Developing a Multi-Timezone Application Using the ABP Framework
When developing multi-timezone applications, we need to handle users from different time zones and make sure they see the correct time. The system also needs to support users changing their timezone (like when traveling or moving) and make sure all time displays update correctly to show accurate time information.
All these scenarios require us to handle timezone conversions correctly in our application. The ABP framework provides a complete solution for these challenges.
In this article, we'll show you step by step how to handle multi-timezone in the ABP framework.
The content mentioned in this article will be available after the ABP 9.2 version
Timezone Settings
The ABP framework provides a setting called Abp.Timing.TimeZone for setting and getting the timezone of users, tenants, or applications. The default value is empty, which means the application will use the server's time zone. Check out the Timing documentation for more information.
ISO 8601 Date Time Format
Different countries and regions may use different time formats:
- Year-Month-Day (YYYY-MM-DD): Mainly used in China, Japan, Korea, Canada (official standard), Germany (ISO standard), ISO 8601 international standard, etc. Example: 2025-03-11
- Day-Month-Year (DD-MM-YYYY): Mainly used in UK, India, Australia, New Zealand, most European countries (like France, Germany, Italy, Spain), some South American countries, etc. Example: 11-03-2025 or 11/03/2025
- Month-Day-Year (MM-DD-YYYY): Mainly used in USA, Philippines, some parts of Canada, etc. Example: 03-11-2025 or 03/11/2025
- Day.Month.Year (DD.MM.YYYY): Mainly used in Germany, Russia, Switzerland, Hungary, Czech Republic, etc. Example: 11.03.2025
Also, different countries/regions might use different separators (like slash /, hyphen -, dot .), and some countries use different month abbreviations or full names (like March 11, 2025).
ISO 8601 uses a standard format to avoid confusion between different date formats and ensure global compatibility.
It has 4 parts:
- Date part:
YYYY-MM-DD Tas a separator- Time part:
HH:MM:SS - Timezone part:
Zor+/-HH:MM
You'll usually see formats like: YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SSZ or YYYY-MM-DDTHH:MM:SS+/-HH:MM, for example: 2025-03-11T10:30:00Z or 2025-03-11T22:30:00+03:00
When our application needs to handle multiple timezones, we usually use ISO 8601 to represent time.
Enabling Multi-Timezone Support
When we set the Kind of AbpClockOptions to DateTimeKind.Utc, the ABP framework will normalize all times. Times written to the database and returned to the frontend will be in UTC. the SupportsMultipleTimezone property will be true in the IClock service.
Configure<AbpClockOptions>(options =>
{
options.Kind = DateTimeKind.Utc;
});
Using DateTime to Store Time
Assuming the DateTime stored in the database is 2025-03-01 10:30:00, then the time returned to the front end will be 2025-03-01T10:30:00Z. This is a time in ISO 8601 format. Because DateTime does not have timezone information, the framework will assume it is UTC time.
Using DateTimeOffset to Store Time
If you use DateTimeOffset to store time, the ABP framework will not normalize DateTimeOffset, but will return it directly to the front end.
Assuming the DateTimeOffset stored in the database is 2025-03-01 13:30:00 +03:00, then the time returned to the front end will be 2025-03-01T13:30:00+03:00. This is also a time in ISO 8601 format.
We recommend using DateTimeOffset to store time because it has timezone information.
Timezone Conversion
Converting UTC Time to User Time
The IClock service has 2 methods to convert a given UTC time to the user time:
DateTime ConvertToUserTime(utcDateTime dateTime)
DateTimeOffset ConvertToUserTime(DateTimeOffset dateTimeOffset)
If
SupportsMultipleTimezoneisfalseordateTime.Kindis notUtcor no timezone is set, it will return the givenDateTimeorDateTimeOffsetwithout any changes.
Example:
If the user's timezone is Europe/Istanbul
// 2025-03-01T05:30:00Z
var utcTime = new DateTime(2025, 3, 1, 5, 30, 0, DateTimeKind.Utc);
var userTime = Clock.ConvertToUserTime(utcTime);
// Europe/Istanbul has 3 hours difference with UTC. So, the result will be 3 hours later.
userTime.Kind.ShouldBe(DateTimeKind.Unspecified);
userTime.ToString("O").ShouldBe("2025-03-01T08:30:00");
// 2025-03-01T05:30:00Z
var utcTime = new DateTimeOffset(new DateTime(2025, 3, 1, 5, 30, 0, DateTimeKind.Utc), TimeSpan.Zero);
var userTime = Clock.ConvertToUserTime(utcTime);
// Europe/Istanbul has 3 hours difference with UTC. So, the result will be 3 hours later.
userTime.Offset.ShouldBe(TimeSpan.FromHours(3));
userTime.ToString("O").ShouldBe("2025-03-01T08:30:00.0000000+03:00");
Converting User Time to UTC
The IClock service has 1 method to convert a given user time to UTC.
DateTime ConvertToUtc(DateTime dateTime)
If
SupportsMultipleTimezoneisfalseordateTime.KindisUtcor no timezone is set, it will return the givenDateTimewithout any changes.
Example:
If the user's timezone is Europe/Istanbul
// 2025-03-01T05:30:00
var userTime = new DateTime(2025, 3, 1, 5, 30, 0, DateTimeKind.Unspecified); //Same as Local
var utcTime = Clock.ConvertToUtc(userTime);
// Europe/Istanbul has 3 hours difference with UTC. So, the result will be 3 hours earlier.
utcTime.Kind.ShouldBe(DateTimeKind.Utc);
utcTime.ToString("O").ShouldBe("2025-03-01T02:30:00.0000000Z");
Handling Timezone in Different UIs
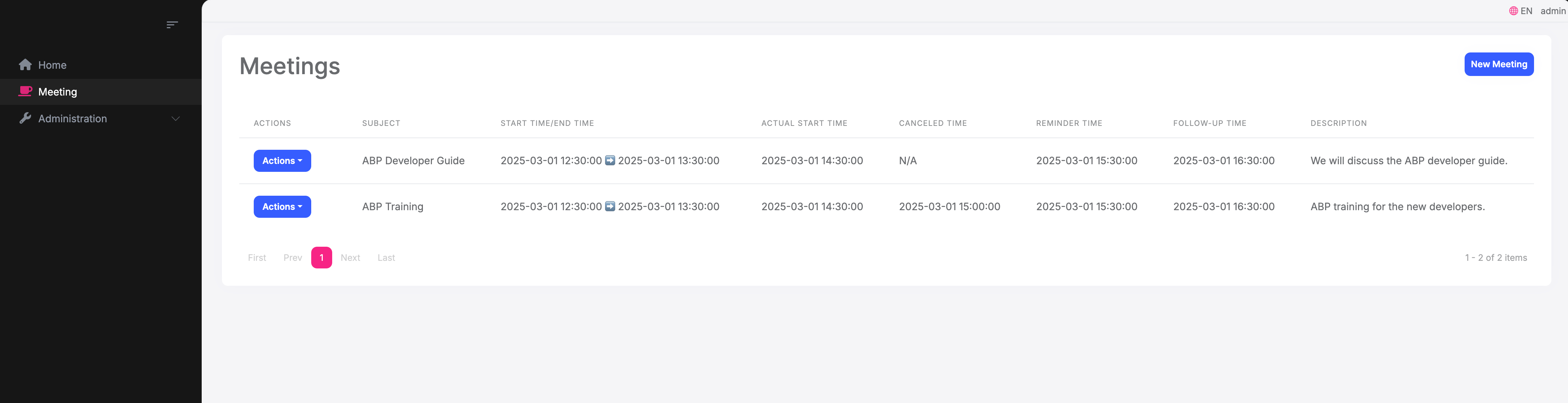
We'll use the TimeZoneApp project to demonstrate handling timezone in different UIs. It has a Meeting entity, with several time properties.
public class Meeting : AggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public string Subject { get; set; }
public DateTime StartTime { get; set; }
public DateTime EndTime { get; set; }
public DateTime ActualStartTime { get; set; }
public DateTime? CanceledTime { get; set; }
public DateTimeOffset ReminderTime { get; set; }
public DateTimeOffset? FollowUpTime { get; set; }
public string Description { get; set; }
}
TimeZoneApp project is an ABP layered architecture project, it sets a global Europe/Istanbul timezone, it contains 4 websites
API.Host: API website, it does not have UI, it returns data in JSON formatAuthServer: Authentication server, it uses Razor Pages as UIWeb: Razor Pages website, it uses JavaScript to manage Meeting creation and editing and displayBlazor: Blazor Server website, it uses Blazor to manage Meeting creation and editing and display
All 4 applications are enabled for multi-timezone support, and use the UseAbpTimeZone middleware.
Blazor WASM and Angular do not need to use the
UseAbpTimeZonemiddleware
DateTime in API Response
In the API response, we usually use the ISO 8601 format time, as you can see, after enabling multi-timezone support, the API returns time to the front end as UTC time.
2025-03-01T09:30:00Z and 2025-03-01T12:30:00+00:00 are ISO 8601 format time.
[
{
"subject": "ABP Developer Guide",
"startTime": "2025-03-01T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2025-03-01T10:30:00Z",
"actualStartTime": "2025-03-01T11:30:00Z",
"canceledTime": null,
"reminderTime": "2025-03-01T12:30:00+00:00",
"followUpTime": "2025-03-01T13:30:00+00:00",
"description": "We will discuss the ABP developer guide.",
"id": "2af0abd3-be06-ecff-5d4c-3a1895ac7950"
},
{
"subject": "ABP Training",
"startTime": "2025-03-01T09:30:00Z",
"endTime": "2025-03-01T10:30:00Z",
"actualStartTime": "2025-03-01T11:30:00Z",
"canceledTime": "2025-03-01T12:00:00Z",
"reminderTime": "2025-03-01T12:30:00+00:00",
"followUpTime": "2025-03-01T13:30:00+00:00",
"description": "ABP training for the new developers.",
"id": "290b0cb6-3e50-6324-1e79-3a1895ac795f"
}
]
Handling Timezone in MVC/Razor Pages
In the AuthServer project, we handle time conversion in a simple way:
- First, we get the
Meetingentities from the database usingIRepository<Meeting, Guid>. At this point, allDateTimevalues are in UTC. - Then, when displaying the times in the view, we use
Clock.ConvertToUserTimeto show them in the user's timezone.
Note: The
ConvertToUserTimemethod will only convert times if multi-timezone support is enabled in the application.
public class IndexModel : AbpPageModel
{
public List<Meeting>? Meetings { get; set; }
protected IRepository<Meeting, Guid> MeetingRepository { get; }
public IndexModel(IRepository<Meeting, Guid> meetingRepository)
{
MeetingRepository = meetingRepository;
}
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
Meetings = await MeetingRepository.GetListAsync();
}
}
<div class="container">
<abp-row>
<div class="table-responsive">
<table class="table table-striped table-hover mt-3">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>@L["Subject"]</th>
<th>@L["StartTime"] / @L["EndTime"]</th>
<th>@L["ActualStartTime"]</th>
<th>@L["CanceledTime"]</th>
<th>@L["ReminderTime"]</th>
<th>@L["FollowUpTime"]</th>
<th>@L["Description"]</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
@foreach (var meeting in Model.Meetings)
{
<tr>
<td>@meeting.Subject</td>
<td>@Clock.ConvertToUserTime(meeting.StartTime) ➡️ @Clock.ConvertToUserTime(meeting.EndTime)</td>
<td>@Clock.ConvertToUserTime(meeting.ActualStartTime)</td>
<td>@(meeting.CanceledTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUserTime(meeting.CanceledTime.Value) : "N/A")</td>
<td>@Clock.ConvertToUserTime(meeting.ReminderTime).DateTime</td>
<td>@(meeting.FollowUpTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUserTime(meeting.FollowUpTime.Value).DateTime : "N/A")</td>
<td>@meeting.Description</td>
</tr>
}
</tbody>
</table>
</div>
</abp-row>
</div>
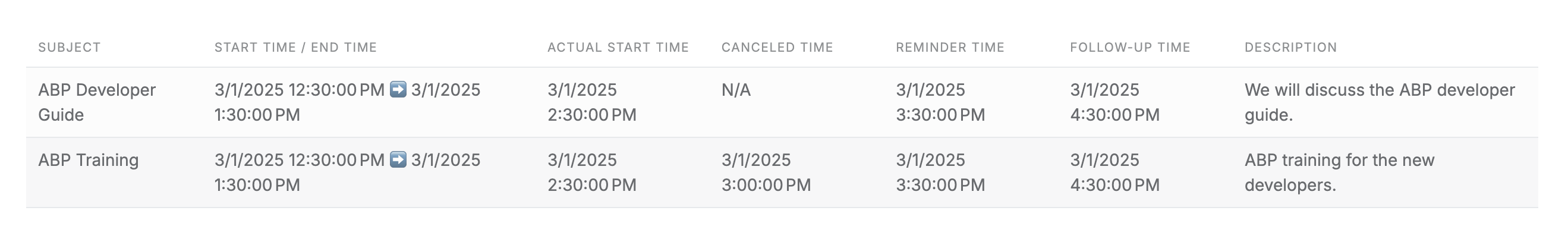
Handling Timezone in JavaScript
In the Web project, we use JavaScript to handle timezone.
Displaying Time in UI
timeZoneApp.meetings.meeting.getListgets allMeetingentities and displays them inDataTablesabp.clock.normalizeToLocaleString()is the ABP JavaScript API, it convertsUTCtime to the current user's timezone, and then calls itstoLocaleStringmethod to format timedataFormat: "datetime"is the ABP DataTable extension method, it calls theabp.clock.normalizeToLocaleStringmethod to convert and format time
If the current application is not enabled for multi-timezone support, then the
abp.clock.normalizeToLocaleStringmethod will not convert the time, it will just call theDateobject'stoLocaleStringmethod.
var dataTable = $('#MeetingsTable').DataTable(
abp.libs.datatables.normalizeConfiguration({
serverSide: true,
paging: true,
order: [[1, "asc"]],
searching: false,
scrollX: true,
ajax: abp.libs.datatables.createAjax(timeZoneApp.meetings.meeting.getList),
columnDefs: [
{
title: l('Actions'),
rowAction: {
items:
[
{
text: l('Edit'),
visible: abp.auth.isGranted('TimeZoneApp.Meetings.Edit'),
action: function (data) {
editModal.open({ id: data.record.id });
},
},
{
text: l('Delete'),
visible: abp.auth.isGranted('TimeZoneApp.Meetings.Delete'),
confirmMessage: function (data) {
return l('MeetingDeletionConfirmationMessage', data.record.subject);
},
action: function (data) {
timeZoneApp.meetings.meeting
.delete(data.record.id)
.then(function() {
abp.notify.info(l('SuccessfullyDeleted'));
dataTable.ajax.reload();
});
}
}
]
}
},
{
title: l('Subject'),
data: "subject"
},
{
title: l('StartTime') + ' / ' + l('StartTime'),
data: "startTime",
render: function (data, type, row) {
return abp.clock.normalizeToLocaleString(row.startTime) + ' ➡️ ' + abp.clock.normalizeToLocaleString(row.endTime);
}
},
{
title: l('ActualStartTime'),
data: "actualStartTime",
dataFormat: "datetime"
},
{
title: l('CanceledTime'),
data: "canceledTime",
render: function (data, type, row) {
return data ? abp.clock.normalizeToLocaleString(data) : 'N/A';
}
},
{
title: l('ReminderTime'),
data: "reminderTime",
dataFormat: "datetime"
},
{
title: l('FollowUpTime'),
data: "followUpTime",
render: function (data, type, row) {
return data ? abp.clock.normalizeToLocaleString(data) : 'N/A';
}
},
{
title: l('Description'),
data: "description"
}
]
})
);
Below is the screenshot of DataTables:
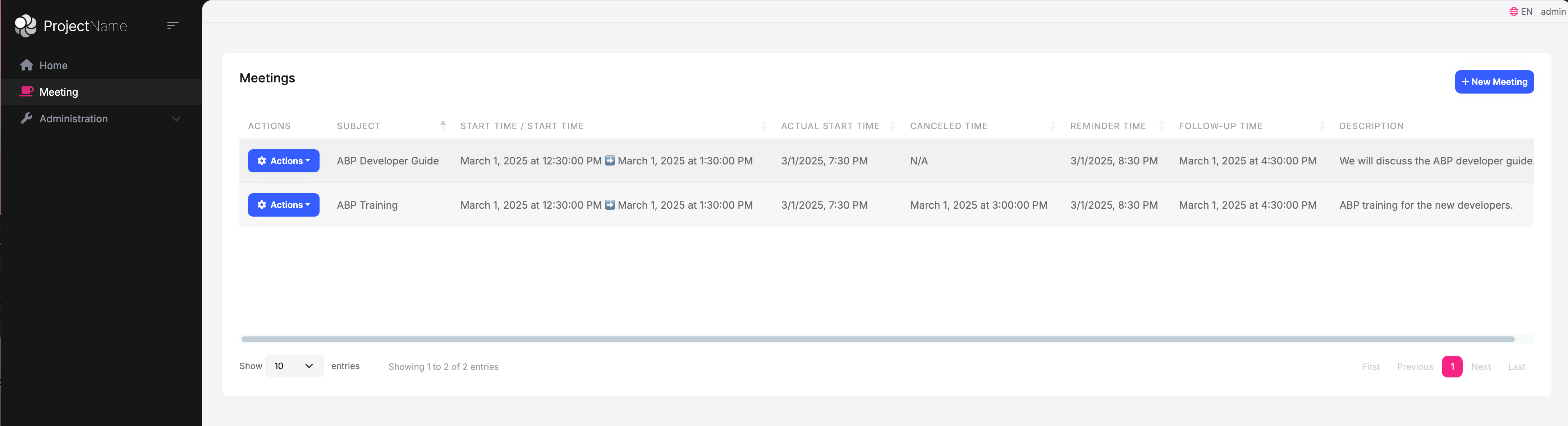
Creating and Editing Meeting
We use JavaScript to create and edit Meeting.
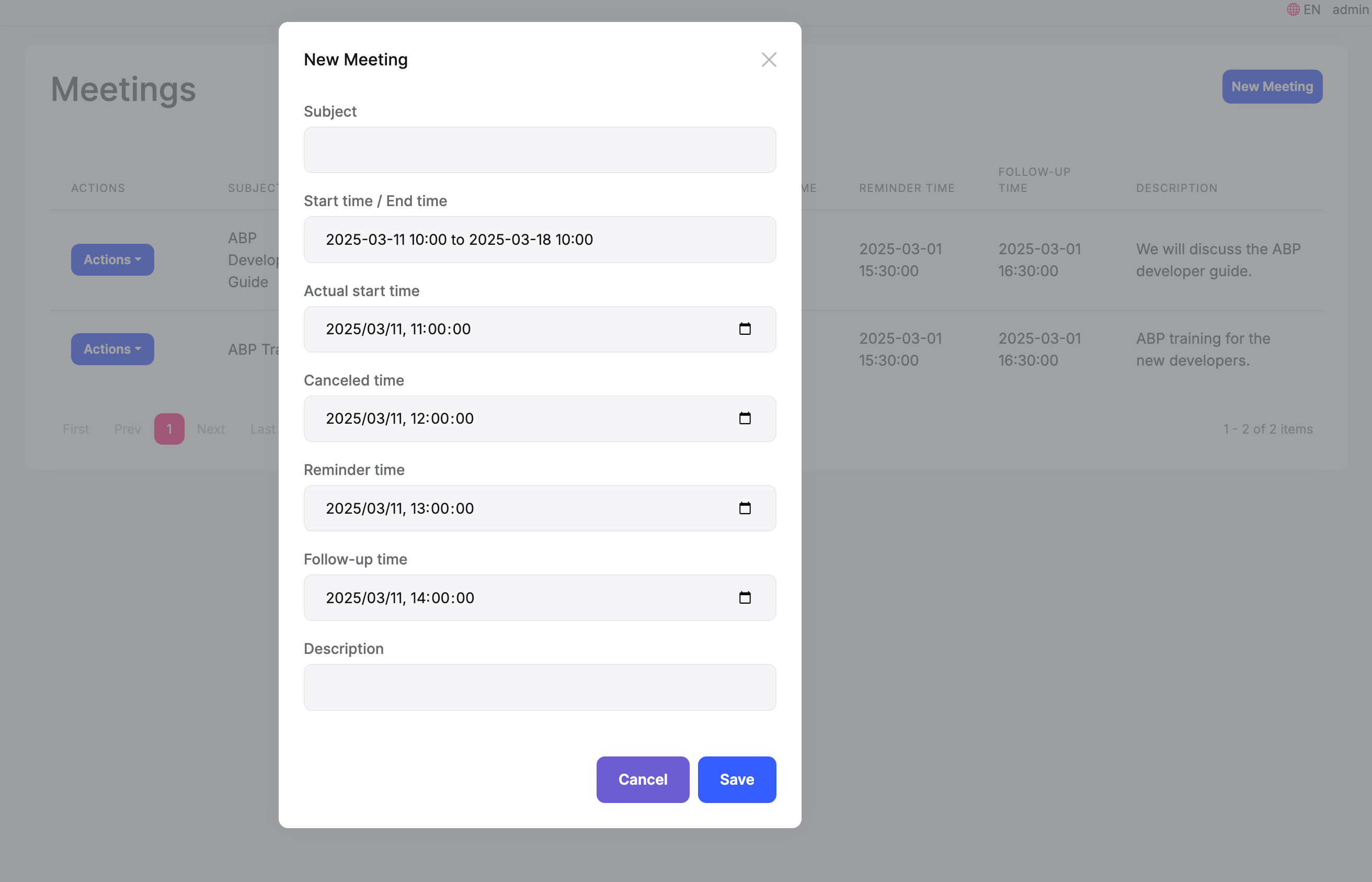
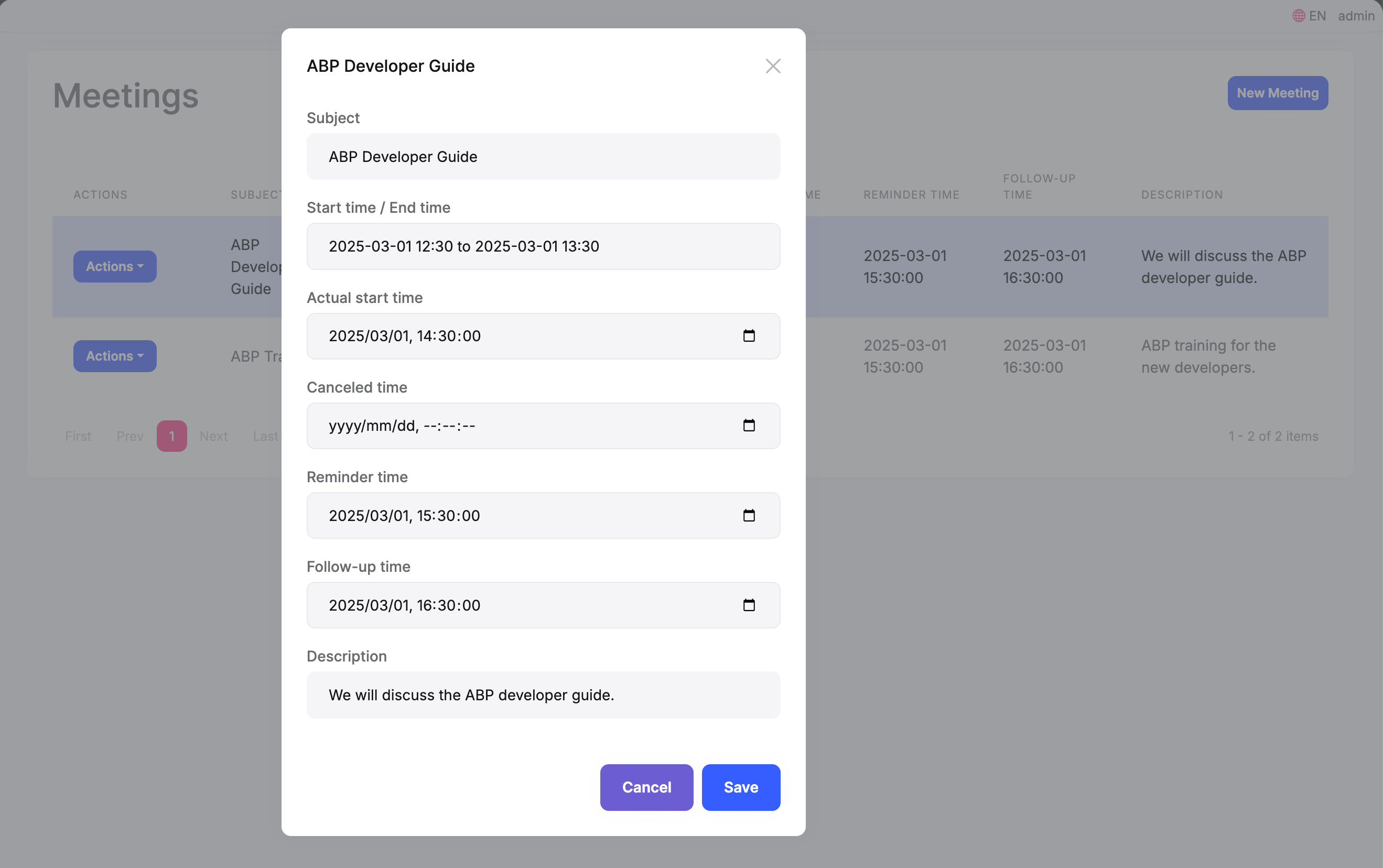
ABP's TagHelper can automatically create forms based on the model, it will generate corresponding HTML tags based on the attributes in the model. For DateTime and DateTimeOffset attributes, it will generate and initialize a DateTimePicker component.
CreateModal and EditModal :
<abp-dynamic-form abp-model="Meeting" asp-page="/Meetings/CreateModal">
<abp-modal>
<abp-modal-header title="@L["NewMeeting"].Value"></abp-modal-header>
<abp-modal-body>
<abp-form-content />
</abp-modal-body>
<abp-modal-footer buttons="@(AbpModalButtons.Cancel|AbpModalButtons.Save)"></abp-modal-footer>
</abp-modal>
</abp-dynamic-form>
<abp-dynamic-form abp-model="Meeting" asp-page="/Meetings/EditModal">
<abp-modal>
<abp-modal-header title="@L["Update"].Value"></abp-modal-header>
<abp-modal-body>
<abp-input asp-for="Id" />
<abp-form-content />
</abp-modal-body>
<abp-modal-footer buttons="@(AbpModalButtons.Cancel|AbpModalButtons.Save)"></abp-modal-footer>
</abp-modal>
</abp-dynamic-form>
You can see that the time in the control has been converted to the current user's timezone.
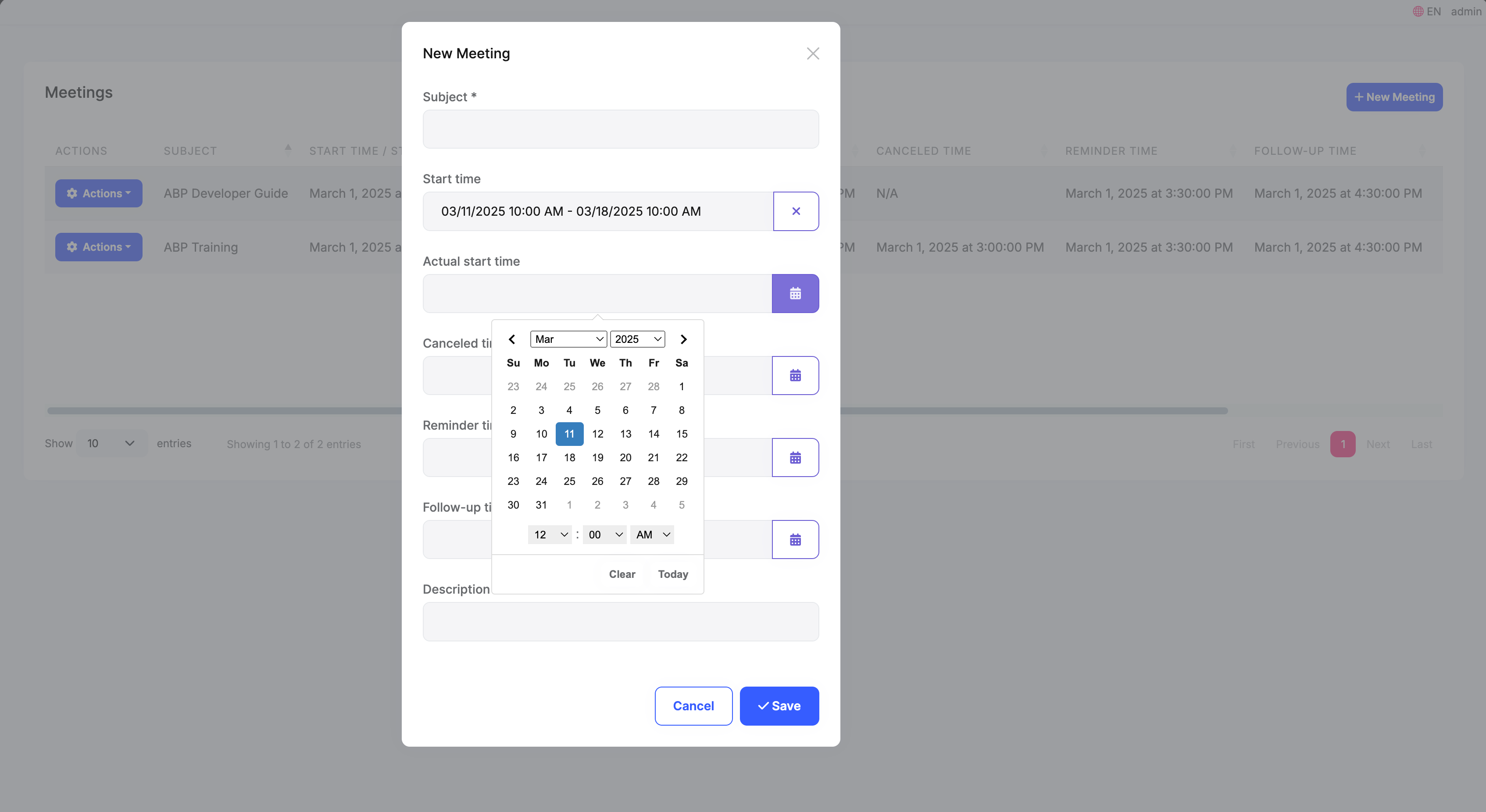
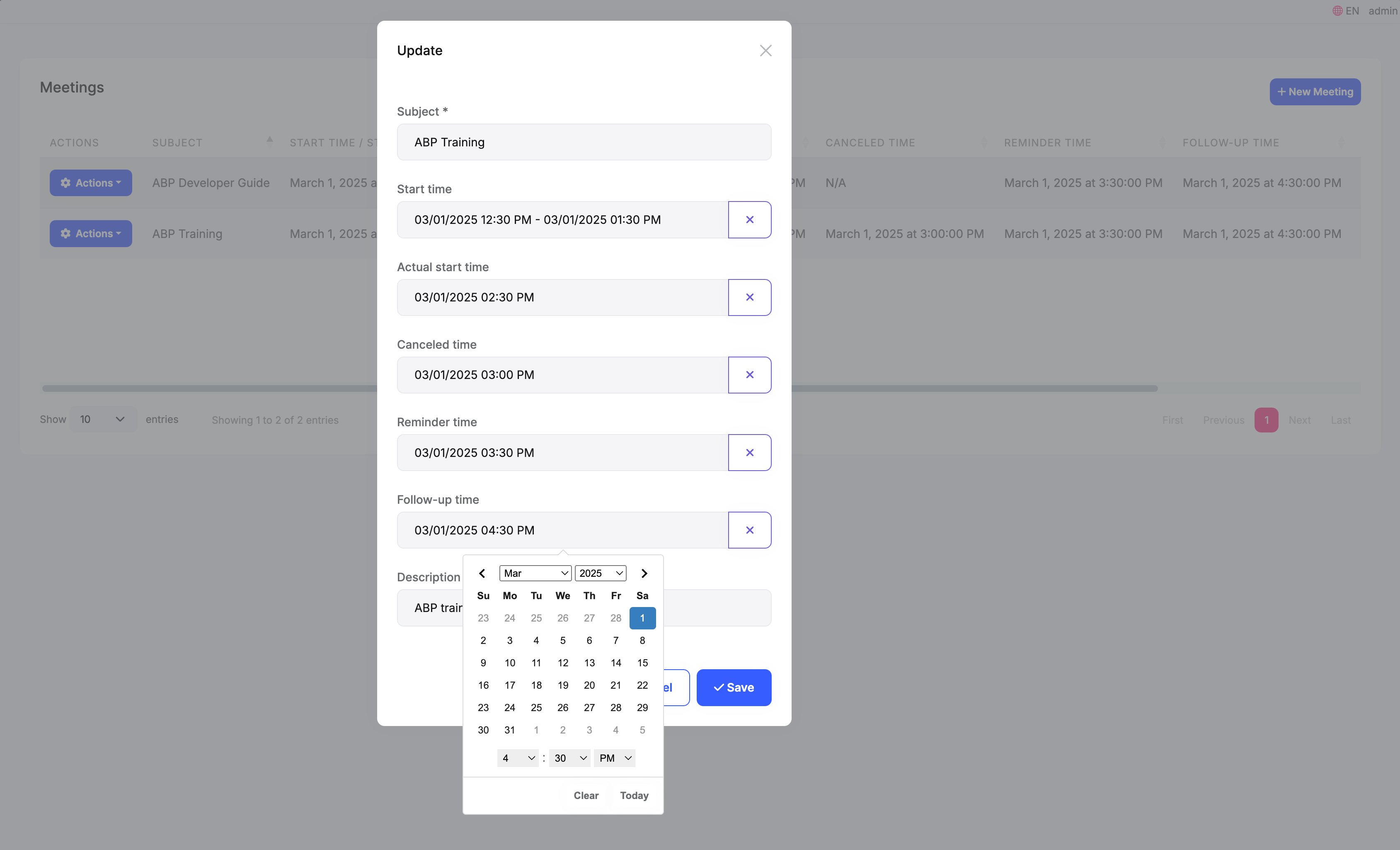
When we submit the form, we need to convert the time to UTC. In the JavaScript of the Create and Edit pages, we use the handleDatepicker this jQuery extension method to handle time in the form, it internally gets the user's local time from the selector input[type="hidden"][data-hidden-datepicker], and then uses the abp.clock.normalizeToString method to convert the date field in the form to the ISO 8601 format UTC time string.
If the current application is not enabled for multi-timezone support, then the
abp.clock.normalizeToStringmethod will not convert the time, it will just convert to the ISO 8601 format time string without timezone.
var abp = abp || {};
$(function () {
abp.modals.meetingCreate = function () {
var initModal = function (publicApi, args) {
var $form = publicApi.getForm();
$form.find('button[type="submit"]').on('click', function (e) {
$form.handleDatepicker('input[type="hidden"][data-hidden-datepicker]');
});
};
return {
initModal: initModal
}
};
});
The requested data is as follows:
Request URL: Meetings/EditModal
Request Method: POST
Payload:
Id: 0803780b-3762-2af8-1c75-3a1895d59c89
Meeting.Subject: ABP Developer Guide
Meeting.StartTime: 2025-03-01T09:30:00.000Z
Meeting.EndTime: 2025-03-01T10:30:00.000Z
Meeting.ActualStartTime: 2025-03-01T11:30:00.000Z
Meeting.CanceledTime:
Meeting.ReminderTime: 2025-03-01T12:30:00.000Z
Meeting.FollowUpTime: 2025-03-01T13:30:00.000Z
Meeting.Description: We will discuss the ABP developer guide.
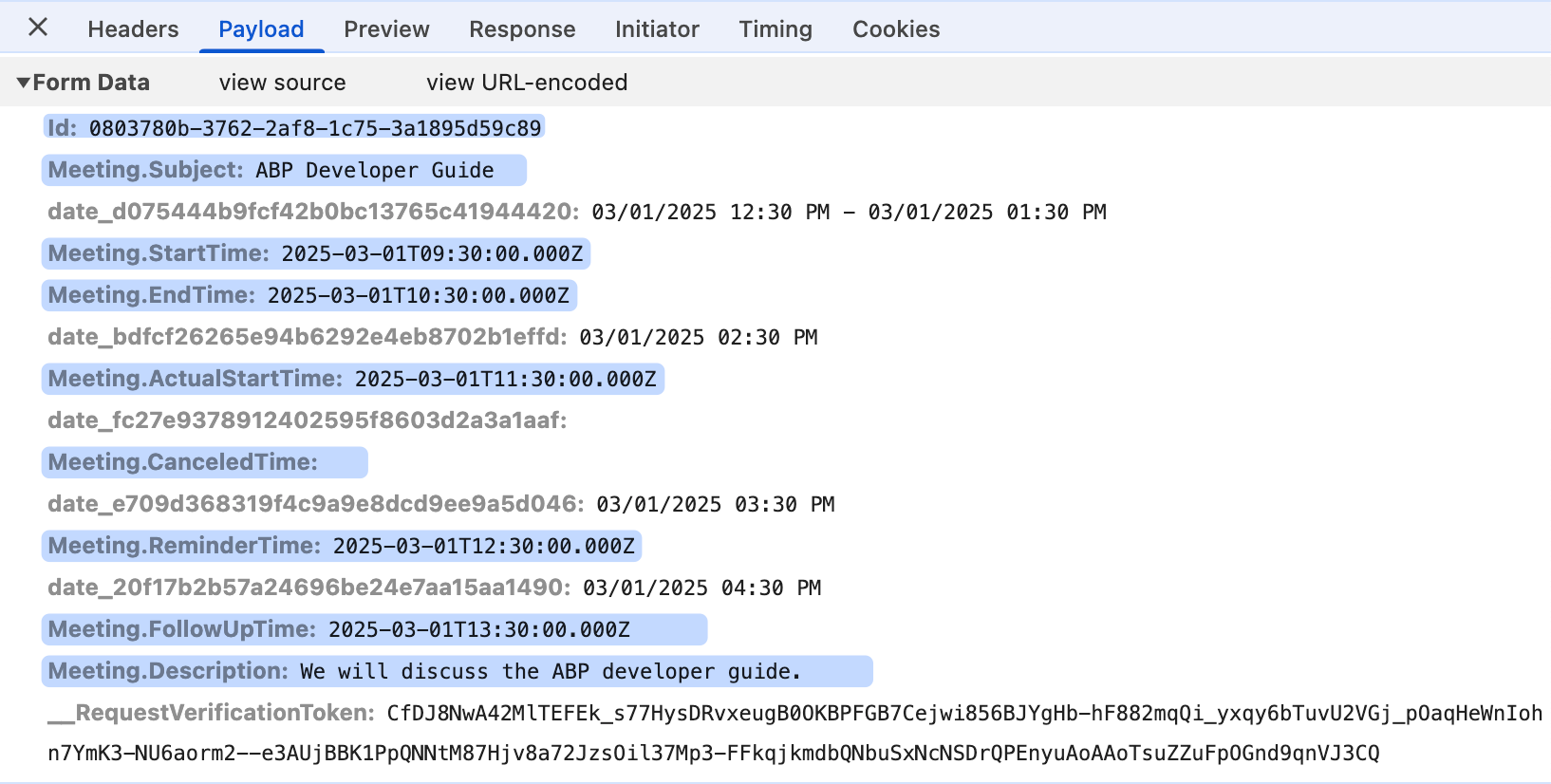
In short, we use the abp.clock.normalizeToLocaleString method to display time, and use the abp.clock.normalizeToString method to modify the time to be submitted. If you submit data via ajax, please remember to use the abp.clock.normalizeToString method to convert time.
Handling Timezone in Blazor
We cannot automatically complete some work in Blazor UI, we need to inject IClock and use the ConvertToUserTime and ConvertToUtc methods to display and create/update entities.
Below is a complete Meeting page, please refer to the usage of Clock in it.
@page "/meetings"
@using Volo.Abp.Application.Dtos
@using Microsoft.Extensions.Localization
@using TimeZoneApp.Meetings
@using TimeZoneApp.Localization
@using TimeZoneApp.Permissions
@using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Components.Web
@inject IStringLocalizer<TimeZoneAppResource> L
@inject AbpBlazorMessageLocalizerHelper<TimeZoneAppResource> LH
@inherits AbpCrudPageBase<IMeetingAppService, MeetingDto, Guid, PagedAndSortedResultRequestDto, CreateUpdateMeetingDto>
<Card>
<CardHeader>
<Row Class="justify-content-between">
<Column ColumnSize="ColumnSize.IsAuto">
<h2>@L["Meetings"]</h2>
</Column>
<Column ColumnSize="ColumnSize.IsAuto">
@if (HasCreatePermission)
{
<Button Color="Color.Primary" Clicked="OpenCreateModalAsync">@L["NewMeeting"]</Button>
}
</Column>
</Row>
</CardHeader>
<CardBody>
<DataGrid TItem="MeetingDto"
Data="Entities"
ReadData="OnDataGridReadAsync"
TotalItems="TotalCount"
ShowPager="true"
PageSize="PageSize">
<DataGridColumns>
<DataGridEntityActionsColumn TItem="MeetingDto" @ref="@EntityActionsColumn">
<DisplayTemplate>
<EntityActions TItem="MeetingDto" EntityActionsColumn="@EntityActionsColumn">
<EntityAction TItem="MeetingDto"
Text="@L["Edit"]"
Visible=HasUpdatePermission
Clicked="() => OpenEditModalAsync(context)" />
<EntityAction TItem="MeetingDto"
Text="@L["Delete"]"
Clicked="() => DeleteEntityAsync(context)"
Visible=HasDeletePermission
ConfirmationMessage="()=>GetDeleteConfirmationMessage(context)" />
</EntityActions>
</DisplayTemplate>
</DataGridEntityActionsColumn>
<DataGridColumn TItem="MeetingDto"
Field="@nameof(MeetingDto.Subject)"
Caption="@L["Subject"]"></DataGridColumn>
<DataGridColumn TItem="MeetingDto"
Field="@nameof(MeetingDto.StartTime)"
Caption="@(L["StartTime"] + "/" + L["EndTime"])">
<DisplayTemplate>
@Clock.ConvertToUserTime(context.StartTime).ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") ➡️ @Clock.ConvertToUserTime(context.EndTime).ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
</DisplayTemplate>
</DataGridColumn>
<DataGridColumn TItem="MeetingDto"
Field="@nameof(MeetingDto.ActualStartTime)"
Caption="@L["ActualStartTime"]">
<DisplayTemplate>
@Clock.ConvertToUserTime(context.ActualStartTime).ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
</DisplayTemplate>
</DataGridColumn>
<DataGridColumn TItem="MeetingDto"
Field="@nameof(MeetingDto.CanceledTime)"
Caption="@L["CanceledTime"]">
<DisplayTemplate>
@(context.CanceledTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUserTime(context.CanceledTime.Value).ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") : "N/A")
</DisplayTemplate>
</DataGridColumn>
<DataGridColumn TItem="MeetingDto"
Field="@nameof(MeetingDto.ReminderTime)"
Caption="@L["ReminderTime"]">
<DisplayTemplate>
@(Clock.ConvertToUserTime(context.ReminderTime).ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") )
</DisplayTemplate>
</DataGridColumn>
<DataGridColumn TItem="MeetingDto"
Field="@nameof(MeetingDto.FollowUpTime)"
Caption="@L["FollowUpTime"]">
<DisplayTemplate>
@(context.FollowUpTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUserTime(context.FollowUpTime.Value).ToString("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss") : "N/A")
</DisplayTemplate>
</DataGridColumn>
<DataGridColumn TItem="MeetingDto"
Field="@nameof(MeetingDto.Description)"
Caption="@L["Description"]">
</DataGridColumn>
</DataGridColumns>
</DataGrid>
</CardBody>
</Card>
<Modal @ref="@CreateModal">
<ModalContent IsCentered="true">
<Form>
<ModalHeader>
<ModalTitle>@L["NewMeeting"]</ModalTitle>
<CloseButton Clicked="CloseCreateModalAsync"/>
</ModalHeader>
<ModalBody>
<Validations @ref="@CreateValidationsRef" Model="@NewEntity" ValidateOnLoad="false">
<Validation MessageLocalizer="@LH.Localize">
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["Subject"]</FieldLabel>
<TextEdit @bind-Text="@NewEntity.Subject">
<Feedback>
<ValidationError/>
</Feedback>
</TextEdit>
</Field>
</Validation>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["StartTime"] / @L["EndTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DatePicker TValue="DateTime?" @bind-Dates="SelectedDates" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime" SelectionMode="DateInputSelectionMode.Range" />
</Field>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["ActualStartTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DateEdit TValue="DateTime" @bind-Date="NewEntity.ActualStartTime" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime"/>
</Field>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["CanceledTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DateEdit TValue="DateTime?" @bind-Date="NewEntity.CanceledTime" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime"/>
</Field>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["ReminderTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DateEdit TValue="DateTimeOffset" @bind-Date="NewEntity.ReminderTime" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime"/>
</Field>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["FollowUpTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DateEdit TValue="DateTimeOffset?" @bind-Date="NewEntity.FollowUpTime" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime"/>
</Field>
<Validation MessageLocalizer="@LH.Localize">
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["Description"]</FieldLabel>
<TextEdit @bind-Text="@NewEntity.Description">
<Feedback>
<ValidationError/>
</Feedback>
</TextEdit>
</Field>
</Validation>
</Validations>
</ModalBody>
<ModalFooter>
<Button Color="Color.Secondary"
Clicked="CloseCreateModalAsync">@L["Cancel"]</Button>
<Button Color="Color.Primary"
Type="@ButtonType.Submit"
PreventDefaultOnSubmit="true"
Clicked="CreateEntityAsync">@L["Save"]</Button>
</ModalFooter>
</Form>
</ModalContent>
</Modal>
<Modal @ref="@EditModal">
<ModalContent IsCentered="true">
<Form>
<ModalHeader>
<ModalTitle>@EditingEntity.Subject</ModalTitle>
<CloseButton Clicked="CloseEditModalAsync"/>
</ModalHeader>
<ModalBody>
<Validations @ref="@EditValidationsRef" Model="@EditingEntity" ValidateOnLoad="false">
<Validation MessageLocalizer="@LH.Localize">
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["Subject"]</FieldLabel>
<TextEdit @bind-Text="@EditingEntity.Subject">
<Feedback>
<ValidationError/>
</Feedback>
</TextEdit>
</Field>
</Validation>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["StartTime"] / @L["EndTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DatePicker TValue="DateTime?" @bind-Dates="SelectedDates" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime" SelectionMode="DateInputSelectionMode.Range" />
</Field>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["ActualStartTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DateEdit TValue="DateTime" @bind-Date="EditingEntity.ActualStartTime" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime"/>
</Field>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["CanceledTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DateEdit TValue="DateTime?" @bind-Date="EditingEntity.CanceledTime" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime"/>
</Field>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["ReminderTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DateEdit TValue="DateTimeOffset" @bind-Date="EditingEntity.ReminderTime" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime"/>
</Field>
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["FollowUpTime"]</FieldLabel>
<DateEdit TValue="DateTimeOffset?" @bind-Date="EditingEntity.FollowUpTime" InputMode="DateInputMode.DateTime"/>
</Field>
<Validation MessageLocalizer="@LH.Localize">
<Field>
<FieldLabel>@L["Description"]</FieldLabel>
<TextEdit @bind-Text="@EditingEntity.Description">
<Feedback>
<ValidationError/>
</Feedback>
</TextEdit>
</Field>
</Validation>
</Validations>
</ModalBody>
<ModalFooter>
<Button Color="Color.Secondary"
Clicked="CloseEditModalAsync">@L["Cancel"]</Button>
<Button Color="Color.Primary"
Type="@ButtonType.Submit"
PreventDefaultOnSubmit="true"
Clicked="UpdateEntityAsync">@L["Save"]</Button>
</ModalFooter>
</Form>
</ModalContent>
</Modal>
@code {
IReadOnlyList<DateTime?> SelectedDates;
public Meeting()
{
CreatePolicyName = TimeZoneAppPermissions.Meetings.Create;
UpdatePolicyName = TimeZoneAppPermissions.Meetings.Edit;
DeletePolicyName = TimeZoneAppPermissions.Meetings.Delete;
}
protected override async Task OpenCreateModalAsync()
{
await base.OpenCreateModalAsync();
var now = DateTime.Now;
SelectedDates = new List<DateTime?> { now.Date.AddHours(10),now.Date.AddDays(7).AddHours(10) };
NewEntity.ActualStartTime = now.Date.AddHours(11);
NewEntity.CanceledTime = now.Date.AddHours(12);
NewEntity.ReminderTime = now.Date.AddHours(13);
NewEntity.FollowUpTime = now.Date.AddHours(14);
}
protected override Task OnCreatingEntityAsync()
{
if (SelectedDates.Count == 2 && SelectedDates[0].HasValue && SelectedDates[1].HasValue)
{
NewEntity.StartTime = Clock.ConvertToUtc(SelectedDates[0]!.Value);
NewEntity.EndTime = Clock.ConvertToUtc(SelectedDates[1]!.Value);
}
NewEntity.ActualStartTime = Clock.ConvertToUtc(NewEntity.ActualStartTime);
NewEntity.CanceledTime = NewEntity.CanceledTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUtc(NewEntity.CanceledTime.Value) : null;
NewEntity.ReminderTime = Clock.ConvertToUtc(NewEntity.ReminderTime.DateTime);
NewEntity.FollowUpTime = NewEntity.FollowUpTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUtc(NewEntity.FollowUpTime.Value.DateTime) : null;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
protected override async Task OpenEditModalAsync(MeetingDto entity)
{
await base.OpenEditModalAsync(entity);
SelectedDates = new List<DateTime?> { Clock.ConvertToUserTime(EditingEntity.StartTime), Clock.ConvertToUserTime(EditingEntity.EndTime) };
EditingEntity.ActualStartTime = Clock.ConvertToUserTime(EditingEntity.ActualStartTime);
EditingEntity.CanceledTime = EditingEntity.CanceledTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUserTime(EditingEntity.CanceledTime.Value) : null;
EditingEntity.ReminderTime = Clock.ConvertToUserTime(EditingEntity.ReminderTime);
EditingEntity.FollowUpTime = EditingEntity.FollowUpTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUserTime(EditingEntity.FollowUpTime.Value) : null;
}
protected override Task OnUpdatingEntityAsync()
{
if (SelectedDates.Count == 2 && SelectedDates[0].HasValue && SelectedDates[1].HasValue)
{
EditingEntity.StartTime = Clock.ConvertToUtc(SelectedDates[0]!.Value);
EditingEntity.EndTime = Clock.ConvertToUtc(SelectedDates[1]!.Value);
}
EditingEntity.ActualStartTime = Clock.ConvertToUtc(EditingEntity.ActualStartTime);
EditingEntity.CanceledTime = EditingEntity.CanceledTime.HasValue ? Clock.ConvertToUtc(EditingEntity.CanceledTime.Value) : null;
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
}
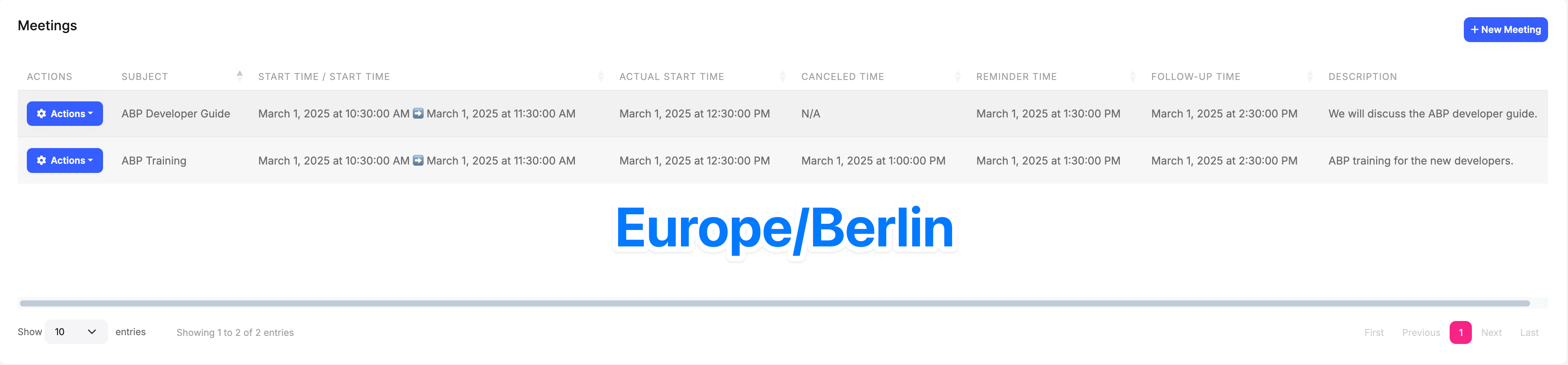
Timezone Settings Change
If the timezone settings change, then all times will be converted to the new timezone. For example, if the current timezone changes from Europe/Istanbul to Europe/Berlin, then all times will be converted to the Europe/Berlin timezone.
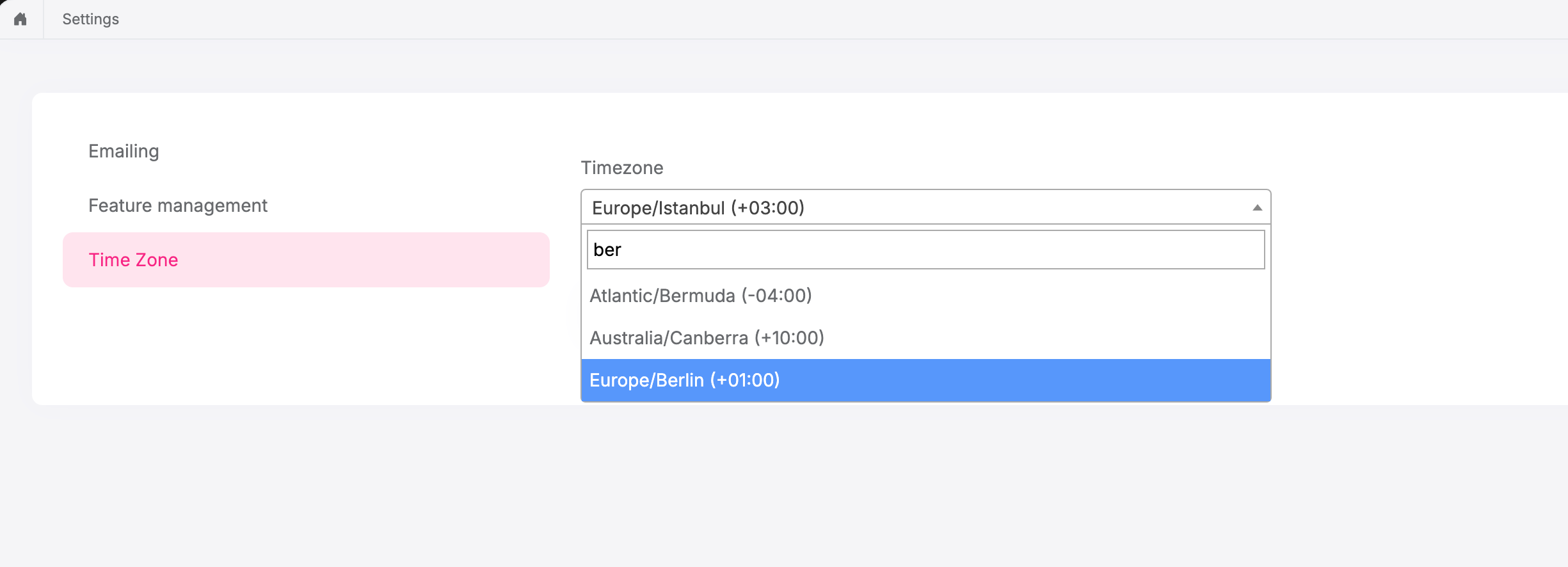
Europe/Istanbul:

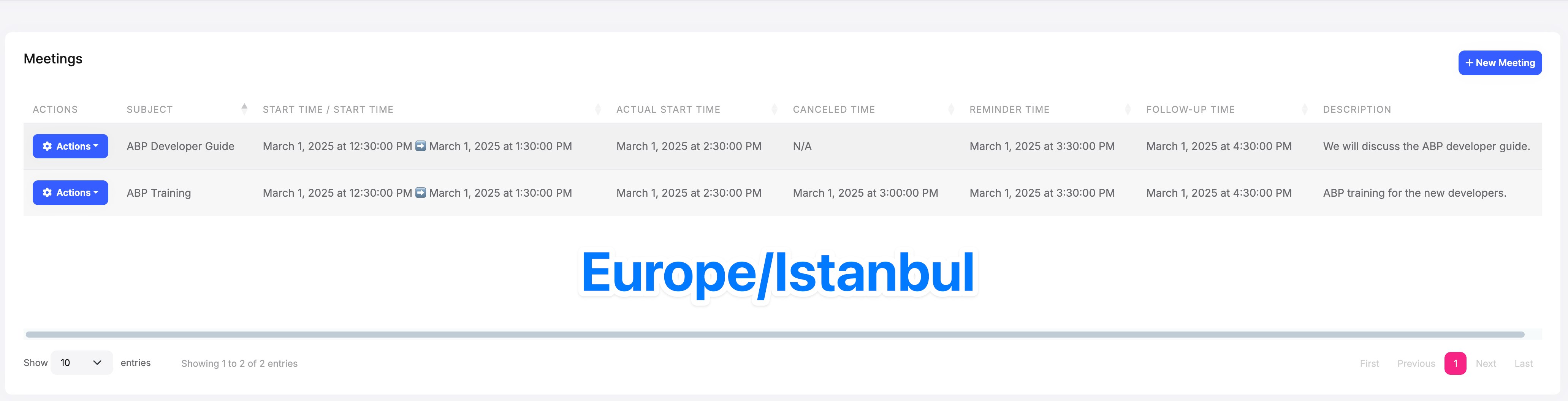
Europe/Berlin:

Browser Timezone Detection
When no timezone setting is configured, ABP's MVC, Blazor, and Angular applications will automatically detect the browser's timezone during initialization. The detected timezone is then stored in either the request's Cookie or Header.
This functionality is implemented by the UseAbpTimeZone middleware, which follows a specific order to determine the appropriate timezone:
- First, it attempts to retrieve the timezone from the application/tenant/user settings
- If no setting is found, it tries to get the timezone from the request information, including Cookie, Header, QueryString, and Form
- Finally, if no timezone information is found, it falls back to using the server's timezone as the default
The timezone information is stored using the key
__timezone
TimeZoneApp Source Code
You can download and view the TimeZoneApp source code for detailed implementation.
Summary
Through this article, we learned how to handle timezone in different types of UIs. I hope this article is helpful to you. If you have any questions, please contact me at any time.

































































Comments
Christopher Ryan 47 weeks ago
Thanks for the information, it is very helpful. We would like to see a recommended approach to incorporating the NodaTime open source library with ABP, to be able to handle some common scenarios better. https://github.com/abpframework/abp/issues/263 Future scheduling - is the meeting at 8:00 AM EST because it was scheduled in November during standard time, or is it 8:00 AM EDT because the meeting won't happen until May, after the switch to daylight saving time? When looking back in history - what was the local time was at the time something happened (your own time zone may not match the one where the event originally occurred). The NodaTime website has many great examples where the standard approach of using UTC storage and converting to the user's local time doesn't work.
Liming Ma 47 weeks ago
hi
All built-in time services can be replaced. You can override them with NodaTime implementation.
Thanks.
Mathias Kowoll 46 weeks ago
I added this code:
Configure<AbpClockOptions>(options => { options.Kind = DateTimeKind.Utc; });
but it didn't appear in settings. I'm using 9.2 rc2
Liming Ma 46 weeks ago
hi
Can you check if current user has SettingManagement.TimeZone permission?
Thanks.
Mathias Kowoll 46 weeks ago
I checked and the permission is set
Liming Ma 46 weeks ago
Can you create an issue here and share your test project?
https://github.com/maliming/TimeZone/issues/new
Thanks.
Mathias Kowoll 46 weeks ago
Hi, Just restart the process and have succesfully configured. Don't know which the error was. Thx for your time
Liming Ma 46 weeks ago
Good news. : )
lataing 36 weeks ago
Hello, I have carefully reviewed the source code you provided, as well as the source code of ABP, but I did not see where to set UTC for the front-end ABP.clock.kind. How does it make ABP.clock.supportsMultipleTimezone result true?
Liming Ma 36 weeks ago
hi
The
ABP.clock.kindwas set by/Abp/ApplicationConfigurationScriptsee: imgur.com/YKaLSVj