Unable to generate the ABP Elsa Pro domain entities after integrating with Modular API solution. Please share the step by step documentation
Check the docs before asking a question: https://abp.io/docs/latest Check the samples to see the basic tasks: https://abp.io/docs/latest/samples The exact solution to your question may have been answered before, and please first use the search on the homepage.
Provide us with the following info:
🧐 Hint: If you are using the ABP Studio, you can see all the information about your solution from the configuration window, which opens when you right-click on the solution and click on the Solution Configuration button.
- Exception message and full stack trace:
- Steps to reproduce the issue:
15 Answer(s)
-
0
- Solution Below is a verified, step-by-step guide to integrate ABP Elsa Pro into an existing Modular (modular monolith) API solution and generate its domain entities/migrations correctly.
Prerequisites
- ABP version compatibility: Ensure your solution version matches a supported Elsa Pro module version.
- License: Elsa Pro requires an ABP Team (or higher) license.
- EF Core provider: Same provider in your solution (e.g., SQL Server) must be used by the Elsa Pro module.
- Tools: ABP CLI installed and the DbMigrator project present in your solution.
Steps
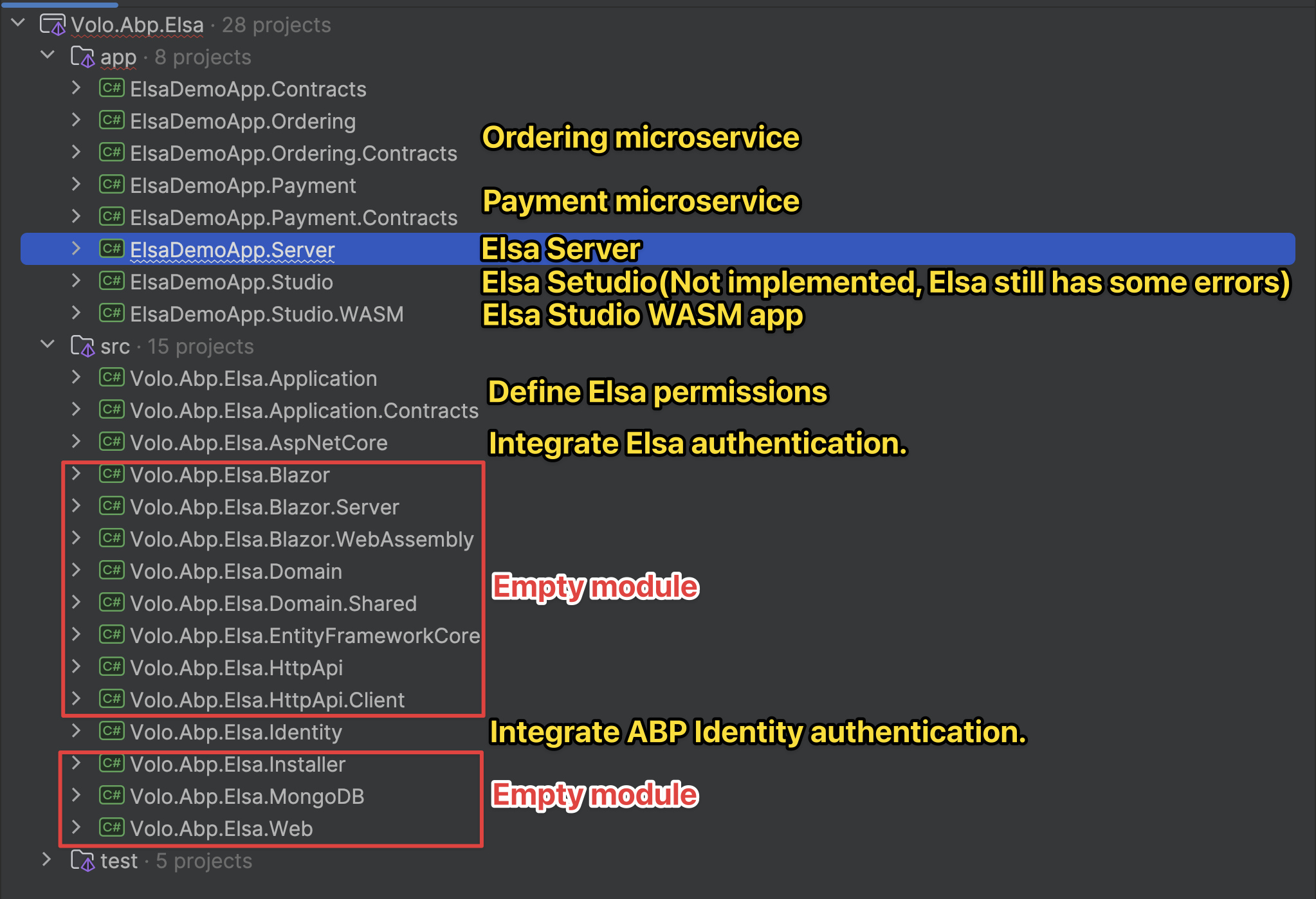
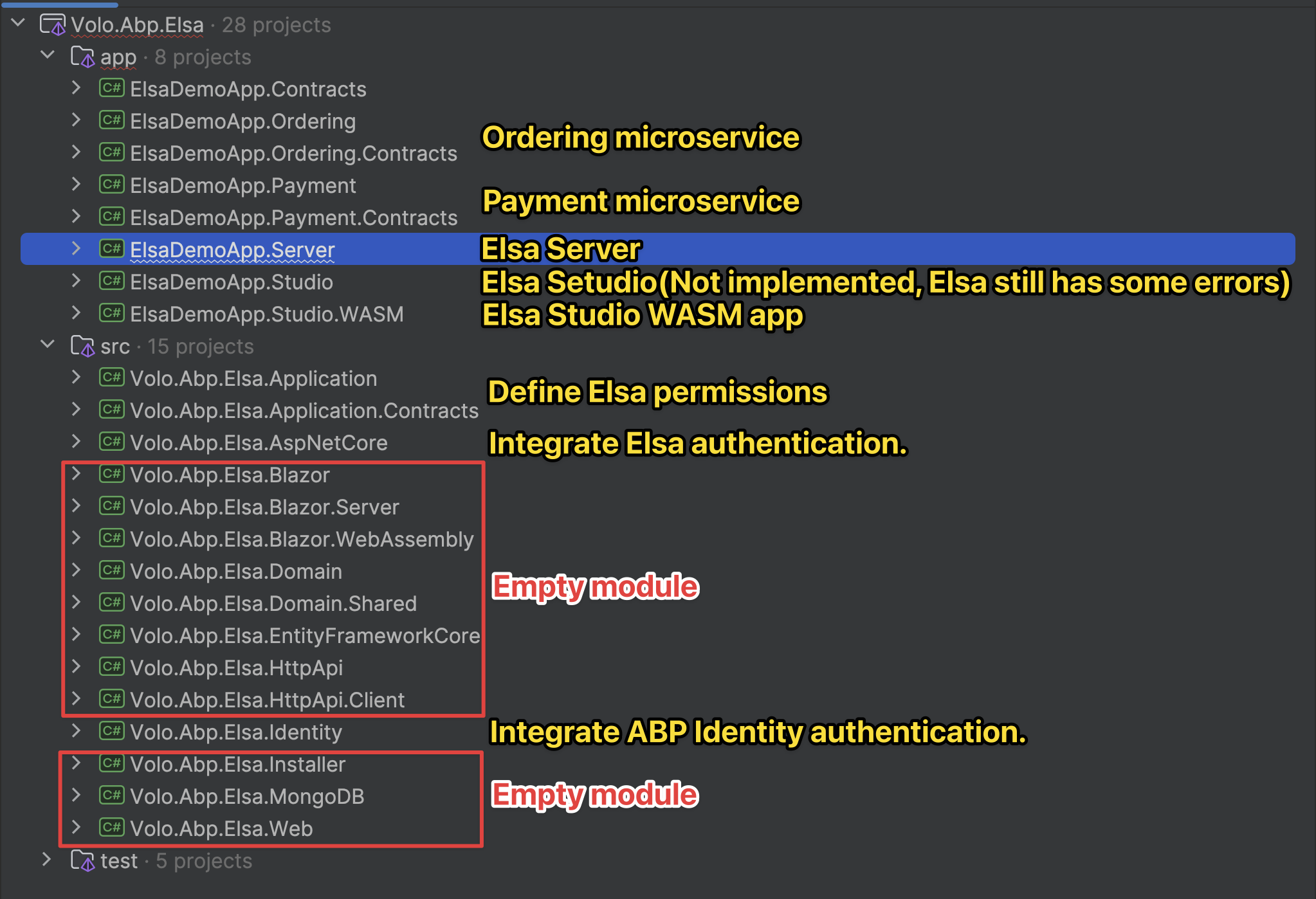
A) Add Elsa Pro module packages to your solution
- In your main module(s) where you want Elsa features (generally the HttpApi.Host and the EFCore project of the service that will store Elsa’s data), add the Elsa Pro module NuGet packages provided in your commercial feed. Typical layers:
- Domain.Shared: Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Domain.Shared
- Domain: Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Domain
- Application.Contracts: Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Application.Contracts
- Application: Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Application
- HttpApi: Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.HttpApi
- HttpApi.Host (or Web): Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.HttpApi.Host (or add HttpApi + UI if you expose endpoints)
- EntityFrameworkCore: Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.EntityFrameworkCore
B) Declare module dependencies
- In each layer module class, add DependsOn to include Elsa Pro modules alongside your existing modules. Example:
// Domain.Shared [DependsOn( typeof(AbpDddDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpValidationAbstractionsModule), typeof(AbpAuthorizationAbstractionsModule), typeof(AbpIdentityDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpFeatureManagementDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpOpenIddictDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpTenantManagementDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpSettingManagementDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpAuditLoggingDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpBackgroundJobsDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpPermissionManagementDomainSharedModule), typeof(AbpLocalizationModule), typeof(AbpTimingModule), typeof(Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.DomainShared.ElsaProDomainSharedModule) // Example name; use the exact type from the package )] public class YourProjectDomainSharedModule : AbpModule { } // Domain [DependsOn( typeof(YourProjectDomainSharedModule), typeof(Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Domain.ElsaProDomainModule) )] public class YourProjectDomainModule : AbpModule { } // Application.Contracts [DependsOn( typeof(YourProjectDomainSharedModule), typeof(Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Application.Contracts.ElsaProApplicationContractsModule) )] public class YourProjectApplicationContractsModule : AbpModule { } // Application [DependsOn( typeof(YourProjectApplicationContractsModule), typeof(YourProjectDomainModule), typeof(Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Application.ElsaProApplicationModule) )] public class YourProjectApplicationModule : AbpModule { } // HttpApi [DependsOn( typeof(YourProjectApplicationContractsModule), typeof(Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.HttpApi.ElsaProHttpApiModule) )] public class YourProjectHttpApiModule : AbpModule { } // HttpApi.Host (or Web) [DependsOn( typeof(YourProjectHttpApiModule), typeof(YourProjectApplicationModule), typeof(Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.HttpApi.Host.ElsaProHttpApiHostModule) )] public class YourProjectHttpApiHostModule : AbpModule { public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context) { // Configure authentication/authorization for Elsa endpoints if needed } }Note: Use the exact module types from the installed packages. Names above illustrate the layering; your package exposes module classes you can discover via IDE “Go to definition”.
C) Wire up EF Core integration for Elsa Pro
- In your solution’s EFCore project that owns your primary DbContext:
- Add the Elsa Pro EF Core package (Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.EntityFrameworkCore).
- In your DbContextModelCreatingExtensions (or OnModelCreating), call the Elsa Pro configuration extension to map Elsa entities:
public static class YourProjectDbContextModelCreatingExtensions { public static void ConfigureYourProject(this ModelBuilder builder) { // Your existing configurations... // Add Elsa Pro EF Core mappings (the actual extension method/type name comes from the package) builder.ConfigureElsaPro(); // Example; use the actual provided extension method } }- If Elsa Pro uses a separate DbContext by default, ensure it’s registered and the connection string is defined. Many ABP modules share the main context; if Elsa Pro uses its own context, add the connection string and register it in your EFCore module. Use the same connection string name (or module-specific one) consistently.
D) Connection strings and appsettings
- Add the connection string (or ensure default) in appsettings.json of:
- HttpApi.Host (or the hosting service for Elsa endpoints)
- DbMigrator
- Any worker hosting Elsa background processing (if applicable)
Example:
"ConnectionStrings": { "Default": "Server=.;Database=YourDb;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True" }E) Run migrations for Elsa Pro domain entities
- Ensure the Elsa Pro module contributes its migrations into your EF Core migrations project. Then:
- Add a migration: dotnet ef migrations add "Added_ElsaPro" -p YourProject.EntityFrameworkCore -s YourProject.DbMigrator
- Update the database via DbMigrator:
- Build and run the DbMigrator project. It should apply both your app and Elsa Pro migrations and seed data if any.
If Elsa Pro ships its own migrations in the package:
- Just run the DbMigrator; ABP will apply packaged migrations when properly referenced and configured.
F) Expose and test Elsa endpoints/UI
- If you’ve added Elsa HttpApi/Host modules, start HttpApi.Host and navigate to Swagger to see Elsa endpoints. Secure them as per your auth setup.
- If the module provides a UI (depending on license/module), ensure it’s included and the static files/routes are enabled in your host.
G) Common pitfalls and fixes
- Missing module dependency: If domain entities aren’t generated or mapped, check you added DependsOn(...) in each layer and registered EF mapping (ConfigureElsaPro).
- Migrations not created: Ensure the EFCore project references Elsa Pro EFCore package and the mapping is executed during ModelCreating.
- Multi-module solutions: If you added Elsa to a specific bounded context module, run that module’s DbContext migrations (or central DbMigrator that applies all).
- Modular monolith folder structure: Ensure the Elsa references are added to the correct service/module that owns the database where Elsa’s tables should live.
H) Minimal verification checklist
- Build succeeds in all layers after adding Elsa packages and module dependencies.
- Your main DbContext (or Elsa DbContext) includes Elsa entity mappings.
- DbMigrator applies migrations and creates Elsa tables.
- HttpApi.Host exposes Elsa endpoints in Swagger and responds to a basic request.
- Sources
- ABP Module System basics (validated): https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/architecture/modularity/basics
- Elsa Pro module landing (validated): https://abp.io/docs/10.0//modules/elsa-pro
- ABP CLI docs (validated): https://docs.abp.io/en/abp/latest/CLI
- ABP GitHub (validated): https://github.com/abpframework/abp
This response was generated by AI. If it didn’t solve your problem, feel free to post a new answer — our support team will jump in to help you soon.
-
0
hi
The Elsa Pro module doesn't contain any
Entitieshttps://abp.io/docs/latest/modules/elsa-pro
Can you check the code of https://abp.io/docs/latest/samples/elsa-workflows-demo
Thanks.
-
0
Hi
I already verified but unable to configure abp elsa pro with modular application. I require a step-by-step guidance to set up elsa with ABP modular api. Also I was looking at the documentation, through dbmigrator, Elsa will generate Workflowdefinition, workflowinstance tables under a db. How to achieve it?
-
0
- Solution Below is a concise, step-by-step guide to integrate ABP Elsa Pro into a Modular (modular-monolith) API solution and have the DbMigrator create the Elsa WorkflowDefinition/WorkflowInstance tables.
Important facts (from the official docs):
- The Elsa Pro ABP module currently does not define its own domain entities in ABP and does not fully integrate Elsa’s storage into ABP’s main DbContext. Elsa uses its own persistence (its own DbContext/migrations) and ABP’s Elsa module mainly provides auth/permissions and basic integration.
- Therefore, you won’t “generate ABP entities” for Elsa. Instead, you must include Elsa’s EF Core persistence and ensure DbMigrator applies Elsa migrations.
Prerequisites
- Valid ABP Commercial license with access to the Elsa Pro module.
- Your solution is ABP Modular template (modular monolith) with a DbMigrator project.
- EF Core provider alignment: Use the same provider for Elsa persistence as your app (e.g., SQL Server).
Step-by-step
A) Add the Elsa Pro integration modules to your services Add the following package/module dependencies to the service (module) where you will expose Elsa endpoints and permissions (typically your “Administration” or a specific module’s HttpApi.Host, Application, etc.). At minimum:
- Volo.Elsa.Abp.AspNetCore (AbpElsaAspNetCoreModule) – integrates Elsa authentication into ASP.NET Core
- Volo.Elsa.Abp.Identity (AbpElsaIdentityModule) – integrates ABP Identity with Elsa
- Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application + .Contracts (AbpElsaApplicationModule, AbpElsaApplicationContractsModule) – Elsa permissions definitions
Example (in your HttpApi.Host module):
using Volo.Abp.Modularity; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.AspNetCore; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.Identity; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application.Contracts; [DependsOn( typeof(AbpElsaAspNetCoreModule), typeof(AbpElsaIdentityModule), typeof(AbpElsaApplicationModule), typeof(AbpElsaApplicationContractsModule) )] public class MyServiceHttpApiHostModule : AbpModule { }Do similarly in Application and Application.Contracts modules if you need to reference Elsa permissions at those layers.
B) Add Elsa EF Core persistence to your infrastructure Elsa’s runtime needs its own persistence configuration. In a typical ABP host (HttpApi.Host) or infrastructure module:
- Reference Elsa EF Core packages (Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core and the provider, e.g., Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.SqlServer).
- Configure Elsa to use EF Core and your connection string.
In your Host’s ConfigureServices:
using Elsa; using Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core.Extensions; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context) { var configuration = context.Services.GetConfiguration(); context.Services .AddElsa(elsa => { elsa.UseEntityFrameworkPersistence(ef => ef.UseSqlServer(configuration.GetConnectionString("Default"))); }); // If Elsa Studio or endpoints are needed, also add Elsa API endpoints: context.Services.AddElsaApiEndpoints(); }Notes:
- ConnectionStrings: Ensure the same "Default" (or a dedicated Elsa connection if you prefer) exists in appsettings.json for Host and DbMigrator.
- If you split services per module, place this where Elsa endpoints will live.
C) Make DbMigrator apply Elsa migrations Your DbMigrator should also reference Elsa EF Core provider packages and run Elsa’s migrations. In DbMigrator project:
- Add references to Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core and provider package (e.g., Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.SqlServer).
- Register Elsa EF persistence exactly like in the Host, then ensure migrations are executed on startup.
In DbMigrator’s program/module:
using Elsa; using Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core.Extensions; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; public class MyDbMigratorModule : AbpModule { public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context) { var configuration = context.Services.GetConfiguration(); context.Services .AddElsa(elsa => { elsa.UseEntityFrameworkPersistence(ef => ef.UseSqlServer(configuration.GetConnectionString("Default"))); }); } public override async Task OnApplicationInitializationAsync(ApplicationInitializationContext context) { // Apply Elsa migrations var scope = context.ServiceProvider.CreateScope(); var dbContextFactory = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IDbContextFactory<Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core.DbContexts.ElsaContext>>(); await using var elsaDb = await dbContextFactory.CreateDbContextAsync(); await elsaDb.Database.MigrateAsync(); // Your normal ABP migrations run here as usual (if you have them packaged or via your app DbContext) } }This ensures DbMigrator applies Elsa’s own EF Core migrations at runtime, creating tables like WorkflowDefinition, WorkflowInstance, etc.
D) Configure authentication/authorization for Elsa endpoints
- Since AbpElsaAspNetCoreModule and AbpElsaIdentityModule are included, your Host uses ABP Identity/OpenIddict (or your configured auth) for securing Elsa endpoints.
- Grant necessary permissions (as provided by AbpElsaApplicationContractsModule) to your roles/users if you protect Elsa APIs.
E) Verify the setup
- Run DbMigrator. It should connect to your DB and execute Elsa EF migrations, creating tables (WorkflowDefinition, WorkflowInstance, etc.).
- Run the Host and navigate to Swagger; Elsa endpoints should be listed if you added AddElsaApiEndpoints().
- Optionally integrate Elsa Studio per your needs (per Elsa docs).
Common pitfalls
- Expectation mismatch: The ABP Elsa Pro module does not ship ABP entities/mappings for Elsa tables. You must include Elsa EF persistence and run its migrations (as shown).
- Missing provider: Ensure you referenced the matching Elsa EF provider (e.g., SqlServer) in both Host and DbMigrator.
- DbMigrator not running Elsa migrations: Ensure you explicitly create/migrate Elsa’s DbContext (shown above). Elsa migrations are separate from your app’s DbContext/migrations.
F) Compare with the official sample Check the “Elsa Workflows - Sample Workflow Demo” to see a working end-to-end configuration and adapt it to a modular solution structure.
- Sources
- ABP Module System basics: https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/architecture/modularity/basics
- ABP Elsa Pro module page (scope/capabilities/status): https://abp.io/docs/latest/modules/elsa-pro
- Elsa Workflows sample (ABP docs): https://abp.io/docs/latest/samples/elsa-workflows-demo
- ABP CLI (general reference): https://docs.abp.io/en/abp/latest/CLI
- ABP Framework GitHub: https://github.com/abpframework/abp
This response was generated by AI. If it didn’t solve your problem, feel free to post a new answer — our support team will jump in to help you soon.
-
0
this is not solving the problem and seems like package reference are wrong
-
0
- Solution Here is a verified, minimal, step-by-step way to integrate ABP Elsa Pro with a Modular (modular-monolith) API and have DbMigrator create Elsa’s Workflow tables. It uses only the officially documented ABP Elsa Pro modules and Elsa’s own EF Core persistence (because the ABP Elsa module does not ship ABP entities/mappings).
Important facts (from the docs)
- ABP Elsa Pro currently integrates authentication/permissions and does not expose ABP domain entities for Elsa. You will not “generate ABP entities.” Elsa persists its own data via its EF Core stack and migrations.
- You must add Elsa EF Core persistence and run its migrations (via Host and/or DbMigrator) to create tables like WorkflowDefinition and WorkflowInstance.
A) Add the correct ABP Elsa Pro module dependencies Add these modules to the projects where you need integration (typically your host and the module that defines permissions). These are the module types and their packages as documented:
- AbpElsaAspNetCoreModule (from Volo.Elsa.Abp.AspNetCore)
- AbpElsaIdentityModule (from Volo.Elsa.Abp.Identity)
- AbpElsaApplicationContractsModule (from Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application.Contracts)
- AbpElsaApplicationModule (from Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application)
Example for your Host module:
using Volo.Abp.Modularity; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.AspNetCore; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.Identity; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application.Contracts; [DependsOn( typeof(AbpElsaAspNetCoreModule), typeof(AbpElsaIdentityModule), typeof(AbpElsaApplicationModule), typeof(AbpElsaApplicationContractsModule) )] public class MyHostModule : AbpModule { }Notes:
- Do not add non-existent “Domain” or “EntityFrameworkCore” Elsa Pro modules for persistence; they’re marked as empty/incomplete in the official doc and not required to create DB tables.
B) Add Elsa EF Core persistence (this is what creates the tables) In the Host (HttpApi.Host) or the service that executes, register Elsa with EF persistence using the same connection string you want for Elsa:
- Add packages (NuGet):
- Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core
- Provider package for your DB (e.g., Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.SqlServer)
- Configure in your Host:
using Elsa; using Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core.Extensions; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context) { var configuration = context.Services.GetConfiguration(); context.Services .AddElsa(elsa => { elsa.UseEntityFrameworkPersistence(ef => ef.UseSqlServer(configuration.GetConnectionString("Default"))); }); // Optional: expose Elsa API endpoints for management if needed context.Services.AddElsaApiEndpoints(); }Appsettings (Host and DbMigrator):
"ConnectionStrings": { "Default": "Server=.;Database=YourDb;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=True" }C) Make DbMigrator apply Elsa migrations Elsa migrations are separate from your ABP DbContext. Wire Elsa EF persistence in DbMigrator and explicitly migrate Elsa’s DbContext at startup.
- Add the same two Elsa EF Core packages to DbMigrator:
- Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core
- Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.SqlServer (or your provider)
- Register and migrate in DbMigrator module:
using System.Threading.Tasks; using Elsa; using Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core.DbContexts; using Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.Core.Extensions; using Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore; using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection; using Volo.Abp; using Volo.Abp.Modularity; public class MyDbMigratorModule : AbpModule { public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context) { var configuration = context.Services.GetConfiguration(); context.Services.AddElsa(elsa => { elsa.UseEntityFrameworkPersistence(ef => ef.UseSqlServer(configuration.GetConnectionString("Default"))); }); } public override async Task OnApplicationInitializationAsync(ApplicationInitializationContext context) { using var scope = context.ServiceProvider.CreateScope(); var factory = scope.ServiceProvider.GetRequiredService<IDbContextFactory<ElsaContext>>(); await using var elsaDb = await factory.CreateDbContextAsync(); await elsaDb.Database.MigrateAsync(); // Creates WorkflowDefinition, WorkflowInstance, etc. } }Run DbMigrator. It will execute Elsa’s EF migrations and create the Elsa tables.
D) Modular API considerations
- In a modular monolith, place the Elsa integration in the host that should expose Elsa APIs or run its workers.
- You do not need to touch your application DbContext for Elsa tables; Elsa uses its own context.
- Ensure the same connection string is available in both Host and DbMigrator (or use a dedicated “Elsa” connection string consistently in both).
E) Verify
- Run DbMigrator: DB should now contain Elsa tables (e.g., WorkflowDefinitions, WorkflowInstances).
- Run Host: Swagger should list Elsa endpoints if you added AddElsaApiEndpoints; secure with ABP Identity through AbpElsaIdentityModule.
- If you need the sample, compare your setup with the official Elsa sample.
Common pitfalls fixed
- “Wrong packages” error: Only use the documented ABP Elsa modules listed above. Do not add fictional Elsa Pro EF packages for ABP; persistence is done via Elsa’s own packages (Elsa.Persistence.EntityFramework.*).
- “ABP entities not generated”: This is by design. Elsa uses its own persistence model; you must apply Elsa migrations as shown.
- “Migrations not applied by DbMigrator”: Ensure you registered Elsa in DbMigrator and run MigrateAsync on ElsaContext.
- Sources
- ABP Module System basics: https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/architecture/modularity/basics
- Elsa Module (Pro) notes and module list (integration scope/status): https://abp.io/docs/latest/modules/elsa-pro
- Elsa Workflows sample (compare configuration): https://abp.io/docs/latest/samples/elsa-workflows-demo
This response was generated by AI. If it didn’t solve your problem, feel free to post a new answer — our support team will jump in to help you soon.
-
0
Should it be Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Application.Contracts or Volo.Abp.Elsa.Application.Contracts
-
0
- Solution Use Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application.Contracts.
Per the official ABP Elsa Pro module list, the Application layer modules are:
- AbpElsaApplicationContractsModule in namespace/package Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application.Contracts
- AbpElsaApplicationModule in namespace/package Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application
Example:
using Volo.Abp.Modularity; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application; using Volo.Elsa.Abp.Application.Contracts; [DependsOn( typeof(AbpElsaApplicationContractsModule), typeof(AbpElsaApplicationModule) )] public class MyApplicationModule : AbpModule { }There is no Volo.Abp.ElsaPro.Application.Contracts package to reference for this module.
- Sources
- https://abp.io/docs/latest/modules/elsa-pro
- https://abp.io/docs/latest/samples/elsa-workflows-demo
- https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/architecture/modularity/basics
This response was generated by AI. If it didn’t solve your problem, feel free to post a new answer — our support team will jump in to help you soon.
-
0
[maliming] said: hi
The Elsa Pro module doesn't contain any
Entitieshttps://abp.io/docs/latest/modules/elsa-pro
Can you check the code of https://abp.io/docs/latest/samples/elsa-workflows-demo
Thanks.
If Abp elsa pro won't generate the entities (workflowdefinitions, workflowinstances etc) , then where workflow and activity informations will store. will it store in in memory db? and will be lost when the application will restart?
Why AI bot is generating the answers saying workflowdefinitions, workflowinstances etc tables will generate with ABP Elsa pro?
If not ABP elsa pro, then should I try Elsa open source 3.x to generate the above entities?
Appreciate for the quick response
-
0
-
0
Hi,
Are you saying adding below line will create the Elsa related tables in the backend. .UseWorkflowRuntime(runtime => runtime.UseEntityFrameworkCore(ef => ef.UseSqlServer(connectionString)))
Does ABP Elsa pro does not generate the Elsa entities? Are you suggesting to use Elsa open source rather than ABP Elsa pro? If we use ABP elsa pro, then will we able to generate Elsa entities? if not, it stores in local storage. Am I right?
-
0
-
0
If I would like to extend WorkflowDefinitions, Workflowinstances tables by using ObjectExtensionManager.Instance.Modules(), will I be able, do it?
The reason for extending with additional columns is to store certain other details in the existing WorkflowDefinitions, Workflowinstances tables rather than creating a newly.
-
0
I am asking like below kind of code snippet.
ObjectExtensionManager.Instance.Modules() .ConfigureElsa(Workflowdefinitions => { identity.ConfigureUser(user => { user.AddOrUpdateProperty<string>( //property type: string "SocialSecurityNumber", //property name property => { //validation rules property.Attributes.Add(new RequiredAttribute()); property.Attributes.Add(new StringLengthAttribute(64) { MinimumLength = 4 }); //...other configurations for this property } ); }); }); -
0
hi
If I would like to extend WorkflowDefinitions, Workflowinstances tables
These two tables are from Elsa instead of the ABP entity.
If you want to add new fields, you can check the Elsa document or the GitHub issues.
https://docs.elsaworkflows.io/getting-started/database-configuration https://github.com/elsa-workflows/elsa-core/issues
Thanks.