ABP Framework version: v8.3.4
UI Type: React
Database System: EF Core (SQL Server)
Tiered (for MVC) or Auth Server Separated (for Angular): yes
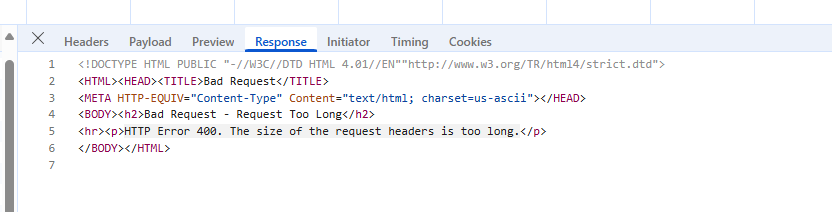
We have recently increased permission for admin user but after adding the permission user started getting error "HTTP Error 400. The size of the request header is too long".
How to fix this ?
9 Answer(s)
-
0
- Solution
Why this happens
- In ABP, the current user’s permissions are sent to the client as claims. With cookie authentication (React UI + separated AuthServer/tiered), these claims are included in the auth cookie. If you grant a very large number of permissions to a user/role, the cookie grows and can exceed server/proxy/browser header size limits, resulting in “HTTP Error 400. The size of the request header is too long”.
Fixes (pick one or combine)
Reduce the amount of data stored in the cookie
- Prefer role-based permissions instead of assigning hundreds/thousands of permissions directly to the user.
- Remove unnecessary claims you may be adding (custom claims, tenant-specific extras, etc.).
Switch to reference tokens (prevent large cookies to the frontend)
- If you are using the AuthServer (OpenIddict/IdentityServer), configure access tokens to be reference tokens or keep the principal small and fetch permissions from the API when needed (AuthorizationService / AbpPermissionDefinitionManager) instead of carrying all permission names as claims in the cookie.
Increase header limits on your front-end/reverse proxy if absolutely necessary
- IIS: increase max request header size limits. Example in web.config for AspNetCoreModuleV2:
- Add or increase limits in the hosting/reverse proxy layer (IIS/ARR, nginx, Azure App Gateway). Note: This is only a mitigator; it’s better to reduce cookie size.
- Browsers still have cookie-size limits (~4 KB per cookie and ~8–16 KB per header chunk), so this may not fully solve it.
- IIS: increase max request header size limits. Example in web.config for AspNetCoreModuleV2:
Ensure antiforgery/cookie settings don’t add extra cookies unnecessarily
- Don’t send cookies from non-browser clients (Postman/mobile). Carrying cookies can trigger antiforgery and add more headers, compounding the size. See ABP guidance: if you remove cookies for API calls, antiforgery isn’t required and avoids extra headers.
Practical steps to reduce cookie size in ABP
- Keep permissions assigned to roles; assign users to roles. Avoid assigning long lists of permissions to a single user.
- Avoid adding each permission as a separate claim at sign-in time. Rely on ABP’s permission checking on the server instead of pushing the full permission list to the client if you customized the claims principal factory.
- If you customized AbpClaimsPrincipalFactory or added claim contributors, remove verbose claims or compress/limit them.
- For React UI, prefer using the Abp Application Configuration endpoint and on-demand authorization checks instead of shipping all permissions in the cookie.
IIS-specific mitigation (optional)
- If you must, increase header limits in IIS/ARR. But the sustainable fix is reducing cookie/claims size.
- Sources
- Validated:
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/security/cookie-sharing#cookie-size-limit
- ABP support reference about cookies/antiforgery behavior (context confirms avoiding cookies for API calls prevents antiforgery requirement):
- https://abp.io/support/questions/1895 (No direct link validation available)
This response was generated by AI. If it didn’t solve your problem, feel free to post a new answer — our support team will jump in to help you soon.
-
0
hi
What is your web server?
IIS, Kestrel or Nginx?
Thanks.
-
0
[maliming] said: hi
What is your web server?
IIS, Kestrel or Nginx?
Thanks.
Hi, it's IIS.
Thanks.
-
0
hi
Try configuring IIS Request Limits in web config like this to increase the allowed query string length:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/iis/configuration/system.webserver/security/requestfiltering/requestlimits/
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <!-- Any existing configuration you may have --> + <system.webServer> + <security> + <requestFiltering> + <requestLimits maxQueryString="4096" /> + </requestFiltering> + </security> + </system.webServer> </configuration>Could you please share the request URL that returns a 400 error?
Thanks
-
0
[maliming] said: hi
Try configuring IIS Request Limits in web config like this to increase the allowed query string length:
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/iis/configuration/system.webserver/security/requestfiltering/requestlimits/
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <configuration> <!-- Any existing configuration you may have --> + <system.webServer> + <security> + <requestFiltering> + <requestLimits maxQueryString="4096" /> + </requestFiltering> + </security> + </system.webServer> </configuration>Could you please share the request URL that returns a 400 error?
Thanks
Hi, I tried to update config, it is still giving the same error. I'm sharing the URL as well, it is when we get permission details.
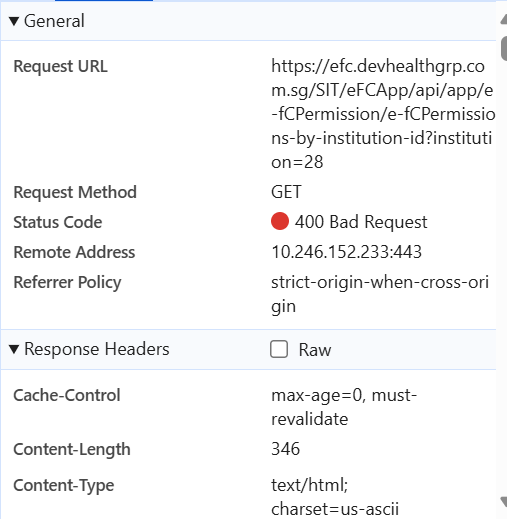
Thanks
-
0
-
0
[maliming] said: hi
Have you restarted the website after changing the Web Config file?
Is there any 400 error in the app logs?
Can you share the full URL?
Thanks.
yes, I restarted, there is no 400 in logs, it's failing as header size is big. Below is the URL.
https://efc.devhealthgrp.com.sg/UAT/eFCApp/api/app/user/user-organization?userName=healthgrp%5Csim0886h
-
0
- Solution
Root cause
- After you granted many permissions, the authenticated principal carries a large number of claims. With cookie-based auth on IIS, these claims are serialized into the auth cookie. IIS (http.sys) enforces request header size limits; when the cookie grows beyond those limits you get “HTTP Error 400. The size of the request headers is too long”.
Fix (recommended)
Reduce auth cookie size
- Assign permissions to roles and add the user to roles instead of assigning hundreds of permissions directly to the user.
- Remove/limit any custom claims you add via contributors or a custom ClaimsPrincipalFactory.
- Avoid putting permission names as individual claims; rely on ABP’s permission check on the server side instead of duplicating all permissions in the cookie.
Use tokens that don’t bloat headers
- If you use the Auth Server (OpenIddict), prefer bearer access tokens on API calls (Authorization: Bearer …) and keep the cookie principal minimal for the interactive login. Do not mirror every permission in claims.
IIS-specific mitigations (if you still need more room)
- Increase http.sys header limits (this affects IIS because it sits on http.sys). In registry:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\HTTP\Parameters
- MaxFieldLength (DWORD, in bytes)
- MaxRequestBytes (DWORD, in bytes)
- Reboot the server after changing.
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SYSTEM\CurrentControlSet\Services\HTTP\Parameters
- You can also raise requestFiltering limits, but that affects URL/query length, not header size. Since the error started after adding permissions, the cookie/header size is the actual culprit, not query string length.
- Increase http.sys header limits (this affects IIS because it sits on http.sys). In registry:
Verify no unnecessary cookies are sent
- Remove extra cookies and ensure non-browser clients don’t send cookies to API endpoints to avoid additional headers (antiforgery, etc.).
Minimal ABP-side checklist
- Review any custom claim contributors:
public class MyClaimsContributor : IAbpClaimsPrincipalContributor { public Task ContributeAsync(AbpClaimsPrincipalContributorContext context) { var identity = context.ClaimsPrincipal.Identities.First(); // Remove or avoid adding large/duplicate claims here return Task.CompletedTask; } }- Keep user-to-role assignments and let ABP evaluate permissions by definition, not by dumping all permission names into claims.
- Sources
- Verified:
- IIS request header limits (http.sys): https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/aspnet/core/security/authentication/cookie?view=aspnetcore-8.0
- IIS Request Filtering (query string limit reference; not for headers but often confused): https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/iis/configuration/system.webserver/security/requestfiltering/requestlimits/
This response was generated by AI. If it didn’t solve your problem, feel free to post a new answer — our support team will jump in to help you soon.
-
0