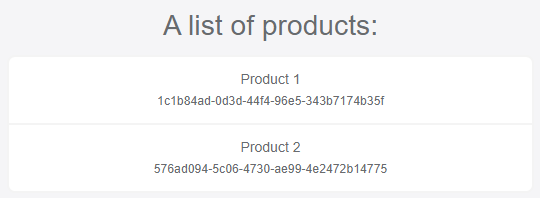
Conclusion
In the first part of this article, I'd demonstrated how to implement a gRPC service and consume it in a client application, using the code-first approach. In this article, I've demonstrated how to consume the same gRPC service from a Blazor WebAssembly application, using the gRPC-Web technology. As you see in these two articles, using gRPC with the ABP Framework is straightforward.
The Source Code
- You can find the completed source code here: https://github.com/abpframework/abp-samples/tree/master/GrpcDemo2
- You can also see all the changes I've done in this article here: https://github.com/abpframework/abp-samples/pull/201/files






























































Comments
No one has commented yet, be the first to comment!