Using Outbox/Inbox Pattern for Reliable Event Handling in a Multi-Module Monolithic Application
This article explains how to implement reliable event handling using the Outbox/Inbox pattern in a modular monolithic application with multiple databases. We'll use the ModularCRM project as an example (how that project was created is explained in this document).
Project Background
ModularCRM is a monolithic application that integrates multiple ABP framework open-source modules, including:
AccountIdentityTenant ManagementPermission ManagementSetting Management- And other open-source modules
Besides the ABP framework modules, the project contains three business modules:
- Order module (
Ordering), usingMongoDBdatabase - Product module (
Products), usingSQL Serverdatabase - Payment module (
Payment), usingMongoDBdatabase
The project configures separate database connection strings for ModularCRM and the three business modules in appsettings.json:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Default": "Server=localhost,1434;Database=ModularCrm;User Id=sa;Password=1q2w3E***;TrustServerCertificate=true",
"Products": "Server=localhost,1434;Database=ModularCrm_Products;User Id=sa;Password=1q2w3E***;TrustServerCertificate=true",
"Ordering": "mongodb://localhost:27017/ModularCrm_Ordering?replicaSet=rs0",
"Payment": "mongodb://localhost:27017/ModularCrm_Payment?replicaSet=rs0"
}
}
Business Scenario
These modules communicate through the ABP framework's DistributedEventBus to implement the following business flow:
This is a simple example flow. Real business flows are more complex. The sample code is for demonstration purposes.
- Order module: Publishes
OrderPlacedEtoevent when an order is placed - Product module: Subscribes to
OrderPlacedEtoevent and reduce product stock - Payment module: Subscribes to
OrderPlacedEtoevent, processes payment, then publishesPaymentCompletedEtoevent - Order module: Subscribes to
PaymentCompletedEtoevent and updates order status toDelivered
When implementing this flow, we need to ensure:
- Transaction consistency between order creation and event publishing
- Transaction consistency when modules process messages
- Reliable message delivery (including persistence, confirmation, and retry mechanisms)
Using the default implementation of the ABP framework's distributed event bus cannot meet these requirements, so we need to add a new mechanism that is also provided by the ABP Framework.
Outbox/Inbox Pattern Solution
To meet these requirements, we use the Outbox/Inbox pattern:
Outbox Pattern
- Saves distributed events with database operations in the same transaction
- Sends events to distributed message service through background jobs
- Ensures consistency between data updates and event publishing
- Prevents message loss during system failures
Inbox Pattern
- First saves received distributed events to the database
- Processes events in a transactional way
- Ensures messages are processed only once by saving processed message records
- Maintains processing state for reliable handling
For how to enable and configure
Outbox/Inboxin projects and modules, see: https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/infrastructure/event-bus/distributed#outbox-inbox-for-transactional-events
Module Configuration
Each module needs to configure separate Outbox/Inbox. Since it's a monolithic application, all message processing classes are in the same project, so we need to configure Outbox/Inbox for each module with Selector/EventSelector to ensure that the module only sends and receives the messages it cares about, avoiding message duplication processing.
ModularCRM Main Application Configuration
It will send and receive messages from all ABP framework open-source modules.
// This selector will match all abp built-in modules and the current module.
Func<Type, bool> abpModuleSelector = type => type.Namespace != null && (type.Namespace.StartsWith("Volo.") || type.Assembly == typeof(ModularCrmModule).Assembly);
Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Inboxes.Configure("ModularCrm", config =>
{
config.UseDbContext<ModularCrmDbContext>();
config.EventSelector = abpModuleSelector;
config.HandlerSelector = abpModuleSelector;
});
options.Outboxes.Configure("ModularCrm", config =>
{
config.UseDbContext<ModularCrmDbContext>();
config.Selector = abpModuleSelector;
});
});
Order Module Configuration
It only sends OrderPlacedEto events and receives PaymentCompletedEto events and executes OrderPaymentCompletedEventHandler.
Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Inboxes.Configure(OrderingDbProperties.ConnectionStringName, config =>
{
config.UseMongoDbContext<IOrderingDbContext>();
config.EventSelector = type => type == typeof(PaymentCompletedEto);
config.HandlerSelector = type => type == typeof(OrderPaymentCompletedEventHandler);
});
options.Outboxes.Configure(OrderingDbProperties.ConnectionStringName, config =>
{
config.UseMongoDbContext<IOrderingDbContext>();
config.Selector = type => type == typeof(OrderPlacedEto);
});
});
Here, the
EventSelectorandHandlerSelectorchecks only a single type. If you have multiple events and event handlers, you can check the given type if it is included in an array of types.
Product Module Configuration
It only receives EntityCreatedEto<UserEto> and OrderPlacedEto events and executes ProductsOrderPlacedEventHandler and ProductsUserCreatedEventHandler. It does not send any events now.
Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Inboxes.Configure(ProductsDbProperties.ConnectionStringName, config =>
{
config.UseDbContext<IProductsDbContext>();
config.EventSelector = type => type == typeof(EntityCreatedEto<UserEto>) || type == typeof(OrderPlacedEto);
config.HandlerSelector = type => type == typeof(ProductsOrderPlacedEventHandler) || type == typeof(ProductsUserCreatedEventHandler);
});
// Outboxes are not used in this module
options.Outboxes.Configure(ProductsDbProperties.ConnectionStringName, config =>
{
config.UseDbContext<IProductsDbContext>();
config.Selector = type => false;
});
});
Payment Module Configuration
It only sends PaymentCompletedEto events and receives OrderPlacedEto events and executes PaymentOrderPlacedEventHandler.
Configure<AbpDistributedEventBusOptions>(options =>
{
options.Inboxes.Configure(PaymentDbProperties.ConnectionStringName, config =>
{
config.UseMongoDbContext<IPaymentMongoDbContext>();
config.EventSelector = type => type == typeof(OrderPlacedEto);
config.HandlerSelector = type => type == typeof(PaymentOrderPlacedEventHandler);
});
options.Outboxes.Configure(PaymentDbProperties.ConnectionStringName, config =>
{
config.UseMongoDbContext<IPaymentMongoDbContext>();
config.Selector = type => type == typeof(PaymentCompletedEto);
});
});
Running ModularCRM Simulation Business Flow
- Run the following command in the
ModularCrmdirectory:
docker-compose up -d
abp install-lib
dotnet run --project ModularCrm --migrate-database
dotnet run --project ModularCrm
- Navigate to
https://localhost:44303/to view the application homepage
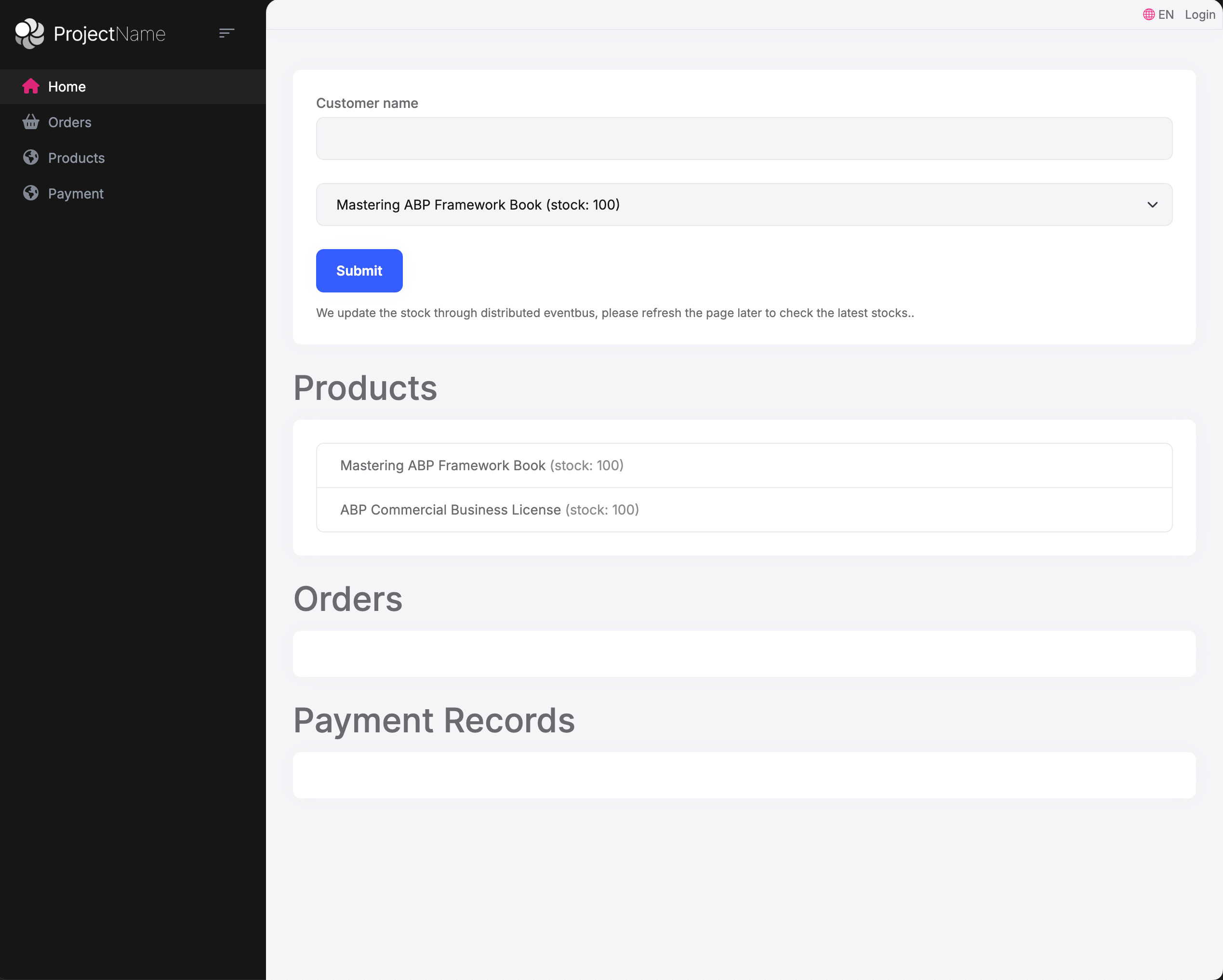
- Enter a customer name and select a product, then submit an order. After a moment, refresh the page to see the order, product, and payment information.
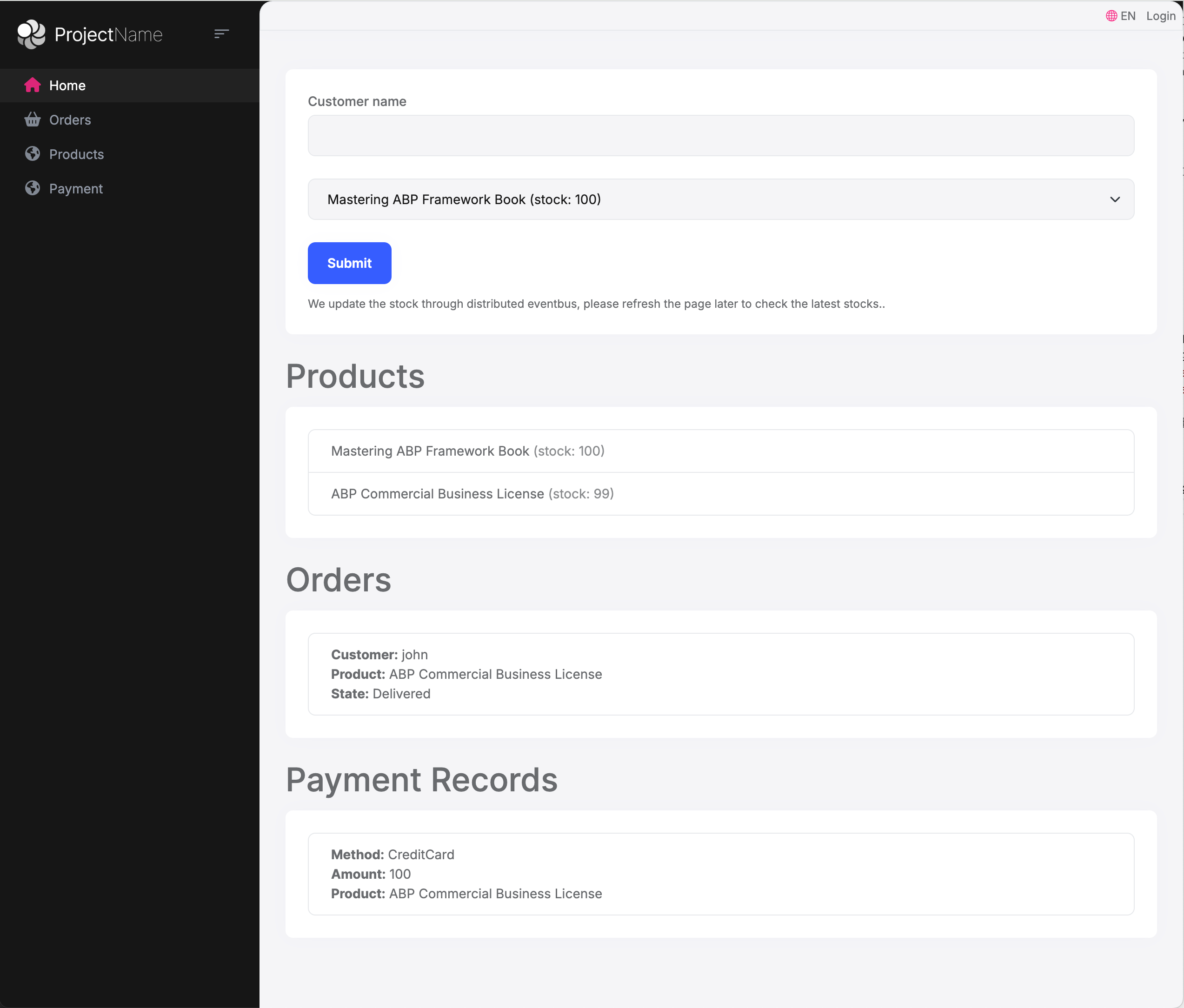
Application logs display the complete processing flow:
[Ordering Module] Order created: OrderId: b7ad3f47-0e77-bb81-082f-3a1834503e88, ProductId: 0f95689f-4cb6-36f5-68bd-3a18344d32c9, CustomerName: john
[Products Module] OrderPlacedEto event received: OrderId: b7ad3f47-0e77-bb81-082f-3a1834503e88, CustomerName: john, ProductId: 0f95689f-4cb6-36f5-68bd-3a18344d32c9
[Products Module] Stock count decreased for ProductId: 0f95689f-4cb6-36f5-68bd-3a18344d32c9
[Payment Module] OrderPlacedEto event received: OrderId: b7ad3f47-0e77-bb81-082f-3a1834503e88, CustomerName: john, ProductId: 0f95689f-4cb6-36f5-68bd-3a18344d32c9
[Payment Module] Payment processing completed for OrderId: b7ad3f47-0e77-bb81-082f-3a1834503e88
[Ordering Module] PaymentCompletedEto event received: OrderId: b7ad3f47-0e77-bb81-082f-3a1834503e88, PaymentId: d0a41ead-ee0f-714c-e254-3a1834504d65, PaymentMethod: CreditCard, PaymentAmount: ModularCrm.Payment.Payment.PaymentCompletedEto
[Ordering Module] Order state updated to Delivered for OrderId: b7ad3f47-0e77-bb81-082f-3a1834503e88
In addition, when a new user registers, the product module will also receive the EntityCreatedEto<UserEto> event, and we will send an email to the new user, just to demonstrate the Outbox/Inbox Selector mechanism.
[Products Module] UserCreated event received: UserId: "9a1f2bd0-5b28-210a-9e56-3a18344d310a", UserName: admin
[Products Module] Sending a popular products email to admin@abp.io...
Summary
By introducing the Outbox/Inbox pattern, we have achieved:
- Transactional message sending and receiving
- Reliable message processing mechanism
- Modular event processing in a multi-database environment
ModularCRM project not only implements reliable message processing but also demonstrates how to handle multi-database scenarios gracefully in a monolithic application. Project source code: https://github.com/abpframework/abp-samples/tree/master/ModularCrm-OutboxInbox-Pattern

































































Comments
Engincan Veske 48 weeks ago
Great article! It is good to see an article that is so practical to explaining the Inbox & Outbox Pattern, good job!
Mohammad Eunus 47 weeks ago
Great article! I was just thinking, even with a single database, if we’re using something like RabbitMQ, don’t we still need the Outbox pattern? Since RabbitMQ isn’t part of the same DB transaction, there’s a risk of losing or duplicating messages if something fails between SaveChanges() (when the data is saved to the database) and Publish() (when the message is sent to RabbitMQ). Just wanted to check, am I getting that right?
MartinEhv 39 weeks ago
Excellent Article!