21 Answer(s)
-
0
- Solution
- How ABP loads localization in a microservice solution
- In the microservice template, the Administration (or LanguageService if dynamic localization is enabled) microservice aggregates localization. All UI/apps get texts from the Application Localization endpoint via the gateway:
- GET /api/abp/application-localization?cultureName=xx
- Each microservice defines its own resources (e.g., BaseSetServiceResource) in its contracts/domain and registers them on startup. The Language Management infrastructure persists/serves these resources to the Administration service, which then responds to the endpoint above.
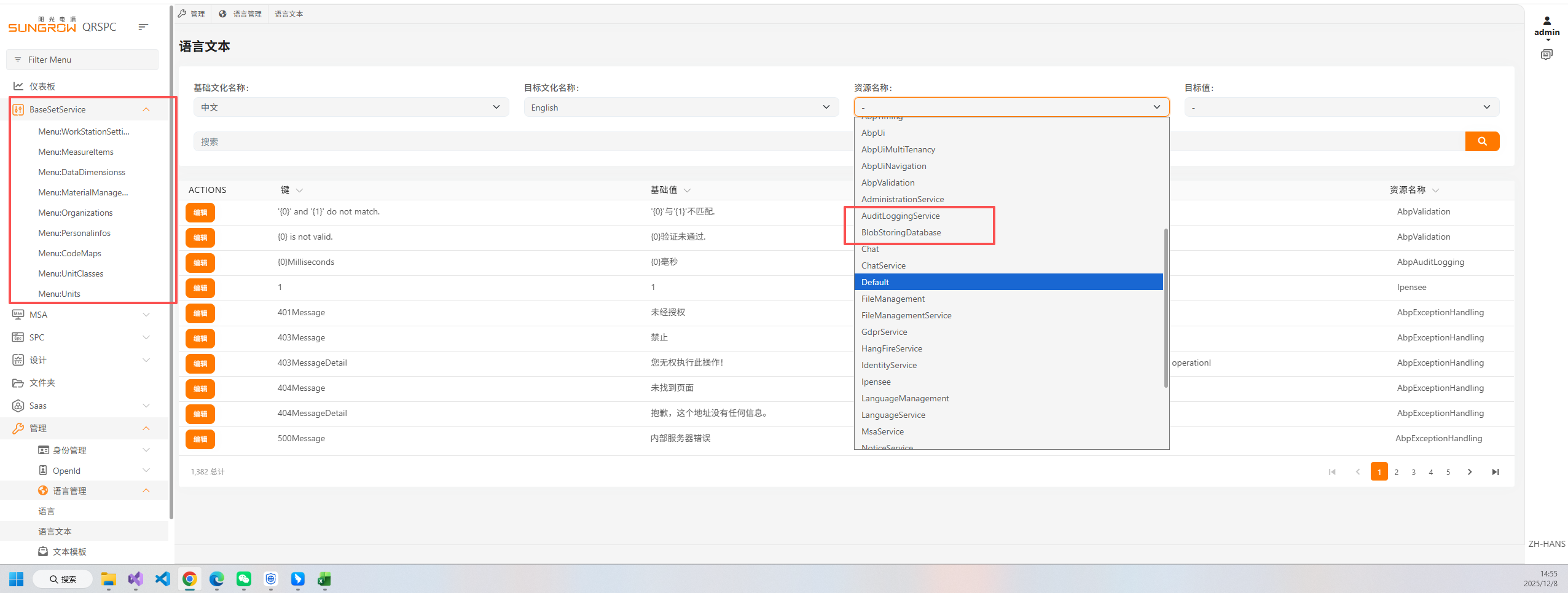
- If a resource intermittently “disappears” from the Language Texts page or from the dropdown, check:
- The microservice hosting that resource is running and has started successfully.
- The resource assembly is referenced by the microservice host and the resource is added in the module class, for example:
- In the microservice template, the Administration (or LanguageService if dynamic localization is enabled) microservice aggregates localization. All UI/apps get texts from the Application Localization endpoint via the gateway:
[DependsOn(/* ... */)] public class QRSPCBaseSetServiceDomainSharedModule : AbpModule { public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context) { Configure<AbpLocalizationOptions>(options => { options.Resources .Add<BaseSetServiceResource>("en") .AddBaseTypes(typeof(AbpValidationResource)) .AddVirtualJson("/Localization/BaseSetService"); // folder with zh-Hans.json etc. }); } }3) The gateway routes /api/abp/application-localization to Administration and no cache inconsistency exists (see next). 4) If dynamic localization is enabled, ensure the Language Management DB contains the resource (initial registration occurs on first start of the resource-owning service). Restarting the service re-registers resources if needed.Caching considerations for intermittent missing resources
- The application-localization response is cached by clients while the backend reads from the Language Management store. In clustered deployments, use a distributed cache (e.g., Redis) for consistent results across instances. If you see intermittent visibility:
- Ensure all services (including Administration) share the same distributed cache and database.
- After deploying a new service or changing localization files, recycle the Administration service and clear distributed cache to avoid stale entries.
- Verify the gateway and Administration instances are healthy; a failing instance behind load-balancer may respond without the new resource.
- The application-localization response is cached by clients while the backend reads from the Language Management store. In clustered deployments, use a distributed cache (e.g., Redis) for consistent results across instances. If you see intermittent visibility:
Why the page returns to Home every ~45 minutes
- This is almost always due to authentication/session validation rather than localization. Two common causes:
- Security stamp validation/sign-in cookie validation cycle (for MVC/Angular with OpenIddict/Identity). If the cookie expires or security-stamp validation fails, the UI is redirected to re-authenticate, which brings the app back to its root.
- Access token expiry/refresh failure in SPA: if the token expires and refresh does not happen (or fails), the app reloads and lands on the root.
- What to check:
- Token lifetimes and cookie expiration/SlidingExpiration in your Auth Server configuration. Make sure the Angular/MVC client refreshes tokens correctly and that the allowed clock skew and refresh token settings are configured.
- If running behind a gateway, ensure the issuer configuration (AuthServer:Authority) is correct for all services so validation doesn’t fail when tokens rotate.
- Confirm data protection keys are persisted and shared across instances, otherwise cookies become invalid after key rotation and users get logged out periodically.
- This is almost always due to authentication/session validation rather than localization. Two common causes:
Diagnostics checklist
- Call, via the gateway, while the problem occurs:
- GET /api/abp/application-localization?cultureName=zh-Hans&onlyDynamics=false
- Confirm “resources” includes your BaseSetService resource name.
- Inspect the Administration service logs when the resource is missing; you should see the resource registration on the service startup. If not, verify the module configuration and that the assembly with localization files is loaded by the host.
- Ensure your JSON files are embedded/virtual (Virtual File System) and the path in AddVirtualJson matches the folder name.
- Verify distributed cache and DB connection strings are the same across all instances.
- For the 45-minute refresh:
- Check token/cookie lifetimes in the Auth Server and whether the SPA is performing silent refresh. If necessary, increase lifetimes to confirm the behavior changes, then tune properly.
- Call, via the gateway, while the problem occurs:
- Sources
- https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/architecture/modularity/basics
- https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/api-development/standard-apis/localization
- https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/fundamentals/localization
- https://abp.io/docs/latest/solution-templates/microservice/localization-system
This response was generated by AI. If it didn’t solve your problem, feel free to post a new answer — our support team will jump in to help you soon.
-
0
你好
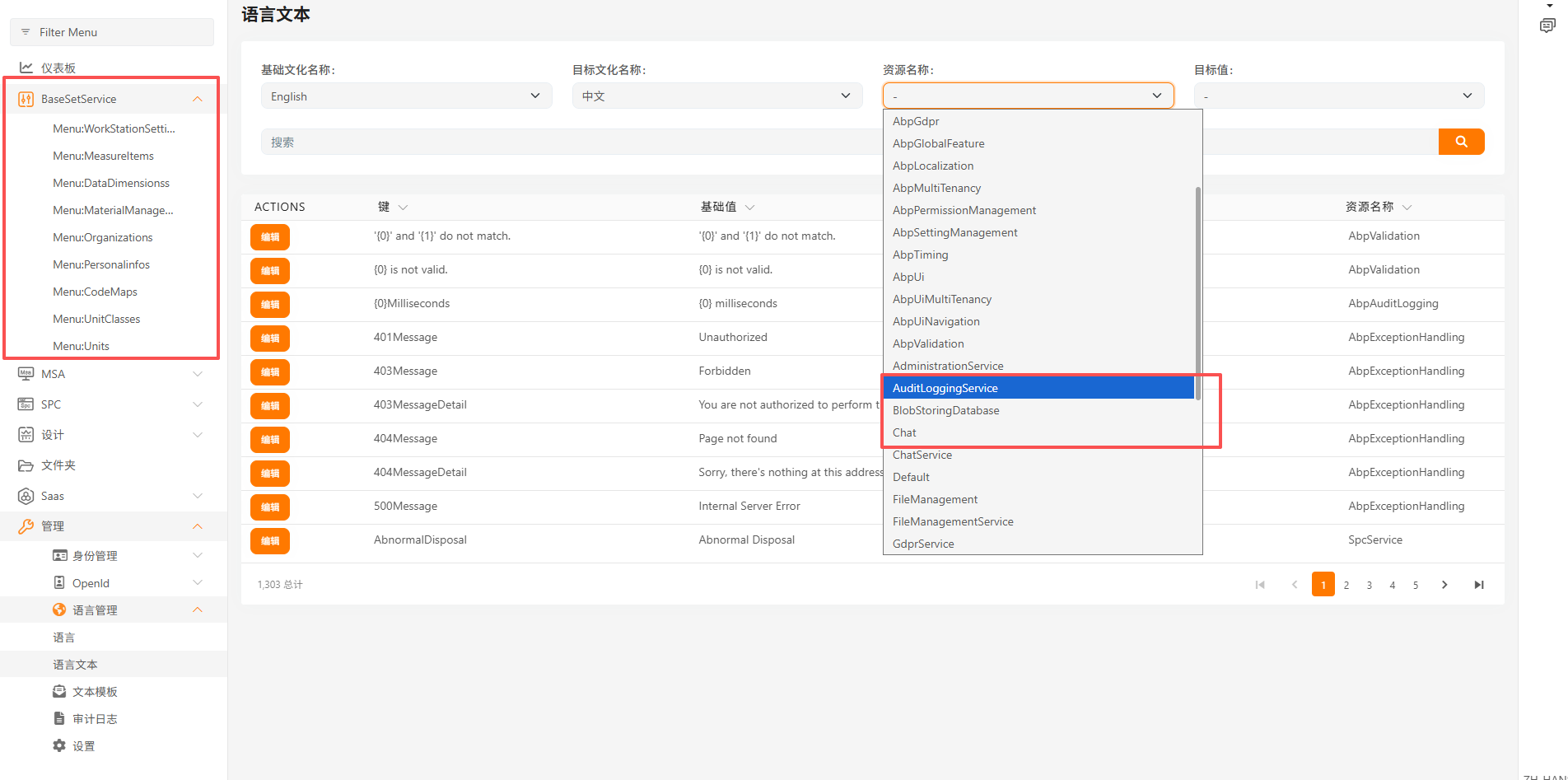
请分享下你的整个解决方案的项目结构
谢谢
-
0
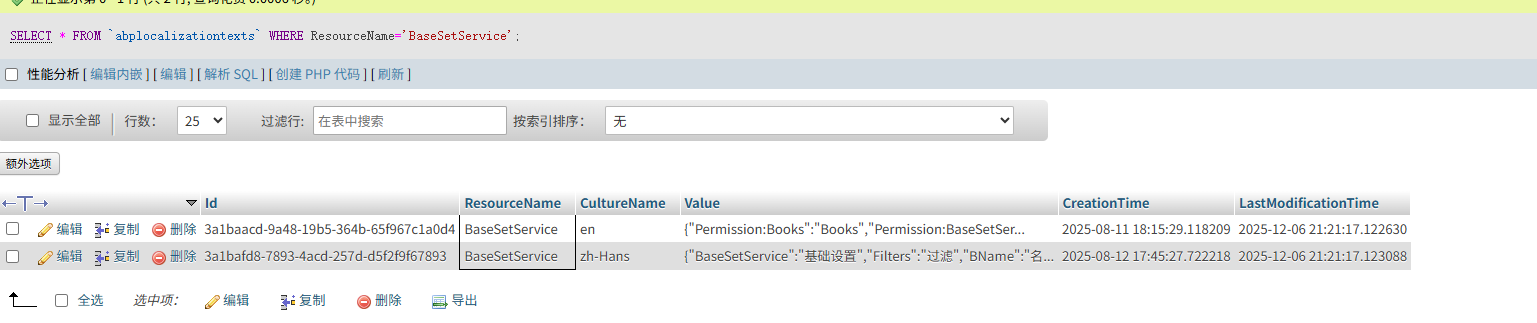
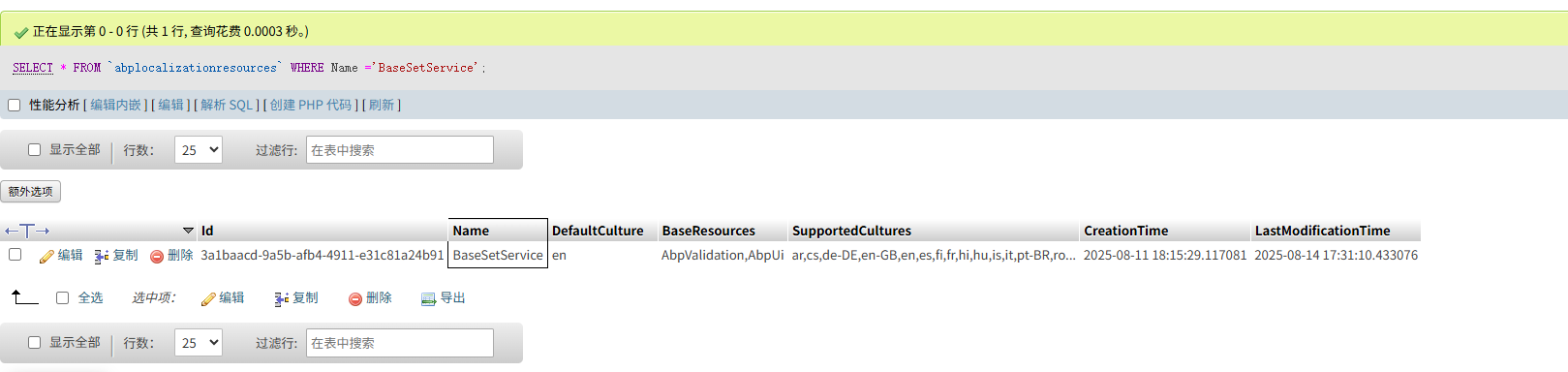
你可以检查下数据库的LocalizationResources表.
另外BaseSetService是否直接或者间接依赖了
LanguageManagementDomainModule? -
0
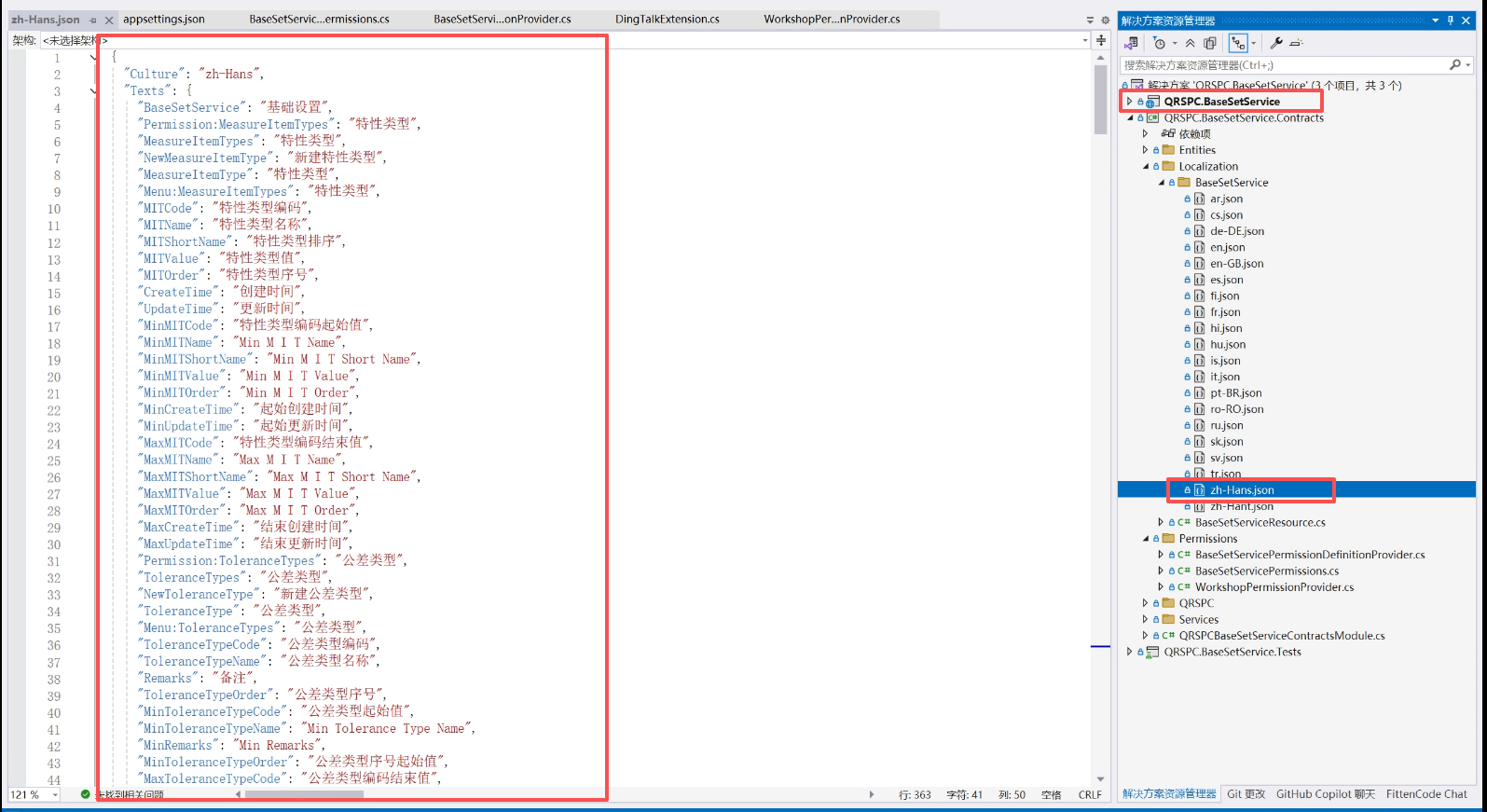
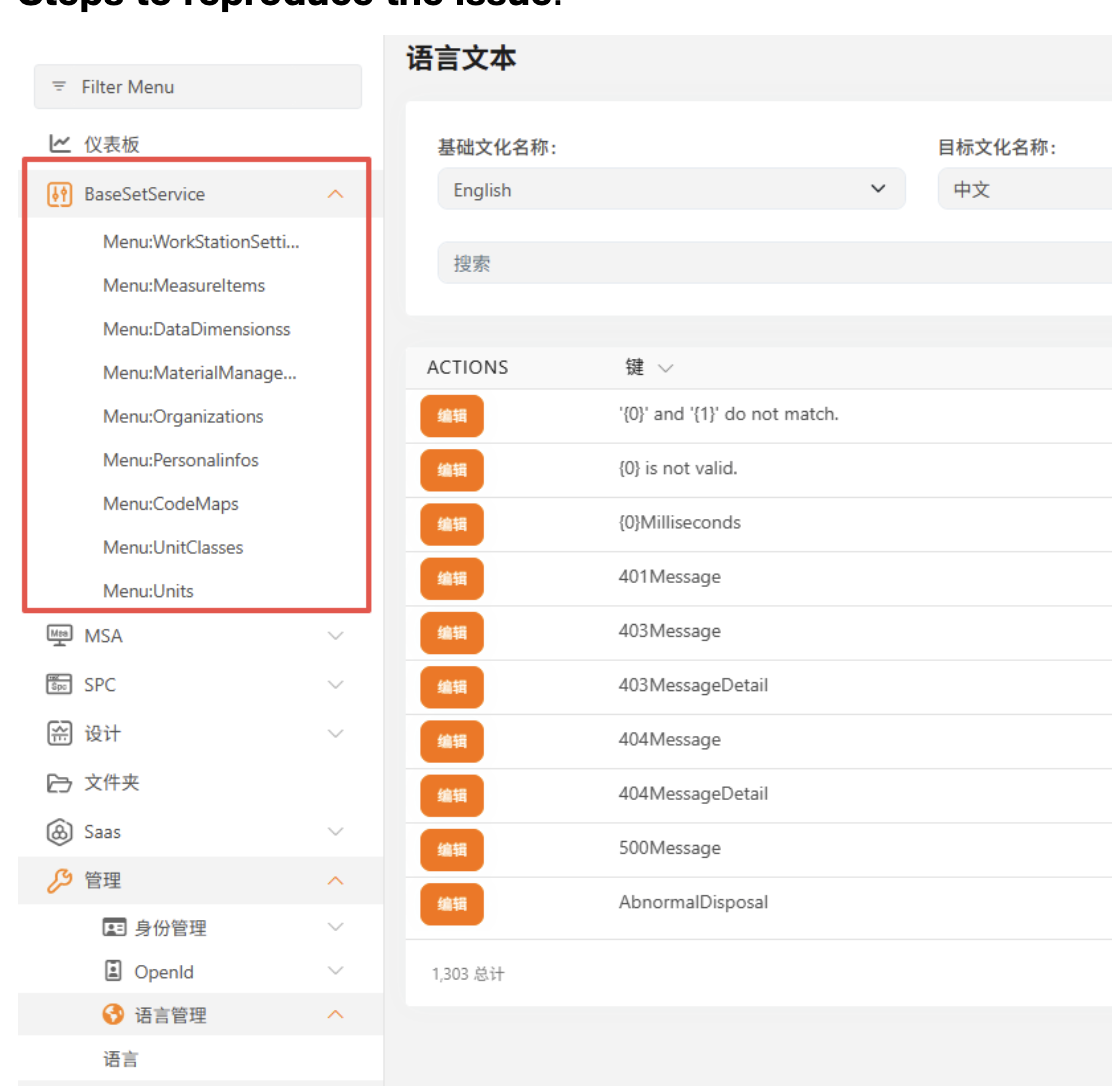
您好!这是我排查及现有的项目结构 麻烦您帮忙看看 这是 BaseSetService 的Module 看上去没有直接引用 LanguageManagementDomainModule, using Localization.Resources.AbpUi; using QRSPC.BaseSetService.Localization; using Volo.Abp.Application; using Volo.Abp.Authorization; using Volo.Abp.Commercial.SuiteTemplates; using Volo.Abp.Domain; using Volo.Abp.Http.Client; using Volo.Abp.Localization; using Volo.Abp.Localization.ExceptionHandling; using Volo.Abp.Modularity; using Volo.Abp.UI; using Volo.Abp.Validation; using Volo.Abp.Validation.Localization; using Volo.Abp.VirtualFileSystem;
namespace QRSPC.BaseSetService;
[DependsOn( typeof(AbpValidationModule), typeof(AbpUiModule), typeof(AbpAuthorizationAbstractionsModule), typeof(VoloAbpCommercialSuiteTemplatesModule), typeof(AbpDddApplicationContractsModule), typeof(AbpDddDomainSharedModule) )] public class QRSPCBaseSetServiceContractsModule : AbpModule { public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context) { Configure<AbpVirtualFileSystemOptions>(options => { options.FileSets.AddEmbedded<QRSPCBaseSetServiceContractsModule>(); });
Configure<AbpLocalizationOptions>(options => { options.Resources .Add<BaseSetServiceResource>("en") .AddBaseTypes(typeof(AbpValidationResource), typeof(AbpUiResource)) .AddVirtualJson("/Localization/BaseSetService"); }); Configure<AbpExceptionLocalizationOptions>(options => { options.MapCodeNamespace("BaseSetService", typeof(BaseSetServiceResource)); }); }} ,另外 检查过数据库 当语言文本管理 资源中不存在BaseSetService的资源时数据库数据也是没有的, 这是我的解决方案的结构
-
0
数据库的LocalizationResources和LocalizationTexts表有BaseSetService的本地化数据吗?
-
0
这是 BaseSetService 的Module 看上去没有直接引用 LanguageManagementDomainModule
它可能是间接引用的, 请看看它依赖的模块尤其是
administration -
0
-
0
namespace QRSPC.AdministrationService;
[DependsOn( typeof(AbpAuditLoggingEntityFrameworkCoreModule), typeof(TextTemplateManagementEntityFrameworkCoreModule), typeof(SaasEntityFrameworkCoreModule), typeof(BlobStoringDatabaseEntityFrameworkCoreModule), typeof(AbpPermissionManagementEntityFrameworkCoreModule), typeof(AbpFeatureManagementEntityFrameworkCoreModule), typeof(AbpSettingManagementEntityFrameworkCoreModule), typeof(LanguageManagementEntityFrameworkCoreModule), typeof(AbpEntityFrameworkCoreMySQLPomeloModule), typeof(AbpOpenIddictProDomainSharedModule), typeof(TextTemplateManagementApplicationModule), typeof(TextTemplateManagementHttpApiModule), typeof(LeptonXThemeManagementApplicationModule), typeof(LeptonXThemeManagementHttpApiModule), typeof(AbpAspNetCoreMvcUiMultiTenancyModule), typeof(QRSPCAdministrationServiceContractsModule), typeof(AbpPermissionManagementApplicationModule), typeof(AbpPermissionManagementHttpApiModule), typeof(AbpPermissionManagementDomainIdentityModule), typeof(AbpPermissionManagementDomainOpenIddictModule), typeof(AbpFeatureManagementApplicationModule), typeof(AbpFeatureManagementHttpApiModule), typeof(AbpSettingManagementApplicationModule), typeof(AbpSettingManagementHttpApiModule), typeof(AbpAutofacModule), typeof(AbpAspNetCoreSerilogModule), typeof(AbpSwashbuckleModule), typeof(AbpEventBusRabbitMqModule), typeof(AbpBackgroundJobsRabbitMqModule), typeof(AbpCachingStackExchangeRedisModule), typeof(AbpDistributedLockingModule), typeof(AbpAspNetCoreAuthenticationJwtBearerModule), typeof(AbpIdentityHttpApiClientModule), typeof(AbpStudioClientAspNetCoreModule) )] 这是administraiton 的依赖模块 是否要加上LanguageManagementDomainModule的引用?
-
0
你好
请先确认几个问题:
- 这个本地化问题是随机出现吗? 也就是刷新可能成功, 可能失败
- 切换到英文后. 刷新页面是否也会随机出现这个问题?
- 可以分享项目源码来复现问题吗?
谢谢
-
0
编译重启后大概率就会出现语言加载问题 这是 baseSet源码 地址Deleted 感谢您!
-
0
-
0
你的缓存服务器是否正常工作?
这些信息都会存储到缓存中.
-
0
-
0
redis 工作正常
-
0
-
0
这大概率是缓存数据存在问题.
Angular 从这个端点获取本地化信息
https://your-web-gateway/api/abp/application-localization?cultureName=zh-Hans&onlyDynamics=false
你可以访问试试.
-
0
你可以在Administration中重写这个应用服务输出一些日志来看看哪里存在问题
https://github.com/abpframework/abp/blob/dev/framework/src/Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc/Volo/Abp/AspNetCore/Mvc/ApplicationConfigurations/AbpApplicationLocalizationAppService.cs#L52
输出所有的resources等信息到日志中.
LocalizationOptions.Resources.Valuesawait ExternalLocalizationStore.GetResourcesAsync()localizedStringsWithDynamics
谢谢
-
0
好的 我先试试 谢谢您
-
0
没问题, 你可以随时反馈
-
0
"QRSPC.BaseSetService.Localization.BaseSetServiceResource": { "texts": { "Permission:Books": "Books", "Permission:BaseSetService": "基础设置", "Permission:Create": "创建", "Permission:Edit": "编辑", "Permission:Delete": "删除", "Books": "Books", "NewBook": "New Book", "Book": "Book", "Menu:Books": "Books", "SeeAdvancedFilters": "Filters", "DeleteConfirmationMessage": "Are you sure you want to delete this record?", "AreYouSure": "Are you sure?", "Search": "Search", "Pick": "Pick", "Actions": "Actions", "SuccessfullyDeleted": "Successfully deleted", "ExportToExcel": "导出Excel", "AllItemsAreSelected": "所有'{0}'项都被选中.", "OneItemOnThisPageIsSelected": "1 item on this page is selected", "NumberOfItemsOnThisPageAreSelected": "All {0} items on this page are selected", "SelectAllItems": "选择所有项", "ClearSelection": "清除选择", "DeleteAllRecords": "Are you sure you want to delete all records?", "DeleteSelectedRecords": "Are you sure you want to delete {0} record(s)?", "UploadFailedMessage": "Upload Failed: Unsupported file format or file size too large. Please ensure the file meets the required format and size limits, and try again.", "DownloadSelectedFile": "Download selected file", "RemoveSelectedFile": "Remove selected file", "Filters": "过滤", "BName": "B Name", "BCode": "B Code", "BMemo": "B Memo", "MinBName": "Min B Name", "MinBCode": "Min B Code", "MinBMemo": "Min B Memo", "MaxBName": "Max B Name", "MaxBCode": "Max B Code", "MaxBMemo": "Max B Memo", "BookDetails": "Book Details", "NewBookDetail": "New Book Detail", "BookDetail": "Book Detail", "Menu:BookDetails": "Book Details", "BDetailName": "B Detail Name", "BDetailCode": "B Detail Code", "MinBDetailName": "Min B Detail Name", "MinBDetailCode": "Min B Detail Code", "MaxBDetailName": "Max B Detail Name", "MaxBDetailCode": "Max B Detail Code", "Permission:BookDetails": "Book Details", "Permission:WorkStationSettings": "工位", "WorkStationSettings": "工位", "NewWorkStationSetting": "新建工位", "WorkStationSetting": "工位", "Menu:WorkStationSettings": "工位", "WorkStationSettingBaseCode": "工位编号", "WorkStationSettingBaseName": "工位名称", "BaseSetService": "基础设置" }, "baseResources": [ "AbpValidation", "AbpUi" ] }, 这是basesetservice中文资源包加载失败时https://spc-msa-sit.sungrow.cn/api/abp/application-localization?cultureName=zh-Hans&onlyDynamics=false 接口返回的bastsetService的资源数据与解决方案中的不一致 是redis的问题吗
-
0
可能是, 还是要输出一些日志看看那个服务返回了错误的数据
参考: https://abp.io/support/questions/10180#answer-3a1e0f79-0c4a-f2ff-5121-227101208275