Microservice Startup Template: Infrastructure
ABP Microservice Startup Template contains shared projects that are used in applications, gateways and microservices. There are also external services run on containers where some of them are mandatory for microservice template to run such as Redis and RabbitMQ.
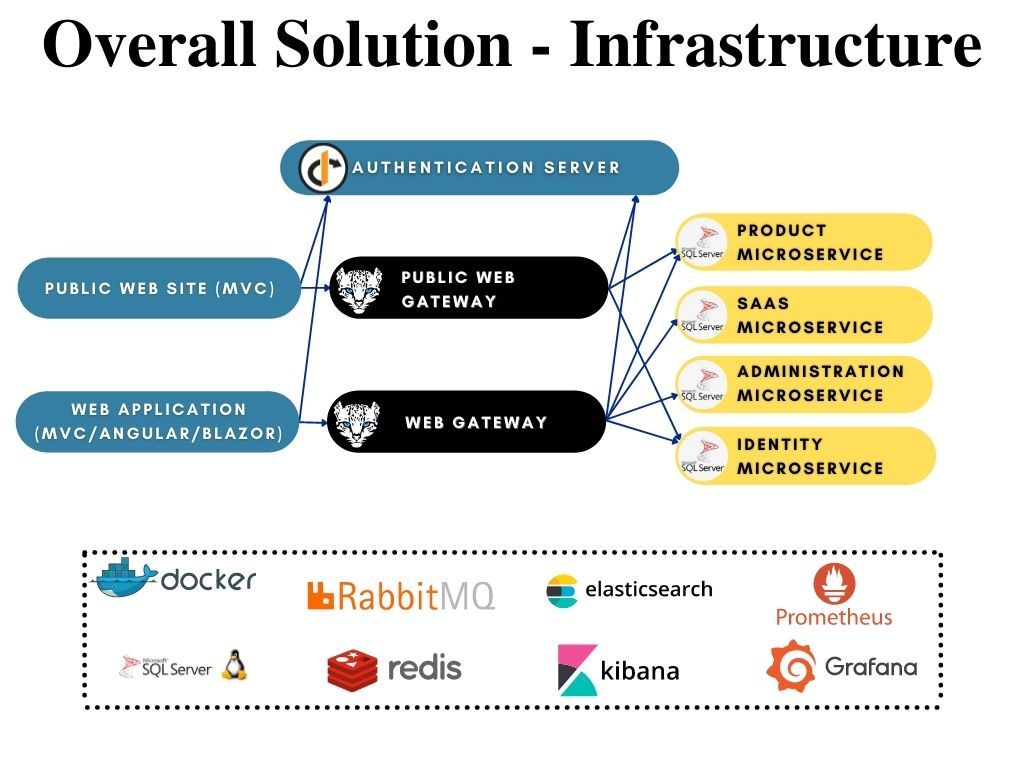
Shared folder in microservice template solution contains DbMigrator project for centralized database migration and data seeding for microservices and shared modules used in applications, microservices and gateways.
Infrastructure services run on docker containers as default and some of the services are required for microservice template to run properly while some of them are optional. Docker compose is used for running the infrastructure services. Two docker-compose.yml files are used for service configurations and they are located under etc/docker folder. While docker-compose.infrastructure.yml file contains image, container_name, network and volume data, docker-compose.infrastructure.override.yml file contains service ports and environment data.
Docker-compose file defines
- Sql-Server (required as default)
- Redis (required)
- RabbitMQ (required)
- ElasticSearch
- Kibana
- Grafana
- Prometheus
services that run on a predefined external docker-network. Use up.ps1 powershell command located in the same etc/docker folder to run the external infrastructure images that will execute the commands
docker network create mycompanyname.myprojectname-network
docker-compose -f docker-compose.infrastructure.yml -f docker-compose.infrastructure.override.yml up -d
which creates the external docker network for infrastructure services and runs the docker-compose files in detached mode. To stop and remove the containers, use down.ps1 powershell command.
You can use a single docker file by merging docker-compose.infrastructure.yml and docker-compose.infrastructure.override.yml files as you desire.

Sql Server & Configuration
Sql Server Docker Image is the default database and a required service for the microservice solution template. It's main configuration is located in docker-compose.infrastructure.yml file under sql-server-db service name. Port and environment information is located in docker-compose.infrastructure.override.yml file. The combined docker-compose service configuration is as below
sql-server-db:
container_name: sql-server-db
image: mcr.microsoft.com/mssql/server:2019-latest
volumes:
- sqldata:/var/opt/mssql
networks:
- mycompanyname.myprojectname-network
ports:
- "1434:1433"
environment:
SA_PASSWORD: "myPassw0rd"
ACCEPT_EULA: "Y"
All the microservices and AuthServer has connection strings configured based on containerized sql server database. All the connection strings used in microservice template solution are shown below
"ConnectionStrings": {
"IdentityService": "Server=(LocalDb)\\MSSQLLocalDB,1434;Database=MyProjectName_Identity;User Id=sa;password=myPassw0rd;MultipleActiveResultSets=true",
"AdministrationService": "Server=(LocalDb)\\MSSQLLocalDB,1434;Database=MyProjectName_Administration;User Id=sa;password=myPassw0rd;MultipleActiveResultSets=true",
"SaasService": "Server=(LocalDb)\\MSSQLLocalDB,1434;Database=MyProjectName_Saas;User Id=sa;password=myPassw0rd;MultipleActiveResultSets=true",
"ProductService": "Server=(LocalDb)\\MSSQLLocalDB,1434;Database=MyProjectName_ProductService;User Id=sa;password=myPassw0rd;MultipleActiveResultSets=true"
},
sql-server-db container exposes 1434 port instead of default 1433 in order to prevent conflicts if there is a local sql-server or sql-server-express is already installed.
You can always use none-containerized installed sql-server-express database but you will need to update all the connection strings in the solution.
Redis Integration & Configuration
Redis cache is a required service for the microservice solution template. It is used for caching permissions and such.
Redis runs on container with the main configurations are located in docker-compose.infrastructure.yml and port information in docker-compose.infrastructure.override.yml file. Redis docker-compose service configuration is as below
redis:
container_name: redis
image: redis:alpine
networks:
- mycompanyname.myprojectname-network
ports:
- "6379:6379"
All the microservices uses AbpCachingStackExchangeRedisModule dependency over SharedHostingMicroservicesModule and applications (AuthServer, Web, PublicWeb) references explicitly to Volo.Abp.Caching.StackExchangeRedis package.
Microservices and applications have their redis configuration in appsettings Redis section
"Redis": {
"Configuration": "localhost:6379"
}
Redis 6.0.10-alpine image is used as default. You can change the image tag in docker-compose.infrastructure.yml file and default exposed 6379 port in docker-compose.infrastructure.override.yml file.
RabbitMQ Integration & Configuration
Distributed Event Bus is the tool for async communication in microservice systems and abp microservice template solution uses RabbitMQ integration for this capability. It is a required service in the solution template used for on-the-fly database migration of the microservices. RabbitMQ docker-compose service configuration is as below
rabbitmq:
container_name: rabbitmq
image: rabbitmq:management-alpine
networks:
- mycompanyname.myprojectname-network
ports:
- "15672:15672"
- "5672:5672"
Default RabbitMQ-management port is 15672 and UI can be accessed with default guest username/password.

All the microservices uses AbpEventBusRabbitMqModule dependency over SharedHostingMicroservicesModule and applications (AuthServer, Web, PublicWeb) references explicitly to Volo.Abp.EventBus.RabbitMQ package.
Each application and microservice has it's configuration under appsettings RabbitMQ section.
"RabbitMQ": {
"Connections": {
"Default": {
"HostName": "localhost"
}
},
"EventBus": {
"ClientName": "MyProjectName_AuthServer",
"ExchangeName": "MyProjectName"
}
}
They all share the same ExchangeName and individual queues will be created after services start running.

Minimal configurations are used to connect RabbitMQ. Check RabbitMQ Integration docs for more configuration settings.
ElasticSearch & Kibana Integration
ElasticSearch is used for Serilog integration for logging and Kibana is used as the visualization tool that integrated to ElasticSearch. Docker-compose service configuration for these services is defined as below
elasticsearch:
container_name: elasticsearch
image: docker.elastic.co/elasticsearch/elasticsearch:8.5.3
volumes:
- esdata:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data
networks:
- mycompanyname.myprojectname-network
environment:
- xpack.monitoring.enabled=true
- xpack.watcher.enabled=false
- "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m"
- discovery.type=single-node
ports:
- "9200:9200"
kibana:
container_name: kibana
image: docker.elastic.co/kibana/kibana:8.5.3
depends_on:
- elasticsearch
networks:
- mycompanyname.myprojectname-network
environment:
- ELASTICSEARCH_URL=http://host.docker.internal:9200
ports:
- "5601:5601"
The ElasticSearch integration of Serilog configuration is done at SerilogConfigurationHelper located in Shared.Hosting.AspNetCore shared project. The IndexFormat is declared as MyProjectName-log-{0:yyyy.MM} under this configuration.
After running ElasticSearch in container, its endpoint should be exposed as below
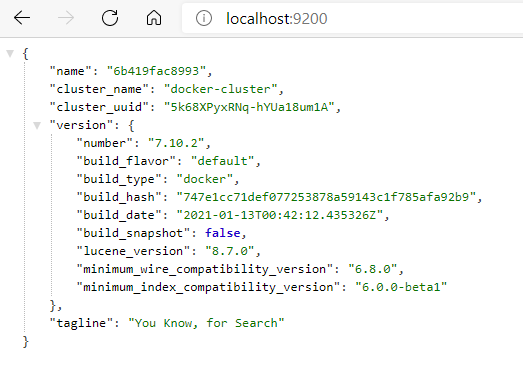
Use the IndexFormat explained above to create preferred UI visualization data.
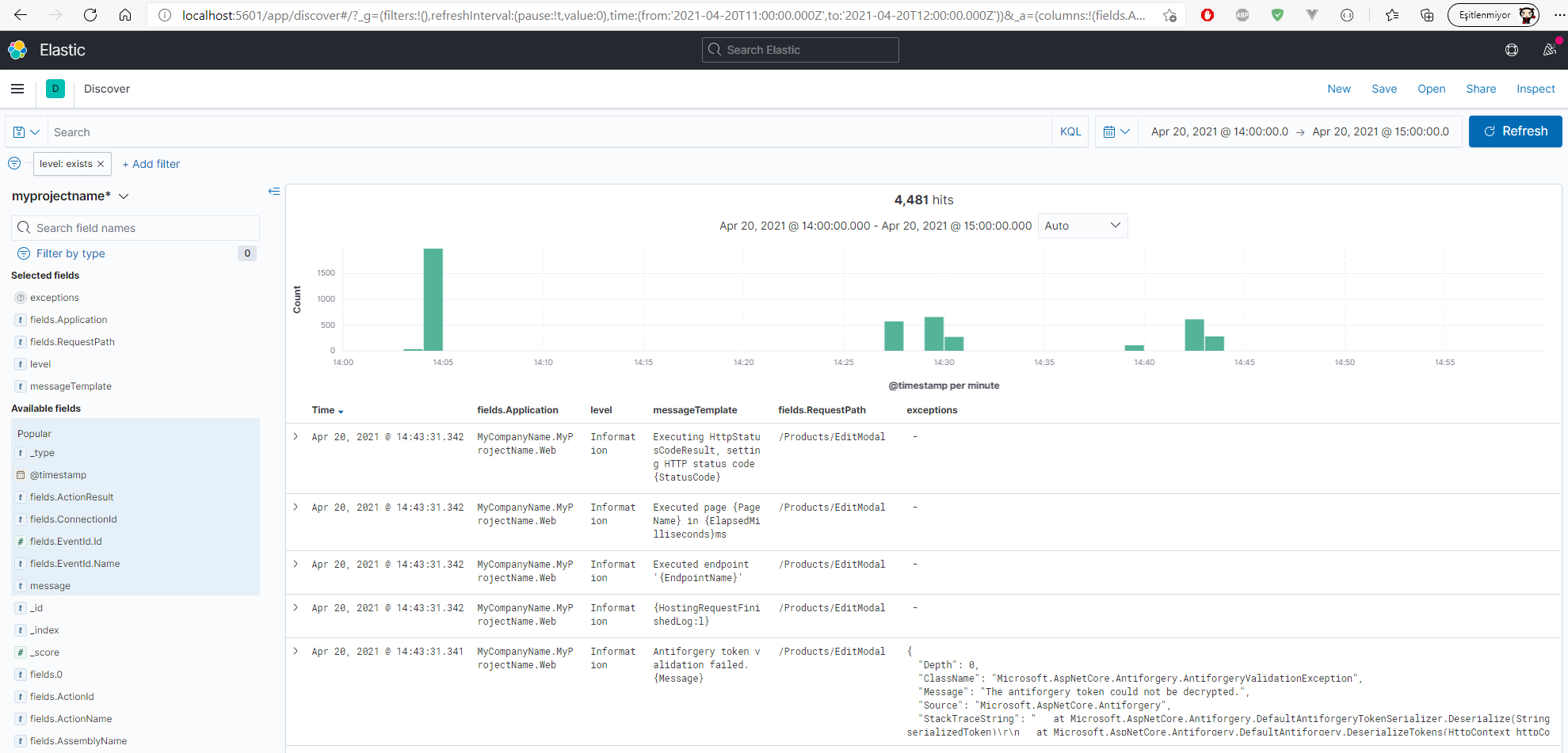
Configuration for each application and microservices is located under ElasticSearch section of appsettings
"ElasticSearch": {
"Url": "http://localhost:9200"
},
Grafana & Prometheus Integration
Grafana provides dashboards and data analysis from Prometheus metrics. Docker-compose service configuration for these services is defined as below
grafana:
container_name: grafana
image: grafana/grafana
volumes:
- ../grafana/storage:/var/lib/grafana
networks:
- mycompanyname.myprojectname-network
ports:
- "3000:3000"
prometheus:
container_name: prometheus
image: prom/prometheus
volumes:
- ../prometheus/prometheus.yml:/etc/prometheus/prometheus.yml
- ../prometheus/storage:/prometheus
networks:
- mycompanyname.myprojectname-network
ports:
- "9090:9090"
Prometheus scrape configuration, prometheus.yml file, is mounted and located under etc/prometheus folder.
Grafana storage directory is mounted from etc/granfana/storage folder and Prometheus storage directory is from etc/prometheus/storage. You can also use docker volumes instead of mounting directories.
Navigate to Prometheus targets to check endpoint targets
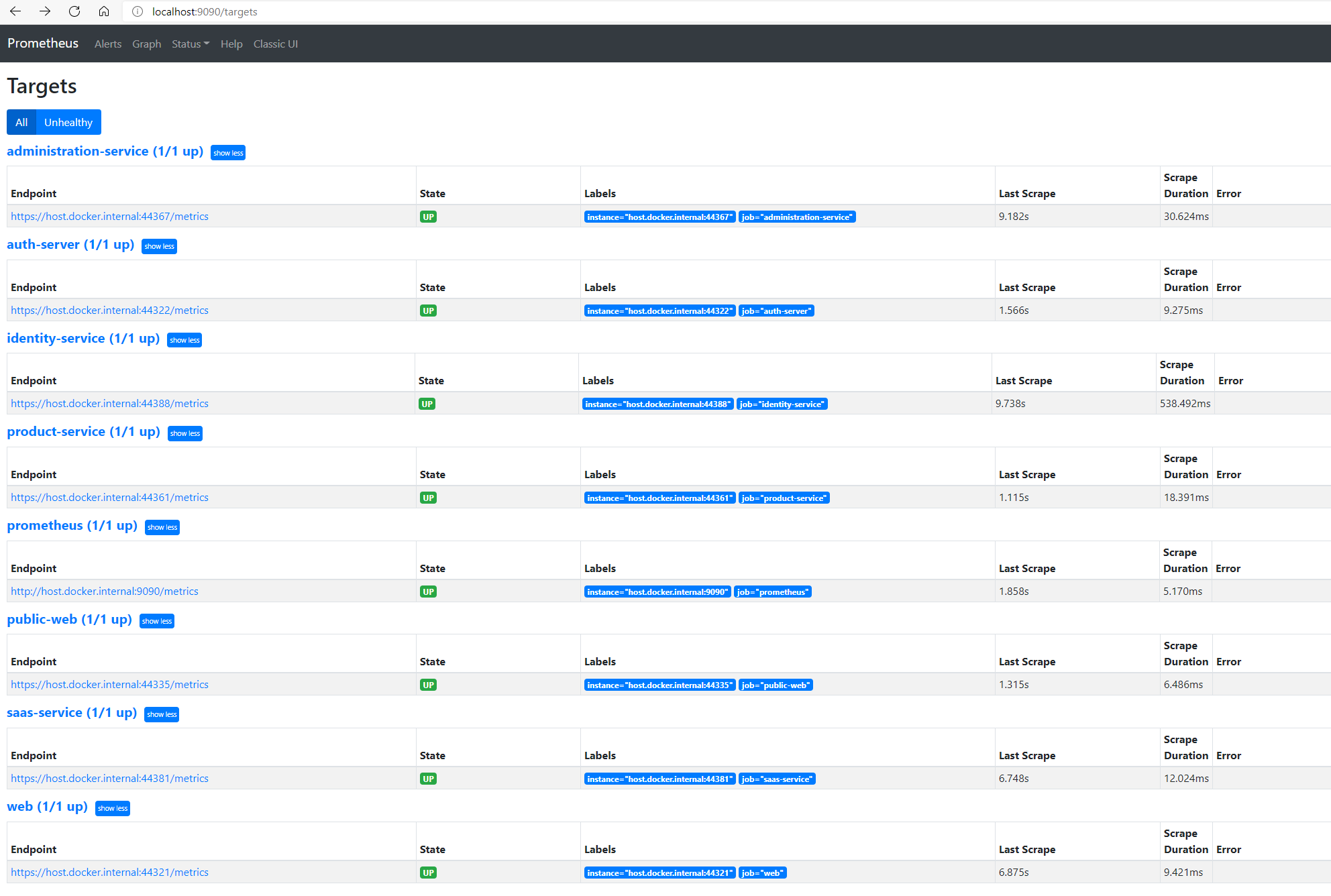
If you are not running the solution on docker, you may have to change the prometheus static_config targets such as
-targets: ['auth-server']to-targets: ['host.docker.internal:44322']
Applications using Prometheus are configured at application initialization
app.UseHttpMetrics();
...
app.UseConfiguredEndpoints(endpoints =>
{
endpoints.MapMetrics();
});
Run Grafana and add Prometheus as Data Source
For first time entry, default user name and password is admin/admin
Add dashboard using prometheus data source

Shared Projects
Shared projects are as the name implies; modules and configurations that are used in other applications, services and/or microservices to prevent code duplication and centralize basic configurations. There are 5 shared projects in ABP Microservice Template solution.
Localization
The Shared.Localization project contains configuration for Virtual File System and solution-wide localization. It is also the localization resource used for public-web application. If you plan to develop monolith UI as the public-web application, this localization resource will be used.
Configure<AbpVirtualFileSystemOptions>(options =>
{
options.FileSets.AddEmbedded<MyProjectNameSharedLocalizationModule>();
});
Configure<AbpLocalizationOptions>(options =>
{
options.Resources
.Add<MyProjectNameResource>("en")
.AddBaseTypes(
typeof(AbpValidationResource)
).AddVirtualJson("/Localization/MyProjectName");
options.DefaultResourceType = typeof(MyProjectNameResource);
});
The SharedLocalizationModule is depended by all applications, gateways and microservices.
Use provided localization files if you want your localization keys available in all applications, gateways and microservices.
Hosting
Shared.Hosting project contains database configurations in SharedHostingModule service configuration which is used in all other hosting modules.
Each module with database connection in abp has its own connection string so that it can be migrated to multiple databases when needed. This is achieved by Connection Strings Management. Since infrastructural microservices such as AdministrationService, IdentityService and SaasService uses one or more modules to perform, each module database configuration must be added to related database explicitly so that the module can connect to it's database.
Instead of adding all module connection strings in microservice connection string configuration explicitly; related connection strings are mapped into a single connection string.
private void ConfigureDatabaseConnections()
{
Configure<AbpDbConnectionOptions>(options =>
{
options.Databases.Configure("SaasService", database =>
{
database.MappedConnections.Add("Saas");
database.IsUsedByTenants = false;
});
options.Databases.Configure("AdministrationService", database =>
{
database.MappedConnections.Add("AbpAuditLogging");
database.MappedConnections.Add("AbpPermissionManagement");
database.MappedConnections.Add("AbpSettingManagement");
database.MappedConnections.Add("AbpFeatureManagement");
database.MappedConnections.Add("AbpLanguageManagement");
database.MappedConnections.Add("TextTemplateManagement");
database.MappedConnections.Add("AbpBlobStoring");
});
options.Databases.Configure("IdentityService", database =>
{
database.MappedConnections.Add("AbpIdentity");
database.MappedConnections.Add("OpenIddict");
});
options.Databases.Configure("ProductService", database =>
{
database.MappedConnections.Add("ProductService");
});
});
}
Hosting AspNetCore
Shared.Hosting.AspNetCore project is a base hosting dependency for applications such as AuthServer, Web, PublicWeb. This module depends on
SharedHostingModuleAbpAspNetCoreSerilogModuleAbpSwashbuckleModule
modules and contains contains:
Base configuration for serilog in
SerilogConfigurationHelperLog.Logger = new LoggerConfiguration() #if DEBUG .MinimumLevel.Debug() #else .MinimumLevel.Information() #endif .MinimumLevel.Override("Microsoft", LogEventLevel.Information) .MinimumLevel.Override("Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore", LogEventLevel.Warning) .Enrich.FromLogContext() .Enrich.WithProperty("Application", $"{applicationName}") .WriteTo.Async(c => c.File("Logs/logs.txt")) .WriteTo.Elasticsearch( new ElasticsearchSinkOptions(new Uri(configuration["ElasticSearch:Url"])) { AutoRegisterTemplate = true, AutoRegisterTemplateVersion = AutoRegisterTemplateVersion.ESv6, IndexFormat = "MyProjectName-log-{0:yyyy.MM}" }) .WriteTo.Async(c => c.Console()) .CreateLogger();Swagger configuration in
SwaggerConfigurationHelperpublic static void Configure( ServiceConfigurationContext context, string apiTitle ) { context.Services.AddAbpSwaggerGen(options => { options.SwaggerDoc("v1", new OpenApiInfo { Title = apiTitle, Version = "v1" }); options.DocInclusionPredicate((docName, description) => true); options.CustomSchemaIds(type => type.FullName); }); } public static void ConfigureWithOidc( ServiceConfigurationContext context, string authority, string[] scopes, string apiTitle, string apiVersion = "v1", string apiName = "v1", string[]? flows = null, string? discoveryEndpoint = null ) { context.Services.AddAbpSwaggerGenWithOidc( authority: authority, scopes: scopes, flows: flows, discoveryEndpoint: discoveryEndpoint, options => { options.SwaggerDoc(apiName, new OpenApiInfo { Title = apiTitle, Version = apiVersion }); options.DocInclusionPredicate((docName, description) => true); options.CustomSchemaIds(type => type.FullName); }); }See API/Swagger Integration for more details.
Hosting Gateways
Shared.Hosting.Gateways project is a base hosting dependency for gateways such as WebGateway and PublicWebGateway.
This module depends on
SharedHostingAspNetCoreModulefor serilog configurationAbpAspNetCoreMvcUiMultiTenancyModulefor tenantId redirection in the http headers
modules along with Ocelot and Ocelot.Provider.Polly libraries.
Ocelot service is configured to use Polly as default
context.Services.AddOcelot(configuration)
.AddPolly();
This module also contains GatewayHostBuilderExtensions to add ocelot.json configuration along with appsettings.json.
Hosting Microservices
Shared.Hosting.Microservices project is a base hosting dependency for microservices such as AdministrationService, IdentityService and SaasService and ProductService. This module depends on SharedHostingModule and contains
Module configuration that has
AbpDistributedCacheOptions,AbpMultiTenancyCacheOptionsandRedisconfigurations,JwtBearerConfigurationHelperhas base JwtBearer authentication configuration,public static void Configure( ServiceConfigurationContext context, string audience) { var configuration = context.Services.GetConfiguration(); context.Services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme) .AddJwtBearer(options => { options.Authority = configuration["AuthServer:Authority"]; options.RequireHttpsMetadata = Convert.ToBoolean(configuration["AuthServer:RequireHttpsMetadata"]); options.Audience = audience; }); }DbMigrations folder that contains
PendingMigrationsCheckerBaseandDatabaseMigrationEventHandlerBasewhich are used for Auto Migration.
This module also depends on EntityFrameworkCore layers of:
- SaasService for making tenant migrations available for all
DatabaseMigrationEventHandlersused for auto migration - AdministrationService for making language seeding available for all
DatabaseMigrationEventHandlersused for auto migration






























































