Microservice Startup Template
This startup template is not feature complete and well documented yet. However, we found it valuable to share with the ABP Commercial customers. That doesn't mean it is not production ready. You can start to develop your real solution today. But we will improve it and write more documentation for different development and deployment scenarios.
The Microservice Startup Template is a generic solution to start a new microservice solution.
While we accept that every microservice solution will be different and every system has its own design requirements and trade-offs, we believe such a startup solution is a very useful starting point for most of the solutions, and a useful example for others.
Overall
This section introduce the solution structure and briefly explains the solution components. The following diagram is an overview of the applications, gateways, services, databases and other components;
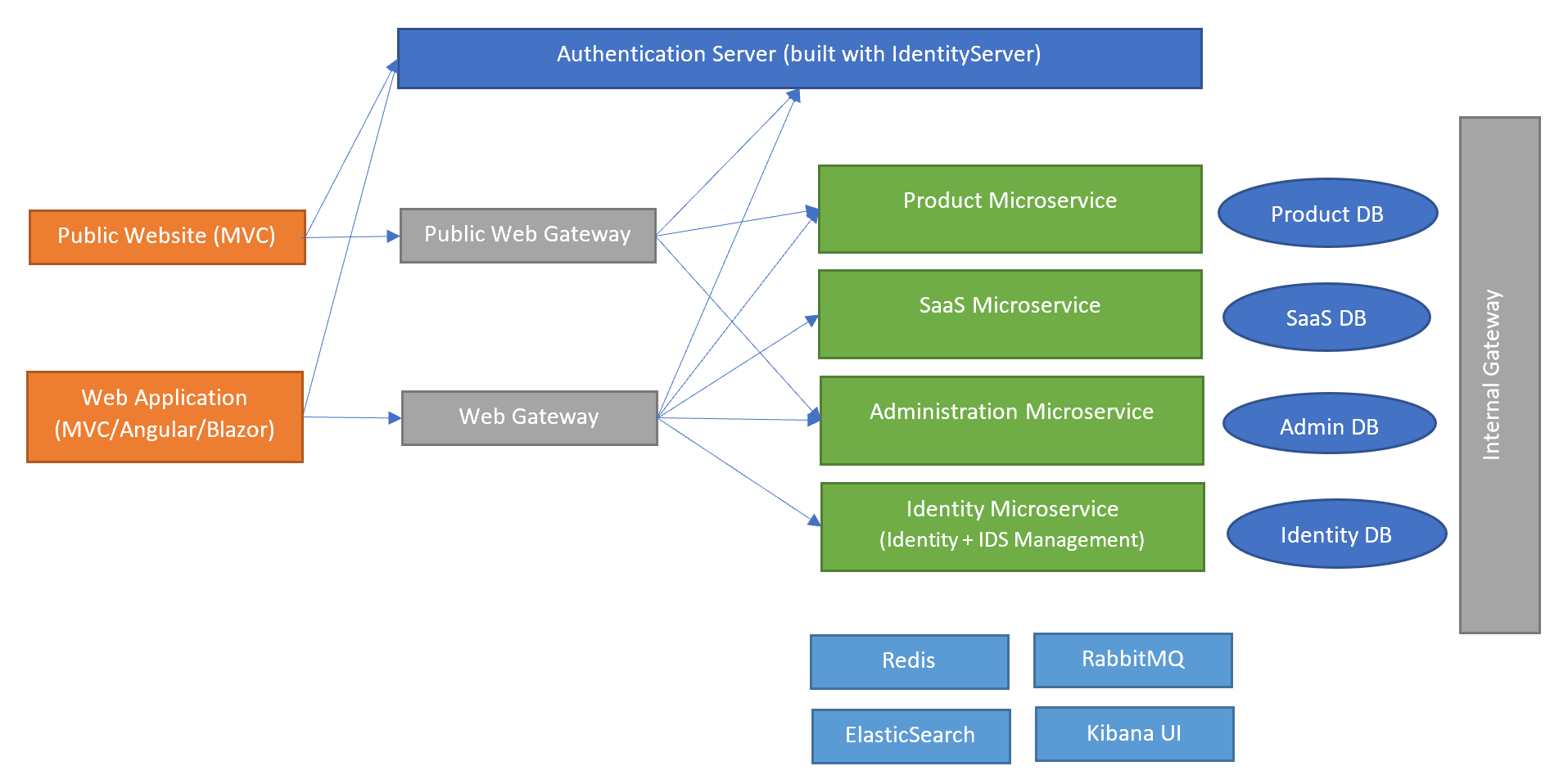
Figure: Overall Diagram of the Solution (not all associations are shown, for the sake of simplicity)
- The Authentication Server is a web application that is used as the single sign-on authentication server. It hosts the login, register, forgot password, two factor authentication, profile management... pages, OAuth endpoints and authentication related APIs. All applications and services use this application as a central authority for the authentication.
- There are two web applications in the solution (you can add more yourself);
- The Web Application is the main UI of the system. It uses the Authentication Server to make users login to the application. Then it uses the Web Gateway to access to the HTTP APIs. You mostly develop your UI here. Based on your preference, it can be an MVC (Razor Pages), Angular or Blazor application.
- The Public Website is a second web application that can be used to develop your landing page for the application. If you don't need, you can just remove it. It uses the Authentication Server to make users login to the application. Then it uses the Public Web Gateway to access to the HTTP APIs.
- There are three API gateways in the solution (you can add more if you need);
- The Web Gateway is a BFF (Backend for Frontend) that provides the necessary HTTP APIs to the Web Application.
- The Public Web Gateway is a BFF (Backend for Frontend) that provides the necessary HTTP APIs to the Public Web Application.
- Internal Gateway is used for communication of microservices internally. We found it useful to access to other microservices over an API Gateway. Details and alternatives will be discussed.
- There are four microservices coming with the solution (you can split existing ones and add new ones);
- Identity Microservice is used to manage users, roles, clients, resources... in the system.
- SaaS Microservice is used to manage tenants and editions for a multi-tenant system. If your system is not multi-tenant, you can remove this service and its database from the solution.
- Administration Microservice is mostly related to infrastructure requirements like permissions, settings, audit logs, dynamic localizations and BLOB storing. This service and the related database can be splitted based on your design decisions.
- Product Microservice is an example microservices that can be investigated to learn how to develop your own microservices.
- There are four databases, each is owned by the related microservice. Databases are SQL Server with EF Core integrated in the applications. You can switch to another RDBMS or MongoDB for any of them. Administration and SaaS databases are used by other services since they contains cross-cutting style data (like permissions and audit logs) that is needed by all services. The reasons behind this design decision will be discussed and alternative implementations will be explained.
- There are some infrastructure services are configured in the solution (they are configured to run with docker-compose);
- Redis is used as a distributed cache server.
- RabbitMQ is used a a distributed event/message bus.
- ElasticSearch is used as a central point to write application logs.
- Kibana is used to visualize the logs in the Elasticsearch database.
Get Started
This document explains how to start development with this solution template.
Pre-Requirements
The following tools are required in order to run the solution;
- Visual Studio 2019 (v16.8+) or another suitable IDE.
- SQL Server (If you want to use localdb, you need to change the connection strings. If you want to use another RDBMS, you need to switch the provider)
- .NET 5.0+ SDK
- NPM v14+ (or Yarn 1.20+).
- Powershell 5.0+
- Docker Desktop v3.0+
Other dependencies (like Redis and RabbitMQ) comes with a docker-compose configuration, so no external installation required.
Downloading the Solution
Use the ABP Suite to create a new solution by selecting the Microservice as the project type.
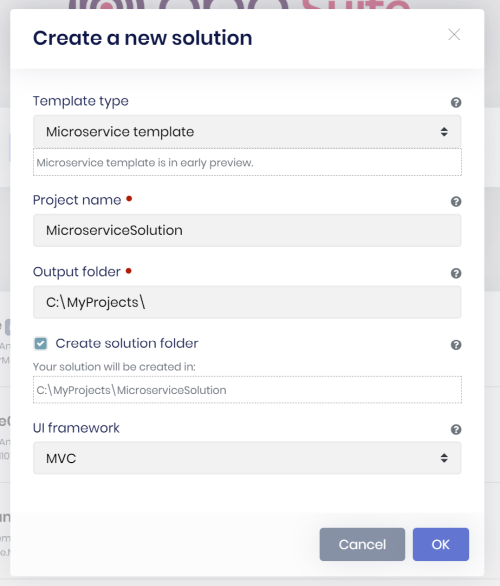
Type
abp suitein a command line terminal to start the ABP Suite.
Run the Infrastructure
The root folder of the solution contains a run-infrastructure.ps1 file. Execute it to run the necessary infrastructure services:
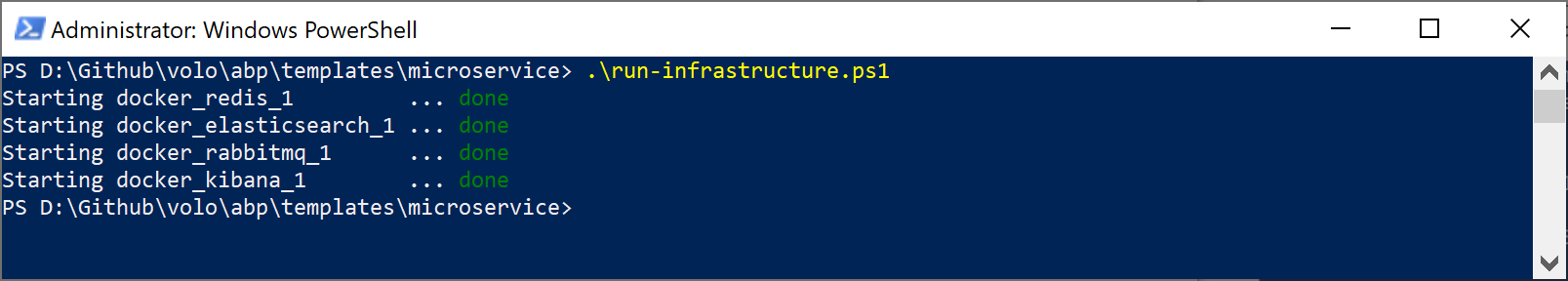
First running may contain additional steps and take a long time since it will download the missing Docker images.
Create the Databases
The root folder of the solution contains a update-databases.ps1 file. Execute it to create all the databases in one step:
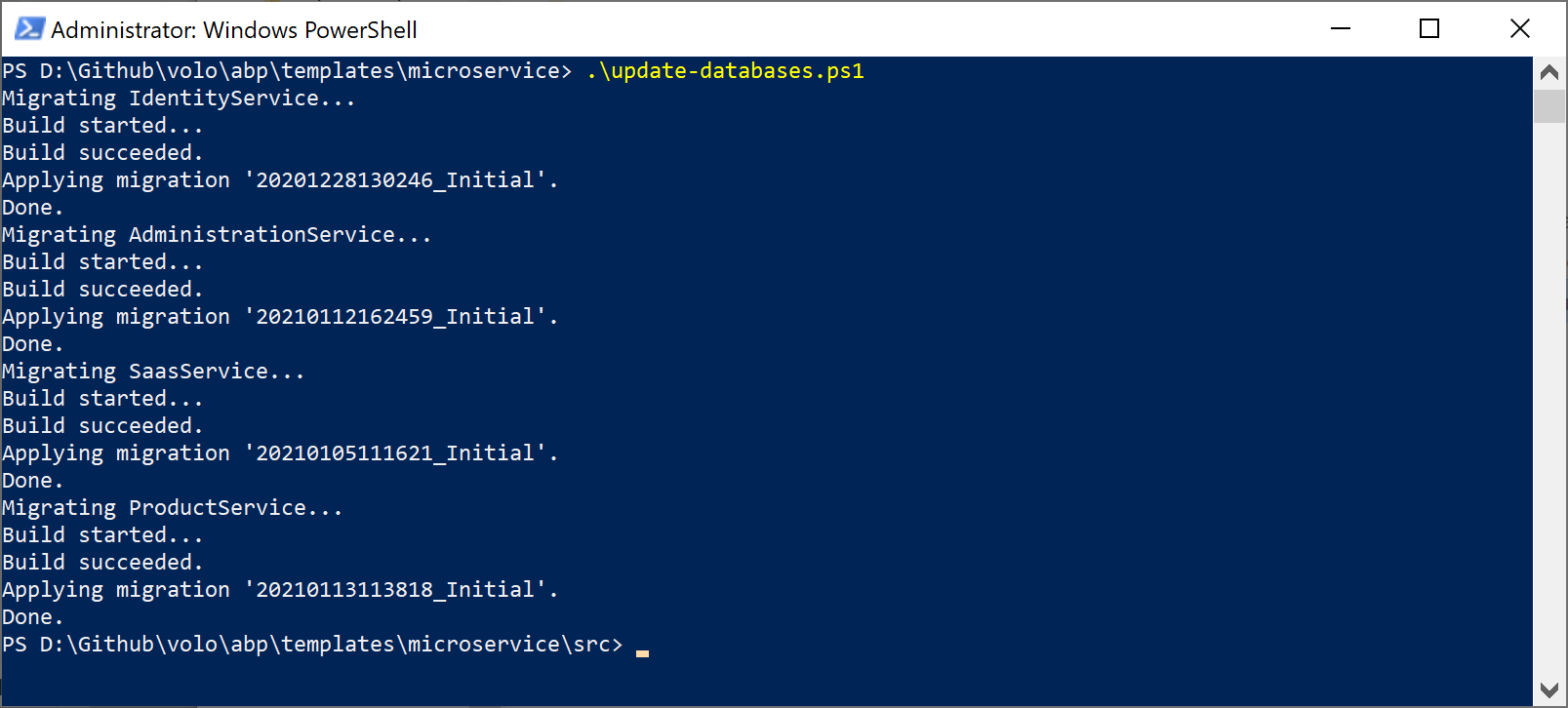
It creates four databases in the SQL Server:

Open the Solution
Now, you can open the solution in Visual Studio or your favorite IDE. You will see a solution structure similar to the figure below (solution and project names will be different based on your naming preference);
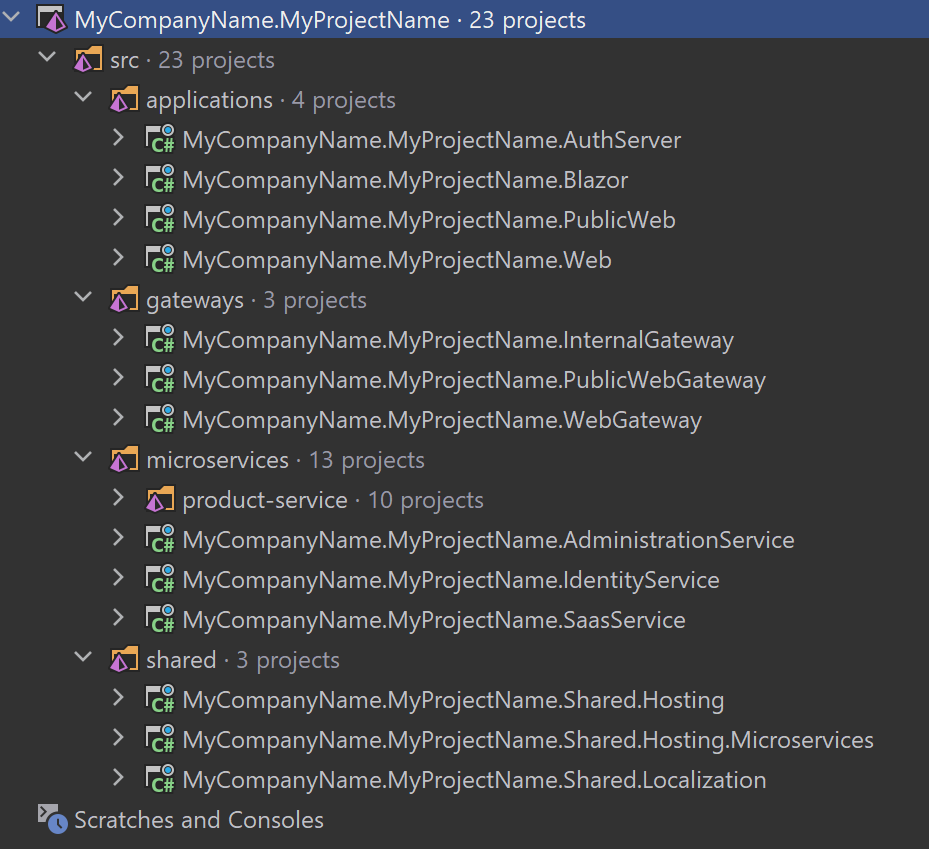
Figure: The solution structure (it will be a slightly different based on your UI preference).
Run the Solution
The system consists of multiple applications should be running together.
Running the Authentication Server
First, run the AuthServer application.
Right click to the project, Set as Startup Project and hit Ctrl+F5 while running the applications if you don't need to DEBUG it.
It will open a Login page:
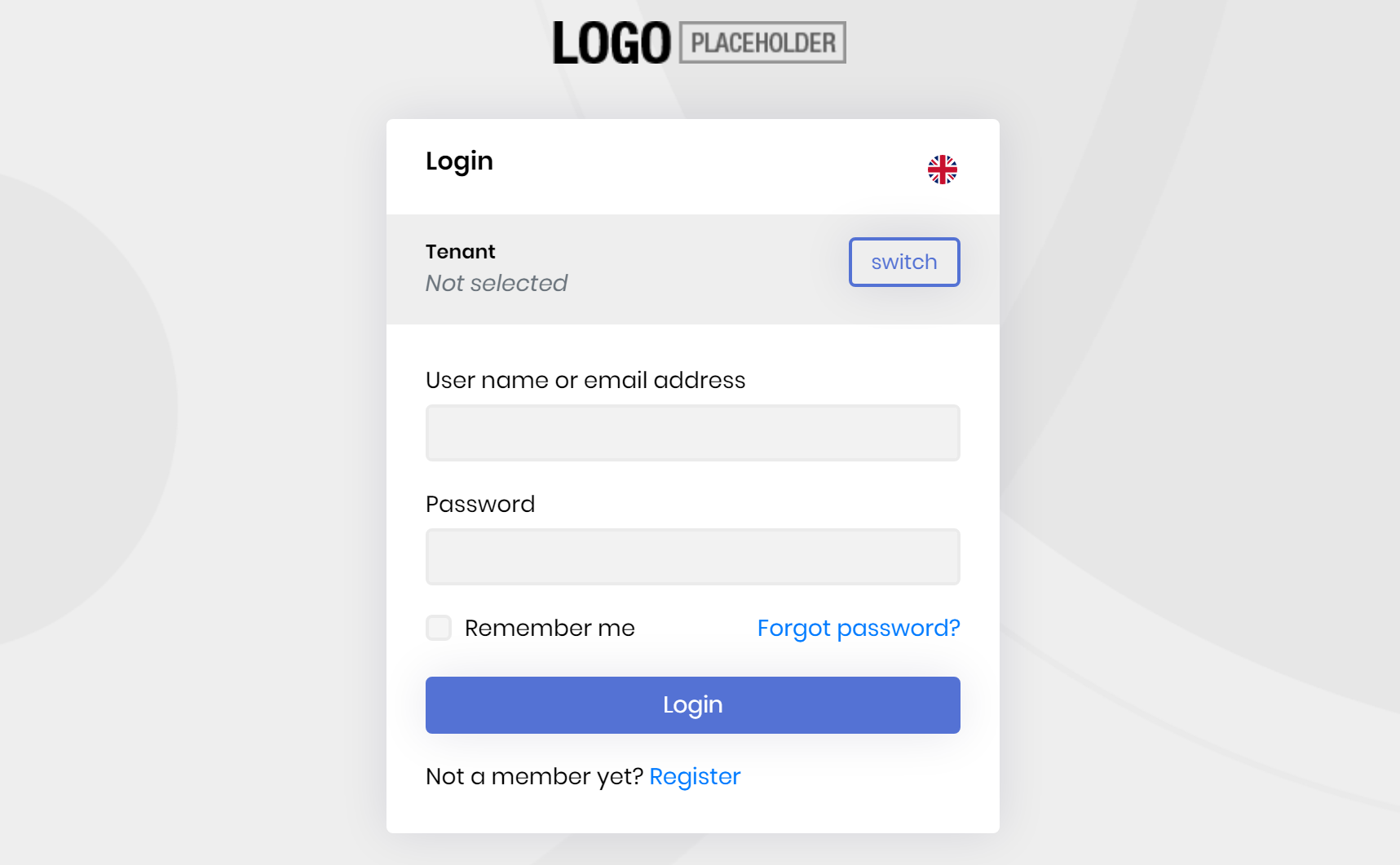
If you want to test it, enter admin as the username and 1q2w3E* as the password and hit ENTER. If you login successfully, you are redirected a developer test page that lists the current user claims:

You can change this page however you like. Users are typically redirected to the Authentication Server from the other applications to login the system and they are automatically redirected to the client application after the login process. If you want, this test page can be converted to a landing page that contains links to your actual applications.
Running the Services
Run the following applications in the given order (right click to each project, Set as Startup Project and hit Ctrl+F5) to make the services running;
- InternalGateway
- AdministrationService
- IdentityService
- SaasService
- product-service/HttpApi.Host
Notice: Visual Studio may stop a previously started service (we think it is kind of a bug of the VS). In this case, re-start the stopped application. Alternatively, you can run the project or projects in a command line terminal, using the
dotnet runcommand.
All these applications open a Swagger UI to explore the HTTP APIs. For example, the screenshot below was taken from the SaasService:
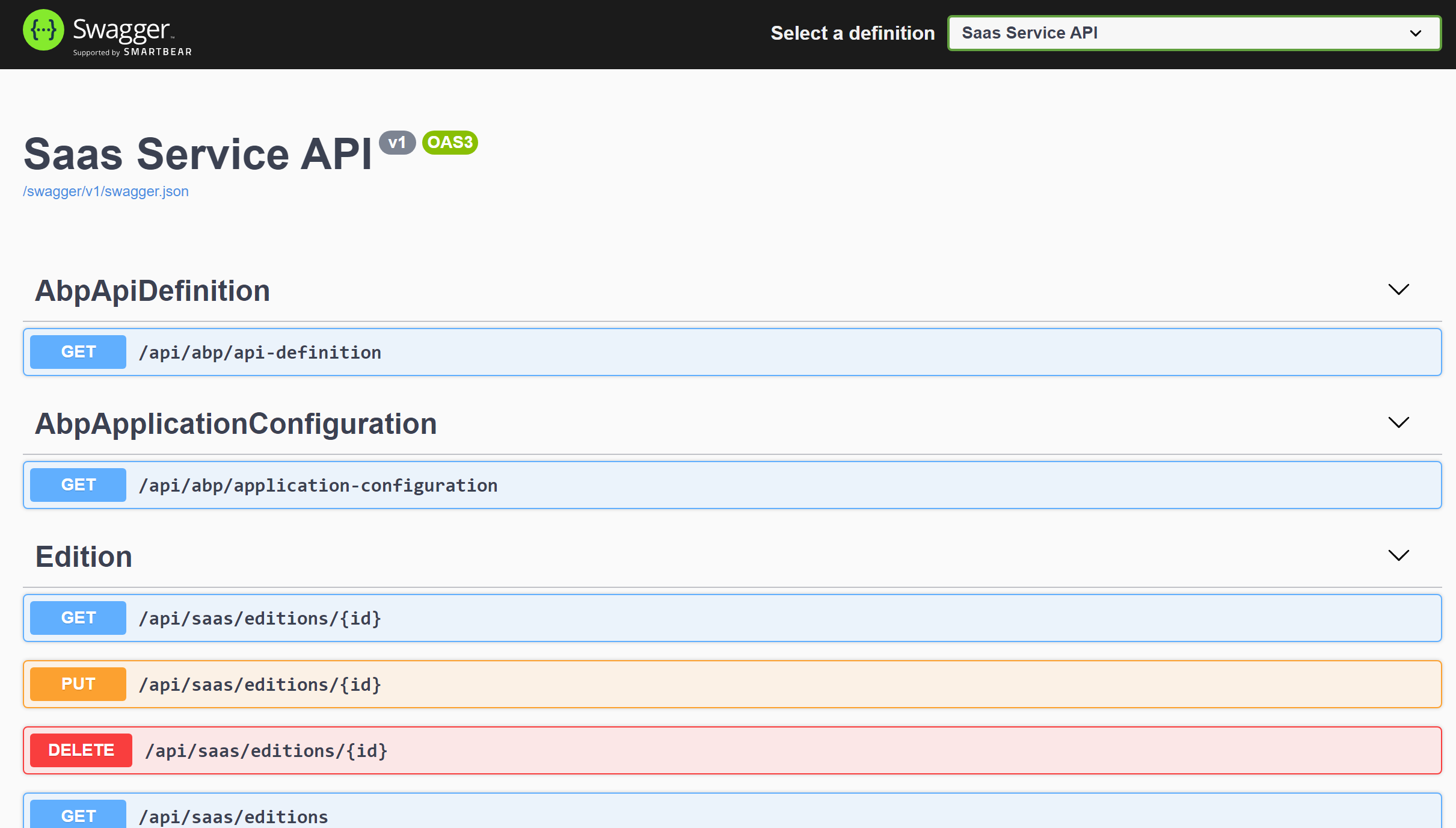
Running the Main Web Application
The main Web Application can be an MVC (Razor Pages), Angular or Blazor application based on your preference. Regardless of your frontend application, you first need to run the WebGateway application.
Run the Web Gateway
When you run the WebGateway application, it opens a Swagger UI to explore the HTTP APIs provided by this API Gateway:
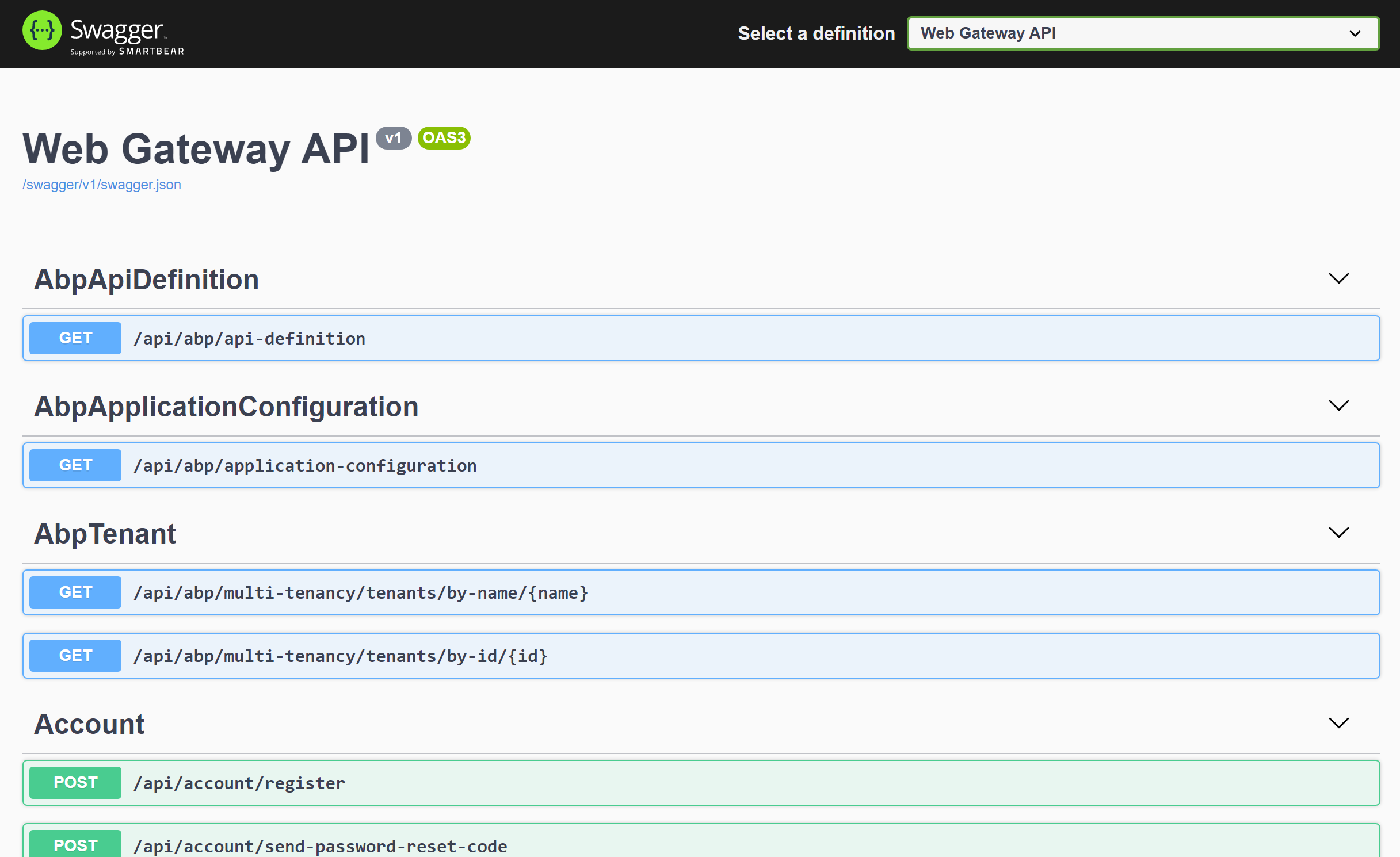
API Gateways in this solution truly shows the APIs they expose. That's normally not possible with using Swagger and Ocelot. However, we have developed a solution to make this possible by using a proper layering and code sharing. Details will be covered later.
Run the MVC (Razor Pages) Web Application
You can skip this section if you haven't selected the MVC (Razor Pages) as the main web application UI framework.
Run the Web application in the solution.
Run the Blazor Web Application
You can skip this section if you haven't selected the Blazor as the main web application UI framework.
Run the Blazor application in the solution.
Run the Angular Web Application
You can skip this section if you haven't selected the Angular as the main web application UI framework.
- Open a command line terminal in the
angularfolder in the root folder of the solution. - Execute
npm install(oryarnif you prefer Yarn as the package manager). - Execute
yarn start.
Login to the Web Application
This will begin the Main Web Application:
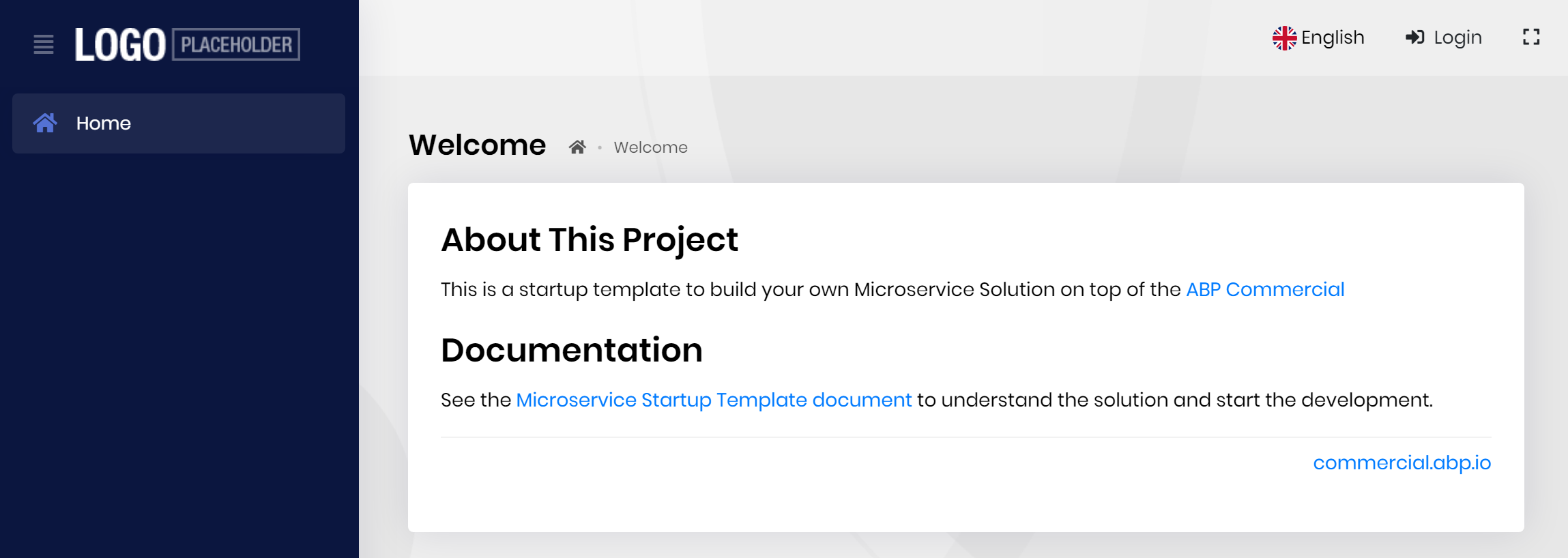
Click to the Login link. It will redirect to the Authentication Server. Enter admin as the username and 1q2w3E* as the password to login to the system. You will be redirected back to the web application.
If you have previously logged into the Authentication Server then you are automatically login to this application when you click to the Login link thanks to the single sign on system.
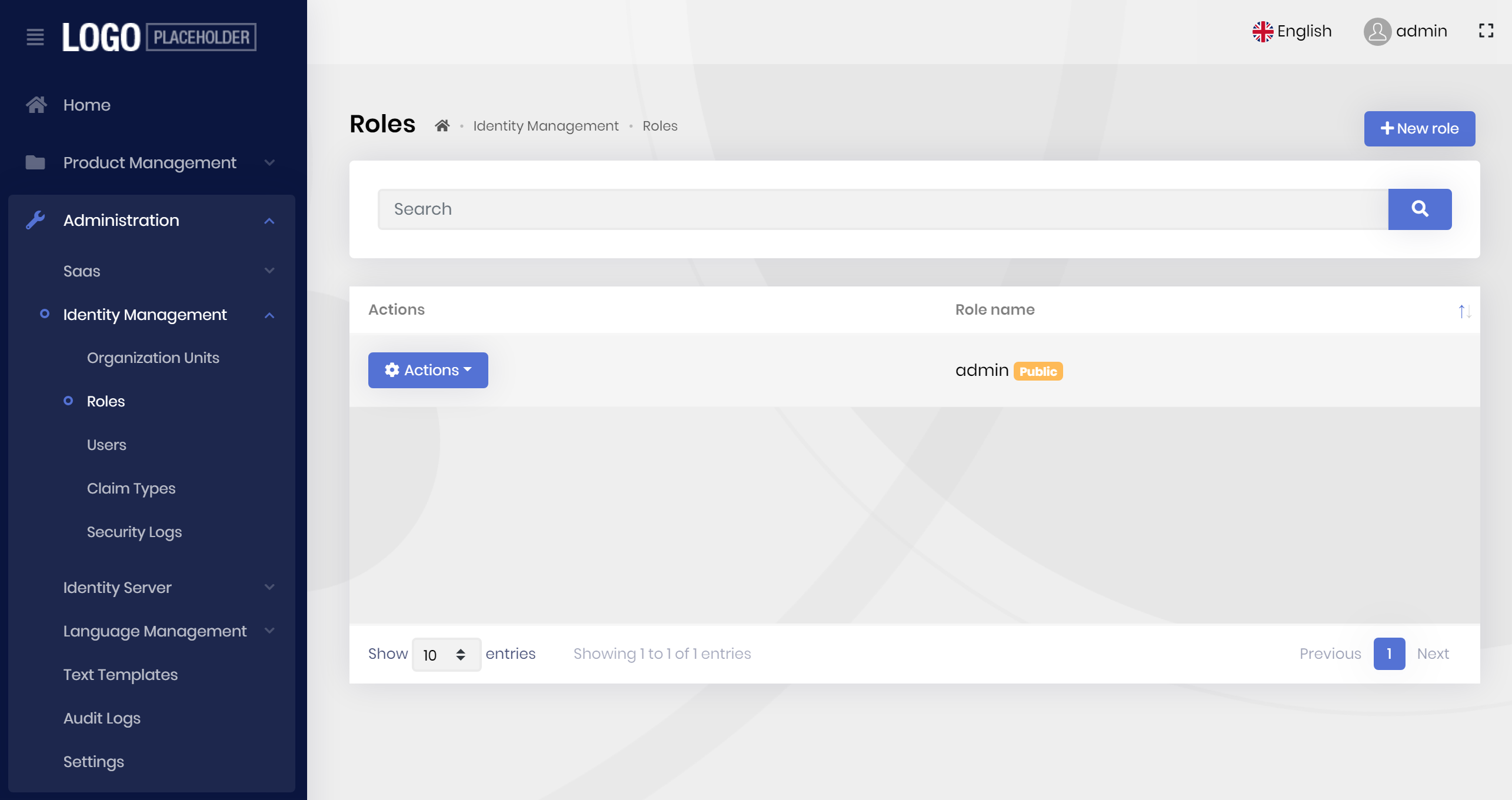
Grant the Permissions
When you first login the the application, you won't see much items on the main menu:

This is because not all the permissions have been granted for the admin role. Click to the Actions menu for the admin role and grant all the permissions as shown below:
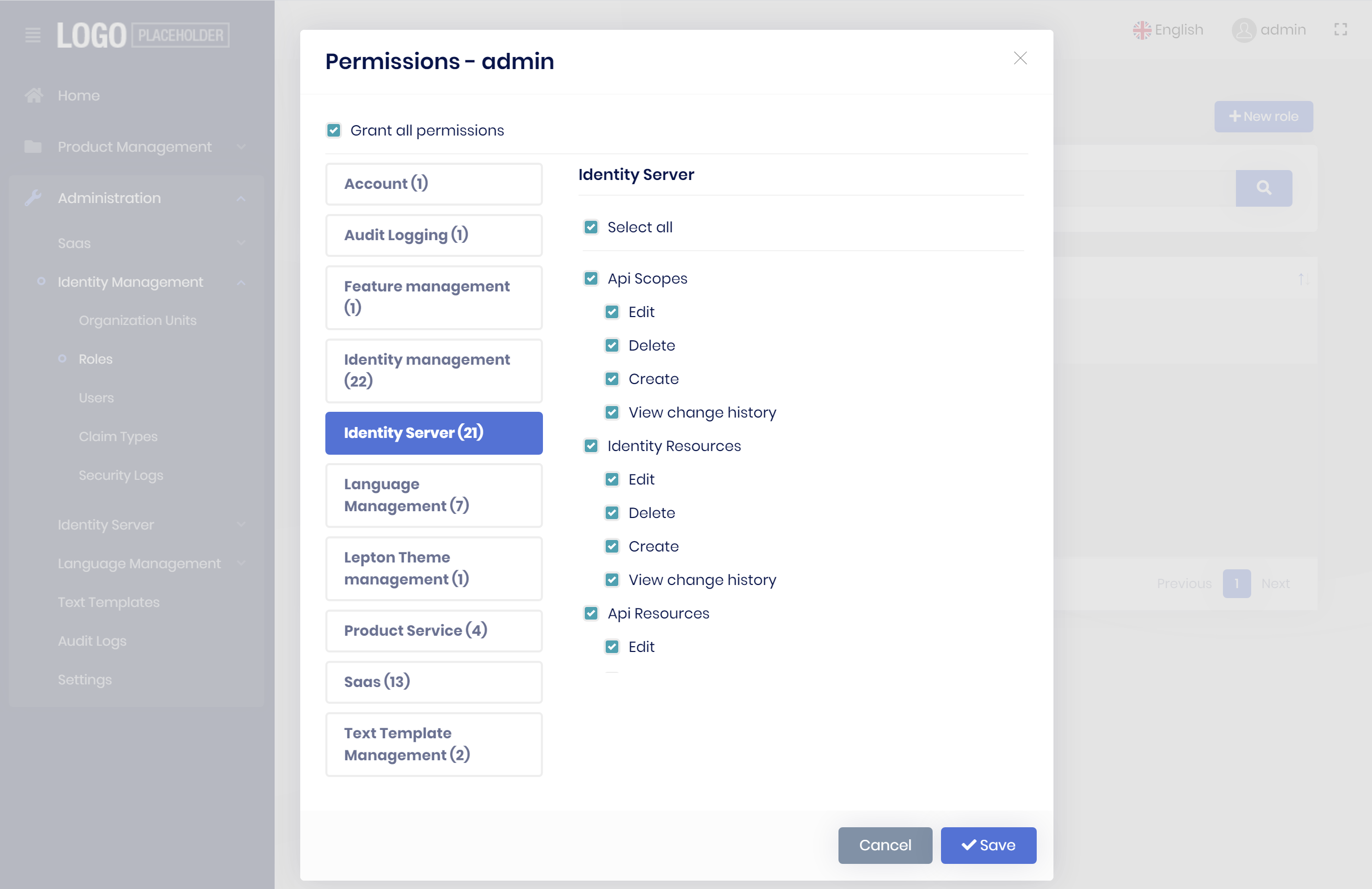
Then you will be able to see all the menu items for the modules pre-installed into the solution:
Running the Public Website
The Public Web Site application uses the Public Web Gateway, so we need to run it first.
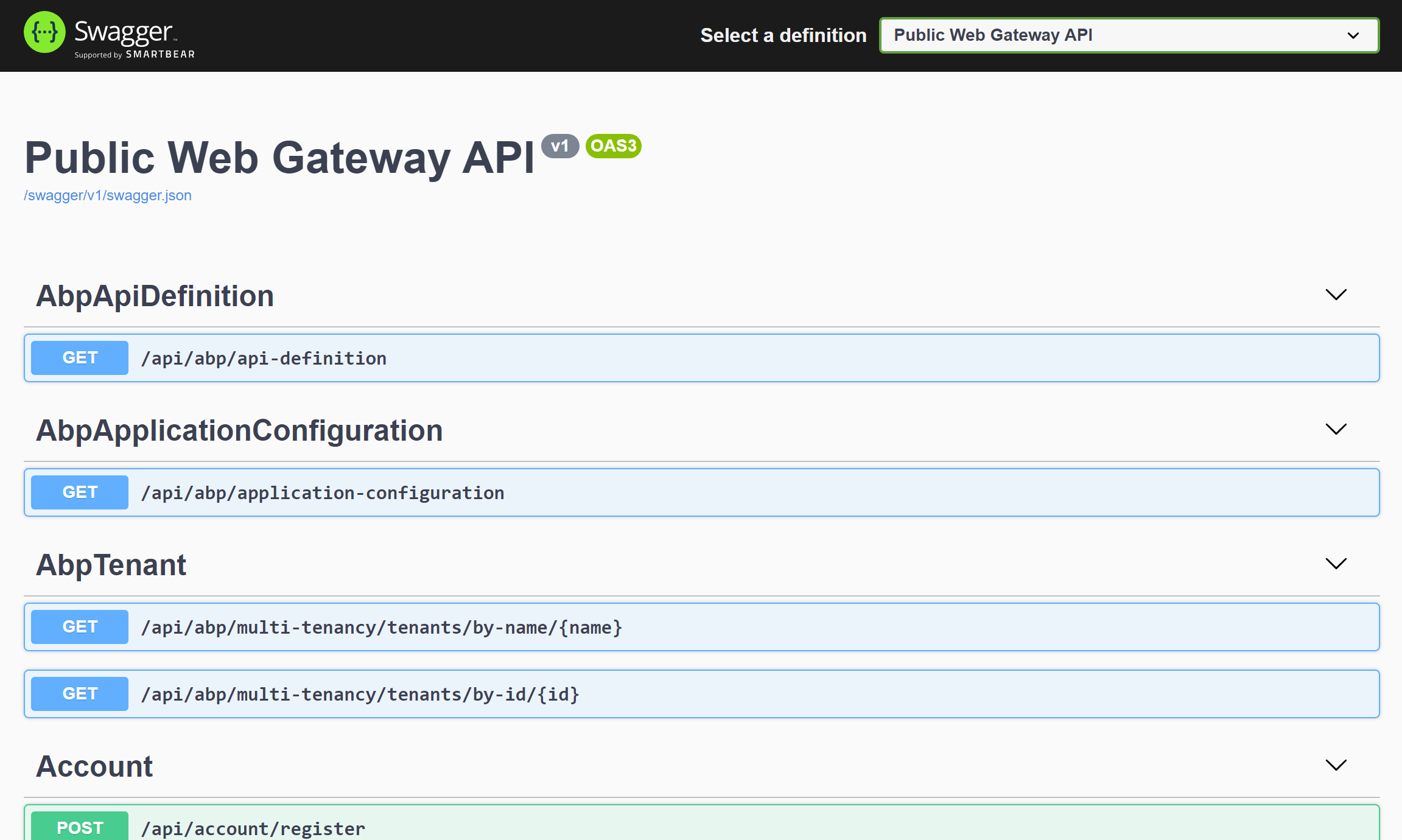
Run the Public Web Gateway
When you run the PublicWebGateway application, it opens a Swagger UI to explore the HTTP APIs provided by this API Gateway:
Run the Public Website
Now, you can run the PublicWeb application:

This is an example application if you need to a public/landing page for your system. It supports login (with single sign-on support) via the Authentication Server.


 Hurry up, ends March 14!
Hurry up, ends March 14!



