CMS Kit: Comments
CMS kit provides a comment system to add comments feature to any kind of resource, like blog posts, products, etc.
Options
The comment system provides a mechanism to group comment definitions by entity types. For example, if you want to use comment system for blog posts and products, you need to define two entity types named BlogPosts and Product, and add comments under these entity types.
CmsKitCommentOptions can be configured in the domain layer, in the ConfigureServices method of your module. Example:
Configure<CmsKitCommentOptions>(options =>
{
options.EntityTypes.Add(new CommentEntityTypeDefinition("Product"));
});
If you're using the blog feature, the ABP framework defines an entity type for the blog feature automatically. You can easily override or remove the predefined entity types in
Configuremethod like shown above.
CmsKitCommentOptions properties:
EntityTypes: List of defined entity types(CmsKitCommentOptions) in the comment system.
CommentEntityTypeDefinition properties:
EntityType: Name of the entity type.
The Comments Widget
The comment system provides a commenting widget to allow users to send comments to resources on public websites. You can simply place the widget on a page like below.
@await Component.InvokeAsync(typeof(CommentingViewComponent), new
{
entityType = "Product",
entityId = "..."
})
entityType was explained in the previous section. entityId should be the unique id of the product, in this example. If you have a Product entity, you can use its Id here.
User Interface
Menu Items
The following menu items are added by the commenting feature to the admin application:
- Comments: Opens the comment management page.
Pages
Comment Management
You can view and manage comments on this page.
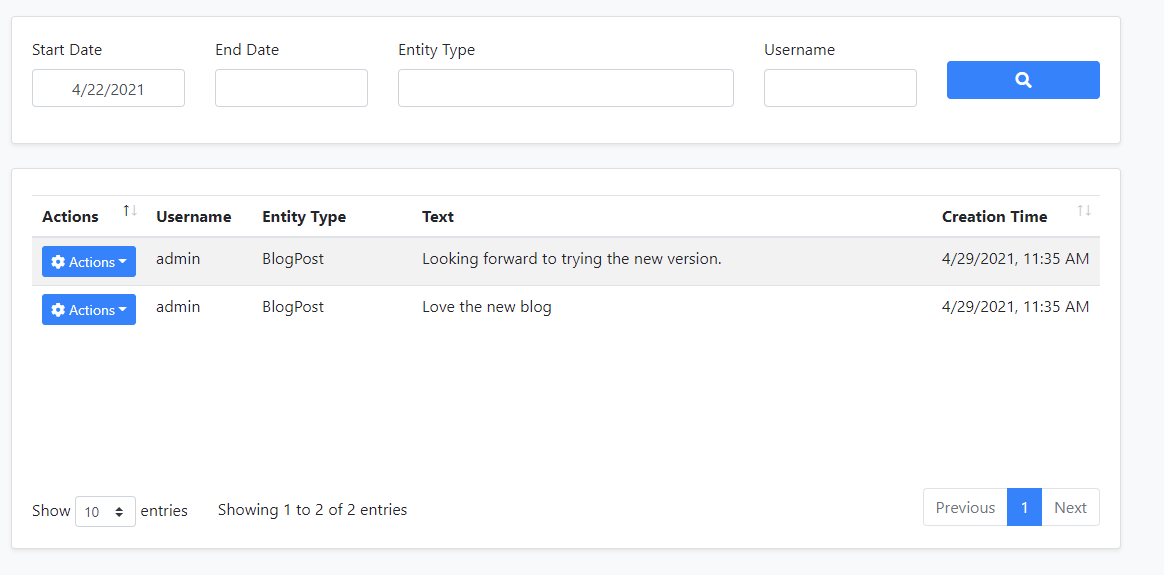
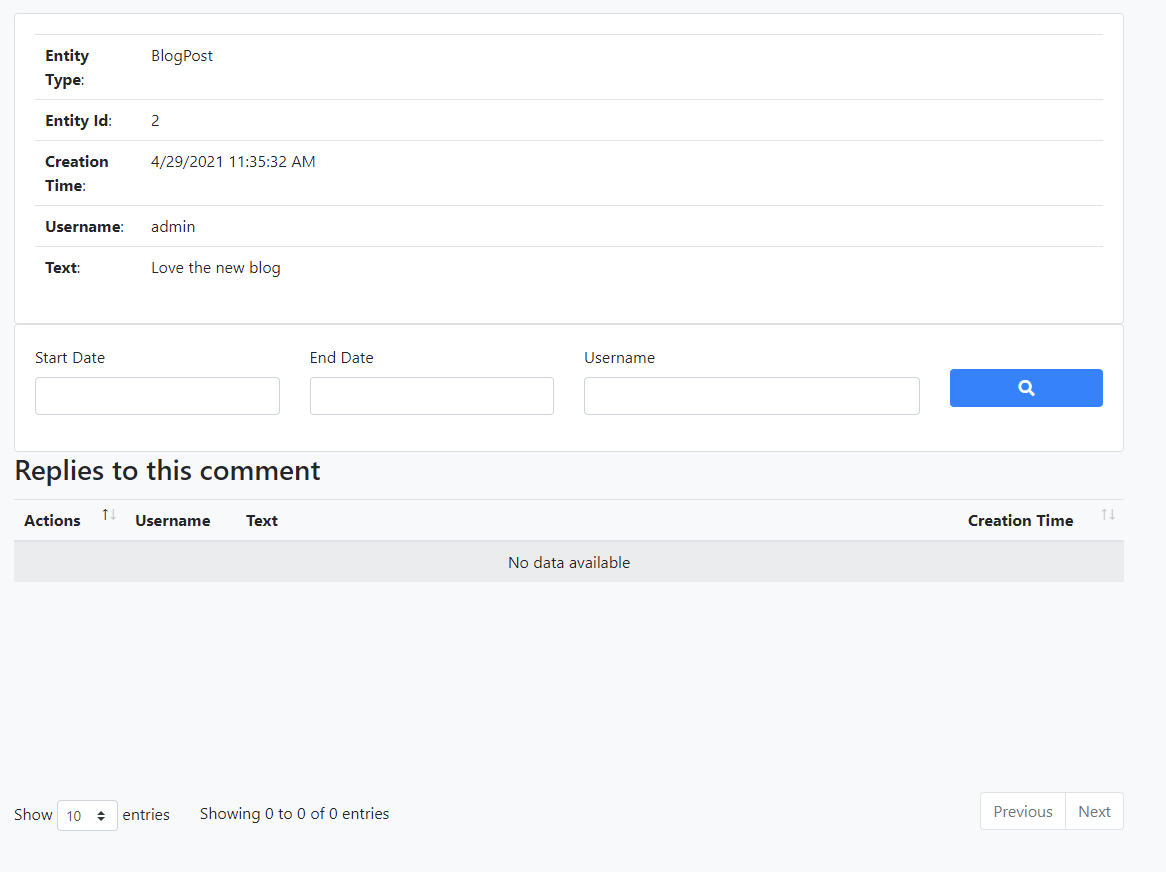
You can also view and manage replies on this page.
Internals
Domain Layer
Aggregates
This module follows the Entity Best Practices & Conventions guide.
Comment
A comment represents a written comment from a user.
Comment(aggregate root): Represents a written comment in the system.
Repositories
This module follows the Repository Best Practices & Conventions guide.
Following custom repositories are defined for this feature:
ICommentRepository
Domain services
This module follows the Domain Services Best Practices & Conventions guide.
Comment Manager
CommentManager is used to perform some operations for the Comment aggregate root.
Application layer
Application services
CommentAdminAppService(implementsICommentAdminAppService): Implements the use cases of comment management system, like listing or removing comments etc.CommentPublicAppService(implementsICommentPublicAppService): Implements the use cases of comment management on the public websites, like listing comments, adding comments etc.
Database providers
Common
Table / collection prefix & schema
All tables/collections use the Cms prefix by default. Set static properties on the CmsKitDbProperties class if you need to change the table prefix or set a schema name (if supported by your database provider).
Connection string
This module uses CmsKit for the connection string name. If you don't define a connection string with this name, it fallbacks to the Default connection string.
See the connection strings documentation for details.
Entity Framework Core
Tables
- CmsComments
MongoDB
Collections
- CmsComments






























































