Handle Concurrency with EF Core in an ABP Framework Project with ASP.NET Core MVC
In this article, we'll create a basic application to demonstrate how "Concurrency Check/Control" can be implemented in an ABP project.
🛠 Liked this post? I now share all my content on Substack — real-world .NET, AI, and scalable software design.
👉 Subscribe here → engincanveske.substack.com
🎥 Also, check out my YouTube channel for hands-on demos and deep dives: https://www.youtube.com/@engincanv
Creating the Solution
For this article, we will create a simple BookStore application and add CRUD functionality to the pages. Hence we deal with the concurrency situation.
We can create a new startup template with EF Core as a database provider and MVC for the UI Framework.
If you already have a project, you don't need to create a new startup template, you can directly implement the following steps to your project. So you can skip this section.
We can create a new startup template by using the ABP CLI.
abp new Acme.BookStore
After running the above command, our project boilerplate will be downloaded. Then we can open the solution and start the development.
Starting the Development
Let's start with defining our entities.
Creating Entities
Create a Book.cs (/Books/Book.cs) class in the .Domain layer:
public class Book : AuditedAggregateRoot<Guid>
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public BookType Type { get; set; }
public DateTime PublishDate { get; set; }
public float Price { get; set; }
}
To enable Concurrency Check for our entities, our entities should be implemented the
IHasConcurrencyStampinterface, directly or indirectly.Aggregate Root entity classes already implement the
IHasConcurrencyStampinterface, so if we inherit our entities from one of these entity classes then we won't need to manually implement theIHasConcurrencyStampinterface.And we've derived the
Bookentity fromAuditedAggregateRoot<TKey>here, so we don't need to implement theIHasConcurrencyStampinterface becauseAuditedAggregateRootclass already implemented theIHasConcurrencyStampinterface.
You can read more details from the Concurrency Check documentation.
Then, create a BookType (/Books/BookType.cs) enum in the .Domain.Shared layer:
public enum BookType
{
Undefined,
Adventure,
Biography,
Dystopia,
Fantastic,
Horror,
Science,
ScienceFiction,
Poetry
}
Database Integration
Open the BookStoreDbContext (/EntityFrameworkCore/BookStoreDbContext.cs) class in the *.EntityFrameworkCore project and add the following DbSet<Book> statement:
namespace Acme.BookStore.EntityFrameworkCore;
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(IIdentityDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(ITenantManagementDbContext))]
[ConnectionStringName("Default")]
public class BookStoreDbContext :
AbpDbContext<BookStoreDbContext>,
IIdentityDbContext,
ITenantManagementDbContext
{
//Entities from the modules
public DbSet<Book> Books { get; set; } //add this line
}
Then we can navigate to the OnModelCreating method in the same class and configure our tables/entities:
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(builder);
/* Include modules to your migration db context */
builder.ConfigurePermissionManagement();
...
//* Configure your own tables/entities inside here */
builder.Entity<Book>(b =>
{
b.ToTable(BookStoreConsts.DbTablePrefix + "Books",
BookStoreConsts.DbSchema);
b.ConfigureByConvention(); //auto configure for the base class props
b.Property(x => x.Name).IsRequired().HasMaxLength(128);
});
}
After the mapping configurations, we can create a new migration and apply changes to the database.
To do this, open your command line terminal in the directory of the EntityFrameworkCore project and run the below command:
dotnet ef migrations add Added_Books
After this command, a new migration will be generated and then we can run the *.DbMigrator project to apply the last changes to the database such as creating a new table named Books according to the last created migration.
Defining DTOs and Application Service Interfaces
We can start to define the use cases of the application.
Create the DTO classes (under the Books folder) in the Application.Contracts project:
BookDto.cs
public class BookDto : AuditedEntityDto<Guid>, IHasConcurrencyStamp
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public BookType Type { get; set; }
public DateTime PublishDate { get; set; }
public float Price { get; set; }
public string ConcurrencyStamp { get; set; }
}
The
AuditedEntityDto<TKey>class is not implemented from theIHasConcurrencyStampinterface, so for the BookDto class we need to implement theIHasConcurrencyStamp.This is important, because we need to return books with their ConcurrencyStamp value.
CreateBookDto.cs
public class CreateBookDto
{
[Required]
[StringLength(128)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
public BookType Type { get; set; } = BookType.Undefined;
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Date)]
public DateTime PublishDate { get; set; } = DateTime.Now;
[Required]
public float Price { get; set; }
}
UpdateBookDto.cs
public class UpdateBookDto : IHasConcurrencyStamp
{
[Required]
[StringLength(128)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
public BookType Type { get; set; } = BookType.Undefined;
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Date)]
public DateTime PublishDate { get; set; } = DateTime.Now;
[Required]
public float Price { get; set; }
public string ConcurrencyStamp { get; set; }
}
Here, we've implemented the
IHasConcurrencyStampinterface for the UpdateBookDto class.We will use this value while updating an existing book. ABP Framework will compare the current book's ConcurrencyStamp value with the provided one, if values are matched, this means everything is as it is supposed to be and will update the record.
If values are mismatched, then it means the record that we're trying to update is already updated by another user and we need to get the latest changes to be able to make changes on it.
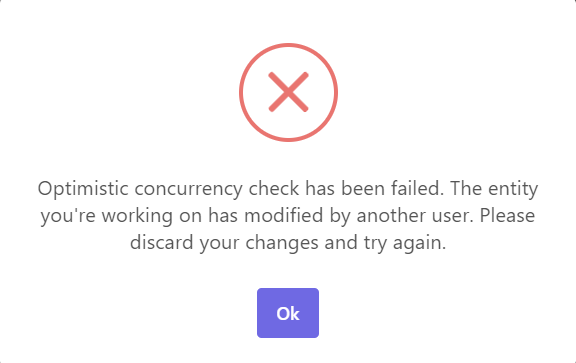
Also, in that case,
AbpDbConcurrencyExceptionwill be thrown by the ABP Framework and we can either handle this exception manually or let the ABP Framework handle it on behalf of us and show a user-friendly error message as in the image below.
Create a new IBookAppService (/Books/IBookAppService.cs) interface in the Application.Contracts project:
public interface IBookAppService :
ICrudAppService<BookDto, Guid, PagedAndSortedResultRequestDto, CreateBookDto, UpdateBookDto>
{
}
- We've implemented the
ICrudAppServicehere, because we just need to perform CRUD operations and this interface helps us define common CRUD operation methods.
Application Service Implementations
Create a BookAppService (/Books/BookAppService.cs) class inside the *.Application project and implement the application service methods, as shown below:
public class BookAppService :
CrudAppService<Book, BookDto, Guid, PagedAndSortedResultRequestDto, CreateBookDto, UpdateBookDto>,
IBookAppService
{
public BookAppService(IRepository<Book, Guid> repository)
: base(repository)
{
}
public override async Task<BookDto> UpdateAsync(Guid id, UpdateBookDto input)
{
var book = await Repository.GetAsync(id);
book.Name = input.Name;
book.Price = input.Price;
book.Type = input.Type;
book.PublishDate = input.PublishDate;
//set Concurrency Stamp value to the entity
book.ConcurrencyStamp = input.ConcurrencyStamp;
var updatedBook = await Repository.UpdateAsync(book);
return ObjectMapper.Map<Book, BookDto>(updatedBook);
}
}
- We've used the
CrudAppServicebase class. This class implements all common CRUD operations and if we want to change a method, we can simply override the method and change it to our needs.
Normally, you don't need to override the
UpdateAsyncmethod to do Concurrency Check. Because theUpdateAsyncmethod of theCrudAppServiceclass by default map input values to the entity. But I wanted to override this method to show what we need to do for Concurrency Check.
We can look closer to the
UpdateAsyncmethod here, because as we've mentioned earlier we need to pass the provided ConcurrencyStamp value to be able to do Concurrency Check/Control to our entity while updating.At that point, if the given record is already updated by any other user, a ConcurrencyStamp mismatch will occur and
AbpDbConcurrencyExceptionwill be thrown thanks to the Concurrency Check system of ABP, data-consistency will be provided and the current record won't be overridden.And if the values are matched, the record will be updated successfully.
After implementing the application service methods, we can do the related mapping configurations, so open the BookStoreApplicationAutoMapperProfile.cs and update the content as below:
public class BookStoreApplicationAutoMapperProfile : Profile
{
public BookStoreApplicationAutoMapperProfile()
{
CreateMap<Book, BookDto>();
CreateMap<CreateBookDto, Book>();
}
}
User Interface
So far, we've applied the all necessary steps for the Concurrency Check system, let's see it in action.
Create a razor page in the .Web layer named Index (/Pages/Books/Index.cshtml), open this file and replace the content with the following code block:
@page
@using Acme.BookStore.Localization
@using Microsoft.Extensions.Localization
@model Acme.BookStore.Web.Pages.Books.Index
@section scripts
{
<abp-script src="/Pages/Books/Index.js" />
}
<abp-card>
<abp-card-header>
<abp-row>
<abp-column size-md="_6">
<abp-card-title>Books</abp-card-title>
</abp-column>
<abp-column size-md="_6" class="text-end">
<abp-button id="NewBookButton"
text="New Book"
icon="plus"
button-type="Primary"/>
</abp-column>
</abp-row>
</abp-card-header>
<abp-card-body>
<abp-table striped-rows="true" id="BooksTable"></abp-table>
</abp-card-body>
</abp-card>
- We've defined a table and "New Book" button inside a card element here, we'll fill the table with our book records in the next step by using the Datatables library.
Create an Index.js (/Pages/Books/Index.js) file and add the following code block:
$(function () {
var l = abp.localization.getResource('BookStore');
var createModal = new abp.ModalManager(abp.appPath + 'Books/CreateModal');
var editModal = new abp.ModalManager(abp.appPath + 'Books/EditModal');
var dataTable = $('#BooksTable').DataTable(
abp.libs.datatables.normalizeConfiguration({
serverSide: true,
paging: true,
order: [[1, "asc"]],
searching: false,
scrollX: true,
ajax: abp.libs.datatables.createAjax(acme.bookStore.books.book.getList),
columnDefs: [
{
title: l('Actions'),
rowAction: {
items:
[
{
text: l('Edit'),
action: function (data) {
editModal.open({ id: data.record.id });
}
}
]
}
},
{
title: l('Name'),
data: "name"
},
{
title: l('Type'),
data: "type",
render: function (data) {
return l('Enum:BookType:' + data);
}
},
{
title: l('PublishDate'),
data: "publishDate",
render: function (data) {
return luxon
.DateTime
.fromISO(data, {
locale: abp.localization.currentCulture.name
}).toLocaleString();
}
},
{
title: l('Price'),
data: "price"
},
{
title: l('CreationTime'),
data: "creationTime",
render: function (data) {
return luxon
.DateTime
.fromISO(data, {
locale: abp.localization.currentCulture.name
}).toLocaleString(luxon.DateTime.DATETIME_SHORT);
}
}
]
})
);
createModal.onResult(function () {
dataTable.ajax.reload();
});
editModal.onResult(function () {
dataTable.ajax.reload();
});
$('#NewBookButton').click(function (e) {
e.preventDefault();
createModal.open();
});
});
We've used the Datatables to list our books.
Also defined create and update modals by using ABP Modal Manager, but we didn't create them yet, so let's create the modals.
First, create a CreateModal razor page and update the CreateModal.cshtml and CreateModal.cshtml.cs files as below:
CreateModal.cshtml
@page
@using Acme.BookStore.Web.Pages.Books
@using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.Bootstrap.TagHelpers.Modal
@model CreateModalModel
@{
Layout = null;
}
<abp-dynamic-form abp-model="Book" asp-page="/Books/CreateModal">
<abp-modal>
<abp-modal-header title="New Book"></abp-modal-header>
<abp-modal-body>
<abp-form-content />
</abp-modal-body>
<abp-modal-footer buttons="@(AbpModalButtons.Cancel|AbpModalButtons.Save)"></abp-modal-footer>
</abp-modal>
</abp-dynamic-form>
We've used
abp-dynamic-formtag-helper and passed it aBookmodel, this tag helper will simply create form contents (inputs, select boxes etc.) on behalf of us.CreateModal.cshtml.cs
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Acme.BookStore.Books;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
namespace Acme.BookStore.Web.Pages.Books;
public class CreateModalModel : BookStorePageModel
{
[BindProperty]
public CreateBookDto Book { get; set; }
private readonly IBookAppService _bookAppService;
public CreateModalModel(IBookAppService bookAppService)
{
_bookAppService = bookAppService;
}
public void OnGet()
{
Book = new CreateBookDto();
}
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
await _bookAppService.CreateAsync(Book);
return NoContent();
}
}
- In this file, we simply define CreateBookDto as a bind property and we'll use this class's properties in the form. Thanks to the
abp-dynamic-formtag-helper we don't need to define all of these form elements one by one, it will generate on behalf of us.
We can create an EditModal razor page and update the EditModal.cshtml and EditModal.cshtml.cs files as below:
EditModal.cshtml
@page
@using Acme.BookStore.Web.Pages.Books
@using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.Bootstrap.TagHelpers.Modal
@model EditModalModel
@{
Layout = null;
}
<form asp-page="/Books/EditModal">
<abp-modal>
<abp-modal-header title="Update"></abp-modal-header>
<abp-modal-body>
<abp-input asp-for="Id"/>
<abp-input asp-for="Book.Name"/>
<abp-input asp-for="Book.Price"/>
<abp-select asp-for="Book.Type"/>
<abp-input asp-for="Book.PublishDate"/>
<abp-input asp-for="Book.ConcurrencyStamp" type="hidden"/>
</abp-modal-body>
<abp-modal-footer buttons="@(AbpModalButtons.Cancel|AbpModalButtons.Save)"></abp-modal-footer>
</abp-modal>
</form>
Here, we didn't use the
abp-dynamic-formtag-helper and added all the necessary form elements to our form one by one.As you may have noticed, we've set the input type as hidden for the ConcurrencyStamp input, because the end-user should not see this value.
Instead of doing it like that, we could create a view model class and use the
[HiddenInput]data attribute for the ConcurrencyStamp property and use theabp-dynamic-formtag-helper. But to simplify the article I didn't want to do that, if you want you can create a view model and define the necessary data attributes for properties.
EditModal.cshtml.cs
public class EditModalModel : BookStorePageModel
{
[HiddenInput]
[BindProperty(SupportsGet = true)]
public Guid Id { get; set; }
[BindProperty]
public UpdateBookDto Book { get; set; }
private readonly IBookAppService _bookAppService;
public EditModalModel(IBookAppService bookAppService)
{
_bookAppService = bookAppService;
}
public async Task OnGetAsync()
{
var bookDto = await _bookAppService.GetAsync(Id);
Book = ObjectMapper.Map<BookDto, UpdateBookDto>(bookDto);
}
public async Task<IActionResult> OnPostAsync()
{
await _bookAppService.UpdateAsync(Id, Book);
return NoContent();
}
}
Lastly, we can define the necessary mapping configurations and run the application to see the result.
Open the BookStoreWebAutoMapperProfile.cs class and update the content as below:
public class BookStoreWebAutoMapperProfile : Profile
{
public BookStoreWebAutoMapperProfile()
{
CreateMap<BookDto, UpdateBookDto>();
}
}
Then we can run the application, navigate to the /Books endpoint and see the result.
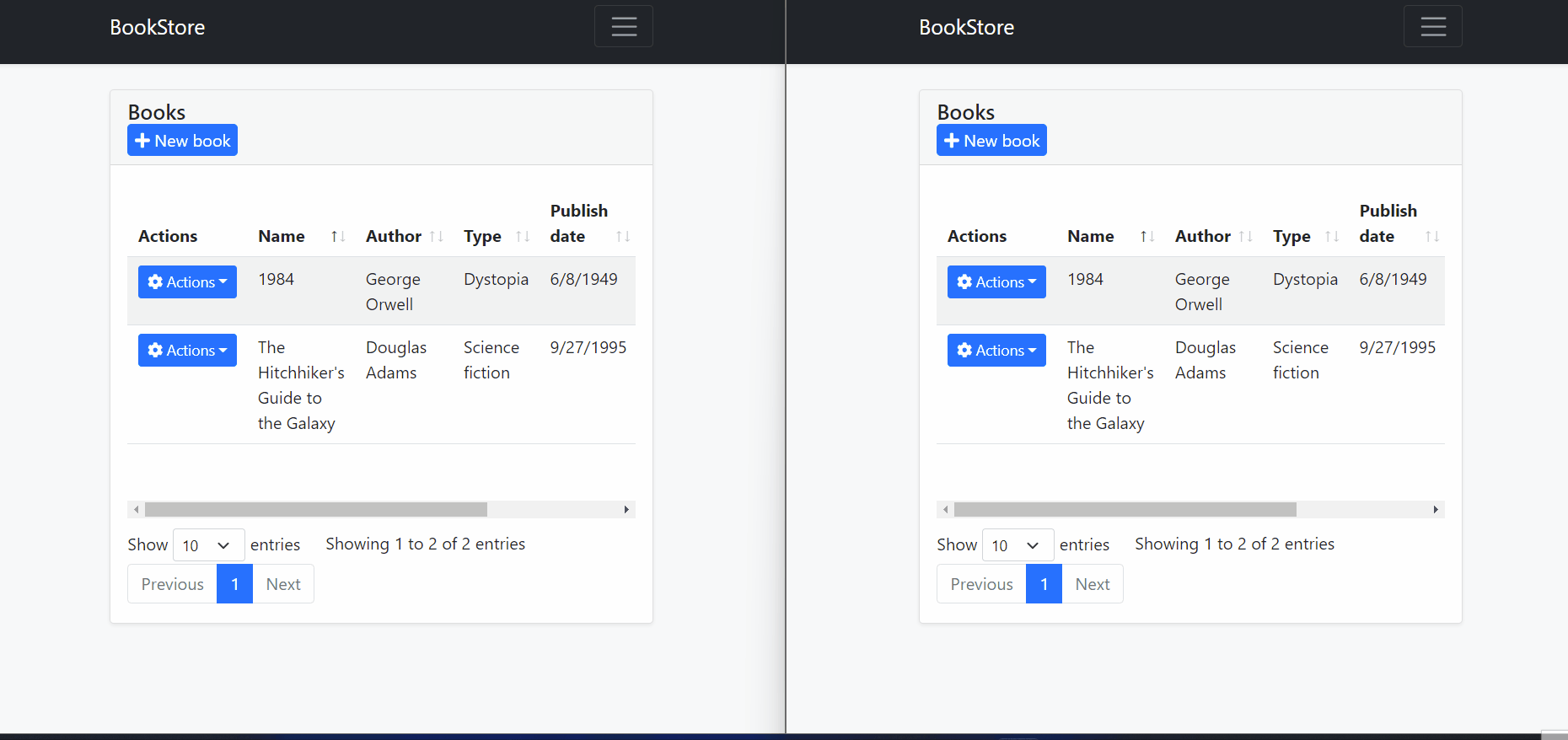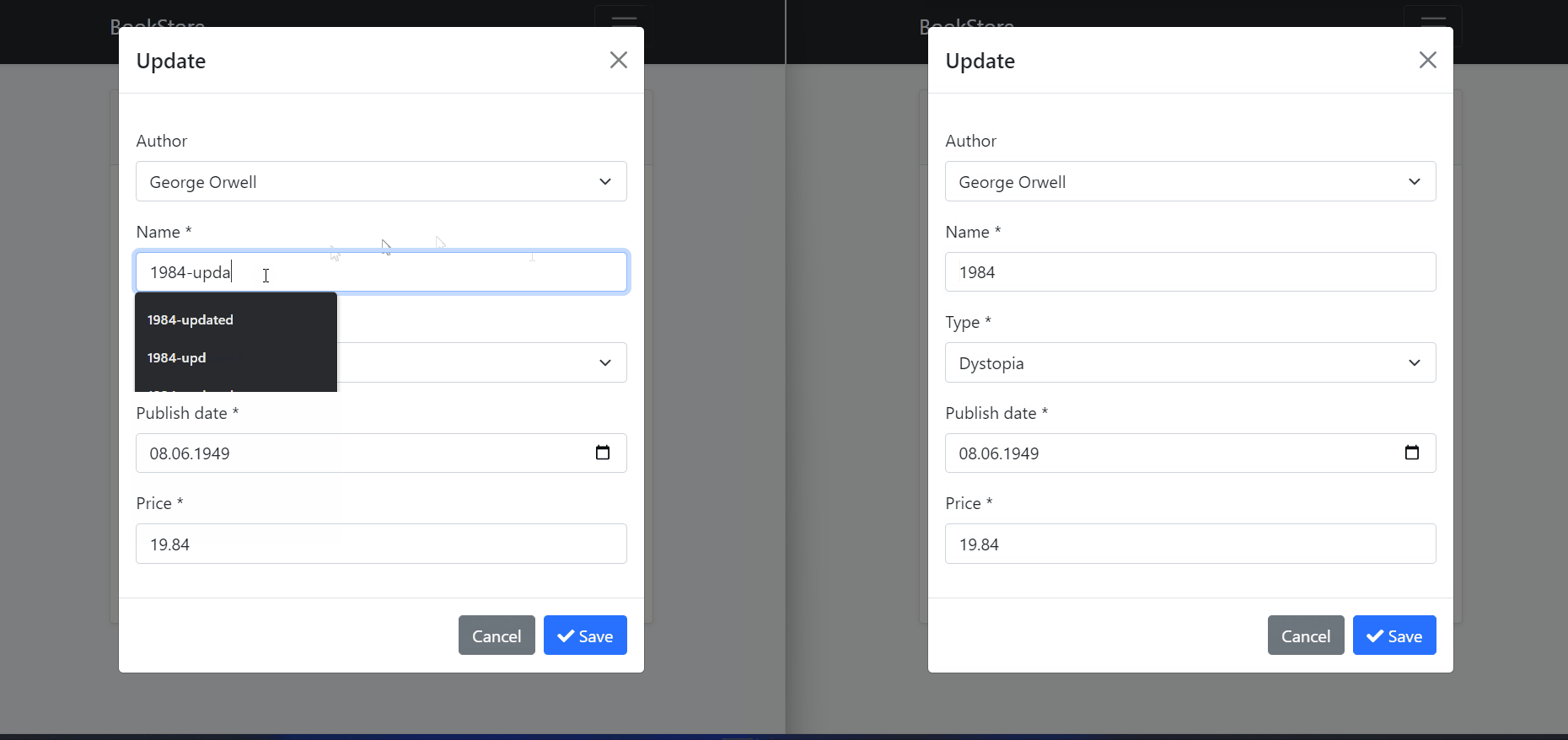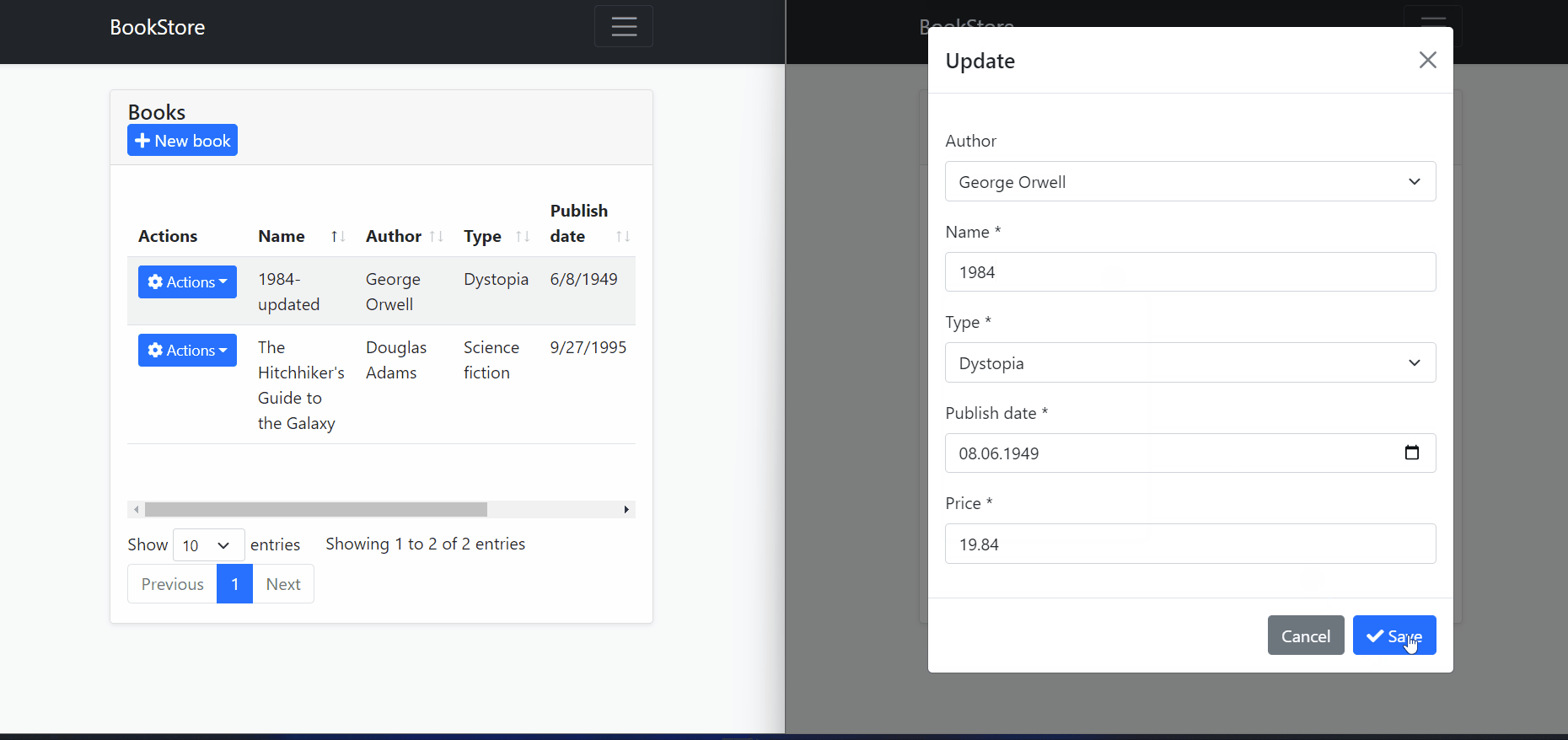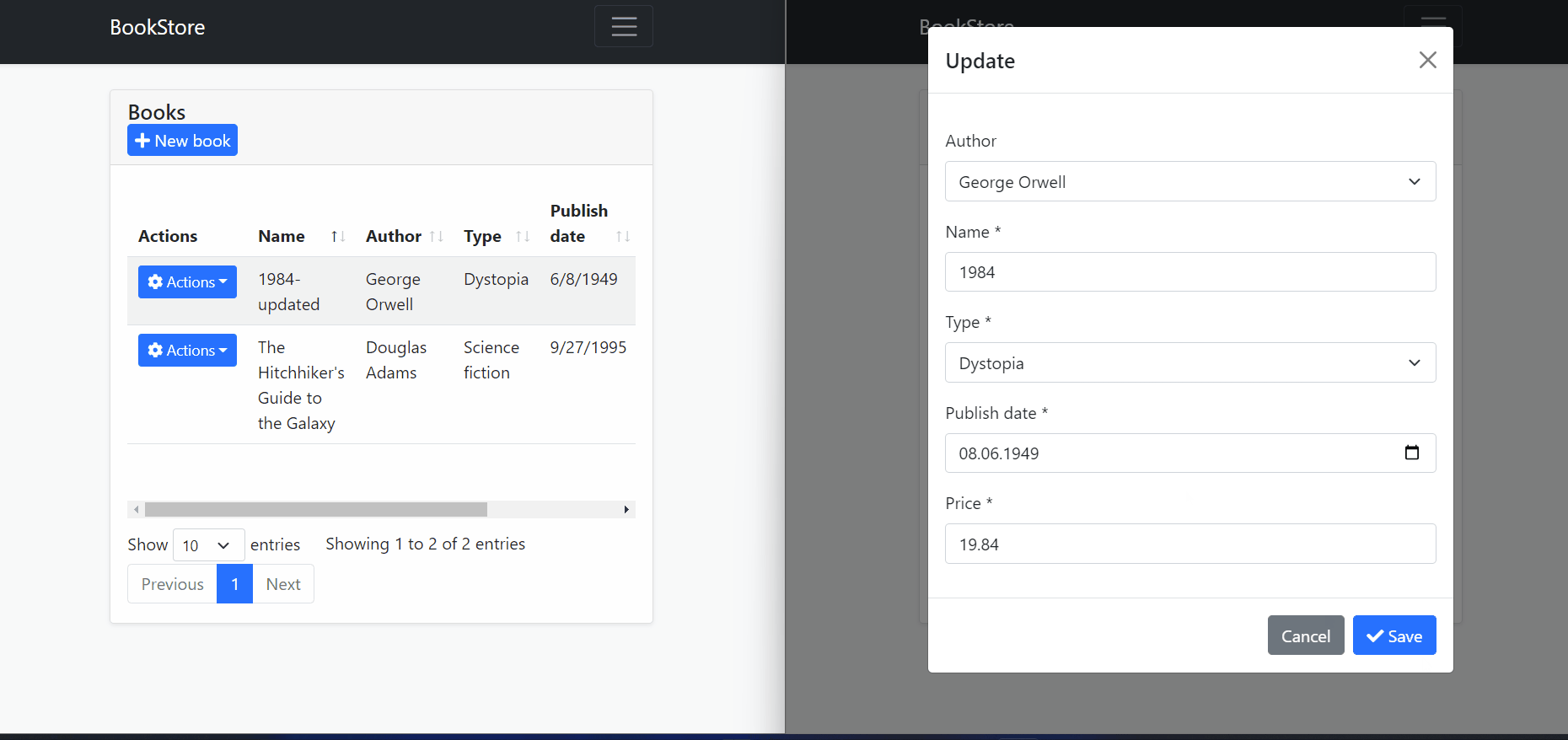
In the image above, we can see that multiple users open the edit model to change a record and try to update the relevant record independently of each other.
After the first user updated the record, the second user tries to update the same record without getting the last state of the record. And therefore
AbpDbConcurrencyExceptionis thrown because ConcurrencyStamp values are different from each other.The second user should close and re-open the model to get the last state of the record and then they can make changes to the current record.
🛠 Liked this post? I now share all my content on Substack — real-world .NET, AI, and scalable software design.
👉 Subscribe here → engincanveske.substack.com
🎥 Also, check out my YouTube channel for hands-on demos and deep dives: https://www.youtube.com/@engincanv

































































Comments
Serdar Genc 199 weeks ago
Thanks Engincan. Your articles are very good.
Engincan Veske 199 weeks ago
Thanks :)
kenanoglu115@gmail.com 173 weeks ago
Merhaba, abp 7.0.0 sürümünde; makaledeki base classlardan concurrencycheck özelliğini alamıyorum.
-AggregateRoot, AggregateRoot<TKey> -CreationAuditedAggregateRoot -CreationAuditedAggregateRoot<TKey> -AuditedAggregateRoot, AuditedAggregateRoot<TKey> -FullAuditedAggregateRoot, FullAuditedAggregateRoot<TKey>
ConcurrencyCheck özelliği bu sınıflarda bulunmadığı için auto increment olmuyor ve makaleyi uygulayamıyorum. Yardımlarınızı rica ederim .