Description
Hello ABP Team,
We are trying to implement tenant resolution by subdomain following the official ABP documentation, but the described approach does not work as expected, even in a clean ABP solution created from the templates.
We have followed the documentation step by step, specifically the section:
https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/architecture/multi-tenancy#domainsubdomain-tenant-resolver
However, the tenant is not resolved correctly from the subdomain, and the application does not behave as expected.
Environment
ABP Framework: 9.1.3
UI: Blazor Interactive (WebAssembly only)
Multi-tenancy: enabled
Reproduced both in:
- Existing project
- Clean ABP solution generated from scratch
URL structure / scenario
Our application is deployed with environment-based subdomains:
- QA:
https://app-qa.example.com - Preproduction:
https://app-pre.example.com - Production:
https://app.example.com
Expected tenant URLs would be, for example:
https://tenant1.app-qa.example.comhttps://tenant2.app-pre.example.comhttps://tenant3.app.example.com
The base subdomain (app, app-qa, app-pre) represents the application, not a tenant.
What we have tried
1. Built-in Domain/Subdomain Tenant Resolver
- Configured exactly as described in the documentation.
- The tenant is not resolved, or the resolver is not triggered as expected.
2. Custom Tenant Resolver
- Implemented a custom
ITenantResolveContributorto handle our URL logic. - The resolver correctly extracts the tenant name from the URL/subdomain.
- The extracted tenant value is available inside the resolver.
However:
- Even though the tenant name is extracted correctly, the application does not work properly.
- The tenant context does not seem to be applied correctly across the request lifecycle.
- Authentication, login, and general request handling break or behave inconsistently.
This suggests the issue is not only related to parsing the URL, but to how the resolved tenant is applied internally by ABP, possibly in a Blazor Interactive WebAssembly scenario.
Expected behavior
- The tenant should be resolved automatically from the subdomain.
- The resolved tenant should be applied correctly to the request context.
- The application should work normally once the tenant is resolved.
- The login process should be able to use the resolved tenant.
Actual behavior
- Built-in resolver does not work as documented.
- Custom resolver extracts the tenant correctly, but the application does not function correctly.
- Same behavior in a clean ABP 9.1.3 Blazor Interactive WebAssembly solution.
Questions
Is the Domain/Subdomain Tenant Resolver fully supported in ABP 9.1.3 with Blazor Interactive (WebAssembly only)?
Is there any additional configuration, middleware order, or Blazor-specific requirement missing from the documentation?
Are there known limitations or issues when:
- Using environment-based subdomains
- Using Blazor Interactive WebAssembly
Is there a recommended or official approach for resolving tenants by subdomain in this setup?
Any clarification, guidance, or updated example would be greatly appreciated.
Thank you in advance.
19 Answer(s)
-
0
- Solution Below is a definitive checklist and working setup to make domain/subdomain tenant resolution work with ABP 9.1.x for Blazor Interactive (WebAssembly-only) and a separated Auth Server (default OpenIddict). It addresses both backend resolution and the Blazor WASM client side, including environment-based subdomains like app-qa.example.com, app-pre.example.com, app.example.com with tenant1.app-qa.example.com, etc.
A) Backend (HttpApi.Host) – Resolve tenant from subdomain and allow wildcard OpenIddict/redirects
- Enable wildcard domain support for OpenIddict (required for subdomain tenants)
- In YourHttpApiHostModule.PreConfigureServices:
// using Volo.Abp.OpenIddict.WildcardDomains; PreConfigure<AbpOpenIddictWildcardDomainOptions>(options => { options.EnableWildcardDomainSupport = true; // Add all authority formats that will be used by the auth server (API host if combined) // Example for environments: options.WildcardDomainsFormat.Add("https://{0}.app-qa.example.com"); options.WildcardDomainsFormat.Add("https://{0}.app-pre.example.com"); options.WildcardDomainsFormat.Add("https://{0}.app.example.com"); // If your API host is also subdomained (like {0}.api.app-qa.example.com), add those too. });- Add Domain/Subdomain tenant resolver
- In YourHttpApiHostModule.ConfigureServices:
// using Volo.Abp.MultiTenancy; Configure<AbpTenantResolveOptions>(options => { // Adjust formats to your real hostnames used for API endpoints receiving requests. options.AddDomainTenantResolver("{0}.app-qa.example.com"); options.AddDomainTenantResolver("{0}.app-pre.example.com"); options.AddDomainTenantResolver("{0}.app.example.com"); // If your API host has a different subdomain pattern, add its formats as well. });- If using a separated Auth Server (or validating tokens issued for wildcard domains)
- Configure JWT bearer validation to accept wildcard issuers when you do token validation on gateway/API hosts that are not the issuer:
// using Owl.TokenWildcardIssuerValidator; context.Services.AddAuthentication(JwtBearerDefaults.AuthenticationScheme) .AddJwtBearer(options => { options.Authority = configuration["AuthServer:Authority"]; // Your base authority options.RequireHttpsMetadata = true; // Allow wildcard issuers for subdomain tenants options.TokenValidationParameters.IssuerValidator = TokenWildcardIssuerValidator.IssuerValidator; options.TokenValidationParameters.ValidIssuers = new[] { "https://{0}.app-qa.example.com/", "https://{0}.app-pre.example.com/", "https://{0}.app.example.com/" }; });- CORS and Redirect URIs for wildcard subdomains
- Use ABP helpers that support wildcard subdomains for CORS and redirect URI validation:
context.Services.AddAbpStrictRedirectUriValidator(); context.Services.AddAbpClientConfigurationValidator(); context.Services.AddAbpWildcardSubdomainCorsPolicyService();- In DbMigrator appsettings.json (Identity/OpenIddict client registrations), set RootUrl with {0} placeholder so redirect URIs and post-logout URIs are generated per-tenant:
"IdentityServer": { "Clients": { "My_Blazor_Wasm": { "ClientId": "My_Blazor_Wasm", "ClientSecret": "1q2w3e*", "RootUrl": "https://{0}.app-qa.example.com" } } }Repeat entries for each environment if you keep per-env DBs; otherwise include each environment’s RootUrl pattern if you use one central auth DB for all envs. Re-run DbMigrator so allowed redirect URIs/CORS origins are updated.
- Issuer URI when using OpenIddict If you customized IssuerUri earlier, ensure it does not conflict with wildcard expectations. Commonly you don’t set a fixed IssuerUri when using wildcard support; instead rely on AbpOpenIddictWildcardDomainOptions above.
B) Blazor Interactive (WebAssembly-only) – Propagate the current tenant’s subdomain to Authority and BaseUrl
For Blazor WebAssembly, there is no server-side tenant resolver in the UI process. You must dynamically shape the Authority and BaseUrl at startup using the current browser URL. This is documented for Angular and demonstrated for Blazor in community samples. Implement the pattern below:
- In the Blazor WASM client’s Program.cs/Module.Initialize:
- Read the current origin (builder.HostEnvironment.BaseAddress) and inject the tenant subdomain into the Authority and the RemoteServices BaseUrl by replacing {0}. The key is: never hardcode a single Authority; compute it based on current host.
Example utility methods:
private static readonly string[] ProtocolPrefixes = { "http://", "https://" }; private static string ConvertToTenantSubDomain(WebAssemblyHostBuilder builder, string configPath) { var baseUrl = builder.HostEnvironment.BaseAddress; // e.g., https://tenant1.app-qa.example.com/ var configUrl = builder.Configuration[configPath]; // e.g., "https://{0}.api.app-qa.example.com" return configUrl.Replace("{0}.", GetTenantNamePrefix(baseUrl)); } // Returns "tenant1." or "" when no tenant private static string GetTenantNamePrefix(string baseUrl) { var hostName = baseUrl.RemovePreFix(ProtocolPrefixes); // tenant1.app-qa.example.com/ var host = hostName.TrimEnd('/').Split('/')[0]; // tenant1.app-qa.example.com var parts = host.Split('.'); // Your rule: "tenant-env.example.com" => first label is tenant, second is env-app // E.g., tenant1.app-qa.example.com => tenant is parts[0], rest identifies environment/app return parts.Length > 2 ? $"{parts[0]}." : string.Empty; }- Apply tenantized Authority and BaseUrl
- When configuring authentication:
builder.Services.AddOidcAuthentication(options => { builder.Configuration.Bind("AuthServer", options.ProviderOptions); options.UserOptions.RoleClaim = "role"; options.ProviderOptions.Authority = ConvertToTenantSubDomain(builder, "AuthServer:Authority"); });- When configuring remote services:
Configure<AbpRemoteServiceOptions>(options => { options.RemoteServices.Default = new RemoteServiceConfiguration( ConvertToTenantSubDomain(builder, "RemoteServices:Default:BaseUrl") ); });- appsettings.json (Blazor client) Provide patterns with {0} in the Blazor client so the above replacement works:
{ "App": { "SelfUrl": "https://{0}.app-qa.example.com" }, "AuthServer": { "Authority": "https://{0}.api.app-qa.example.com", "ClientId": "My_Blazor_Wasm", "ResponseType": "code" }, "RemoteServices": { "Default": { "BaseUrl": "https://{0}.api.app-qa.example.com" } } }Repeat per environment or compute environment from the current host if you prefer a single file with multiple candidates.
C) Cookie/Authentication isolation across tenants in WASM If you observe “login to one tenant logs me into all,” your auth cookie is likely scoped to the parent domain. Always let the auth cookie domain be the exact host (no leading dot, Domain = null). OpenIddict server defaults typically align with this; avoid setting a shared cookie domain. Clear browser cookies after changes.
D) Resolver order and middleware ABP’s default resolver order starts with CurrentUserTenantResolveContributor, then QueryString, Route, Header, Cookie. Adding the domain resolver (as shown) integrates correctly. Ensure app.UseAbpRequestLocalization(), app.UseRouting(), app.UseAuthentication(), app.UseAbpMultiTenancy(), app.UseAuthorization() are in the standard order generated by templates.
E) Environment-based subdomains (app-qa/app-pre/app)
- Add one resolver format per actual host pattern you expect to hit on the API/Auth side:
- "{0}.app-qa.example.com"
- "{0}.app-pre.example.com"
- "{0}.app.example.com"
- Make sure your DNS/ingress forwards those hosts to the API/Auth app.
F) Known limitations and notes for Blazor WASM
- There is no server-side Blazor UI pipeline to run a tenant resolver in WASM; you must shape the Authority and BaseUrl on the client at startup as above. This is the recommended approach for WASM.
- For the backend OpenIddict/redirect handling with subdomains, wildcard configuration is required (as in Section A).
G) Minimal verification steps
- Create a tenant named tenant1.
- Browse to https://tenant1.app-qa.example.com
- Observe the Blazor WASM client sets Authority/BaseUrl to https://tenant1.api.app-qa.example.com (or your pattern).
- Login succeeds; API requests include the correct tenant context, and ICurrentTenant is populated on the server.
- Browse in a separate tab to another tenant’s URL; it should remain isolated.
- Sources
- https://abp.io/docs/latest/framework/architecture/multi-tenancy#domainsubdomain-tenant-resolver
- https://github.com/abpframework/abp-samples/tree/master/DomainTenantResolver
This response was generated by AI. If it didn’t solve your problem, feel free to post a new answer — our support team will jump in to help you soon.
-
0
Unfortunately, the proposed solution does not work for us. We have tested it both in our application and in a clean ABP application, and the behavior is the same.
To make this reproducible, I created a clean ABP 9.1.3 solution (Blazor Interactive – WebAssembly only) and applied the suggested changes.
Reproducible repository: 👉 https://github.com/franciscosl-fnet/abp-app-domain-based
In this sample:
- The tenant name is correctly extracted from the subdomain.
- However, the tenant context is not applied correctly, and the application does not work as expected.
- Same behavior in our real project and in this clean sample.
This suggests the issue is not project-specific. Any guidance after reviewing the repo would be appreciated.
-
0
hi
Reproducible repository: 👉 https://github.com/franciscosl-fnet/abp-app-domain-based
Can you share the steps?
I will check it
Thanks.
-
0
[maliming] said: hi
Reproducible repository: 👉 https://github.com/franciscosl-fnet/abp-app-domain-based
Can you share the steps?
I will check it
Thanks.
Hi, sorry, I thought that the problem description already explained how to reproduce it.
- Start the host (DbMigrator previously runned)
- Start Blazor
- Create a new tenant from the host
- Log out
- Use the URL format described in the ticket to access the newly created tenant (using the local URLs)
-
0
Thanks. I will check it.
-
0
hi
Can you test this PR?
https://github.com/franciscosl-fnet/abp-app-domain-based/pull/1
-
0
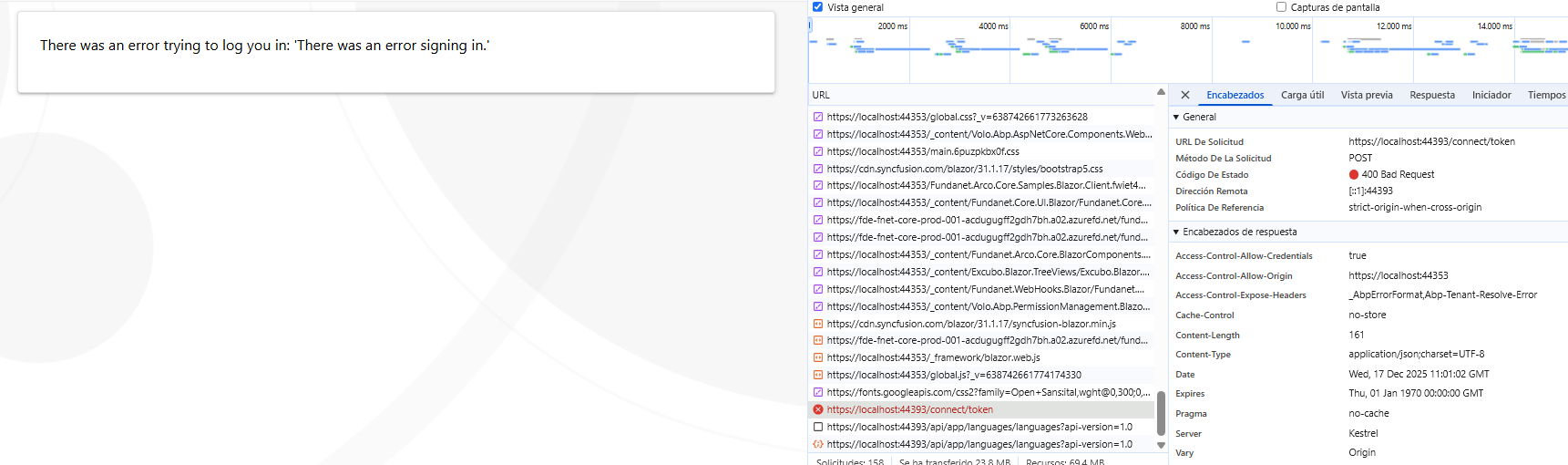
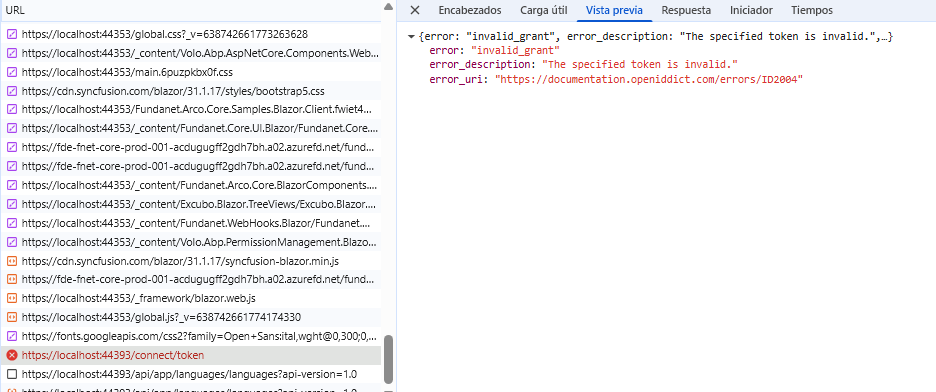
I get the following error:
error:invalid_request error_description:The specified 'redirect_uri' is not valid for this client application. error_uri:https://documentation.openiddict.com/errors/ID2043 culture:es ui-culture:es
I tried with a new database, and I get the same error. In both cases, I ran dbmigrator.
-
0
hi
Delete
N'AbpSolution1_Blazorand instert it againINSERT INTO [dbo].[OpenIddictApplications] ([Id], [ApplicationType], [ClientId], [ClientSecret], [ClientType], [ConsentType], [DisplayName], [DisplayNames], [JsonWebKeySet], [Permissions], [PostLogoutRedirectUris], [Properties], [RedirectUris], [Requirements], [Settings], [ClientUri], [LogoUri], [ExtraProperties], [ConcurrencyStamp], [CreationTime], [CreatorId], [LastModificationTime], [LastModifierId], [IsDeleted], [DeleterId], [DeletionTime]) VALUES ('1959479D-4CEA-A392-FA41-3A1E3CB96F9E', N'web', N'AbpSolution1_Blazor', NULL, N'public', N'implicit', N'Blazor Application', NULL, NULL, N'["ept:end_session","gt:authorization_code","rst:code","ept:authorization","ept:token","ept:revocation","ept:introspection","gt:refresh_token","scp:address","scp:email","scp:phone","scp:profile","scp:roles","scp:AbpSolution1"]', N'["https://localhost:44366/authentication/login-callback", "https://tenant.localhost:44366/authentication/logout-callback"]', NULL, N'["https://localhost:44366/authentication/login-callback", "https://tenant.localhost:44366/authentication/login-callback"]', NULL, NULL, N'https://{0}.localhost:44366', N'/images/clients/blazor.svg', N'{}', N'6739bff0e772468f861b23c73b91a488', '2025-12-17 12:23:35.5845410', NULL, NULL, NULL, '0', NULL, NULL); -
0
Now it works, I can access the new tenant via URL, but when I do so, the website is marked as unsafe.
Now I need to transfer it to my production application. Could you explain how you solved it and how everything works so that I can understand what I need to do, rather than just copying and pasting?
Thank you very much!
-
0
hi
I just added code to get the current tenant from your Blazor URL and use it.
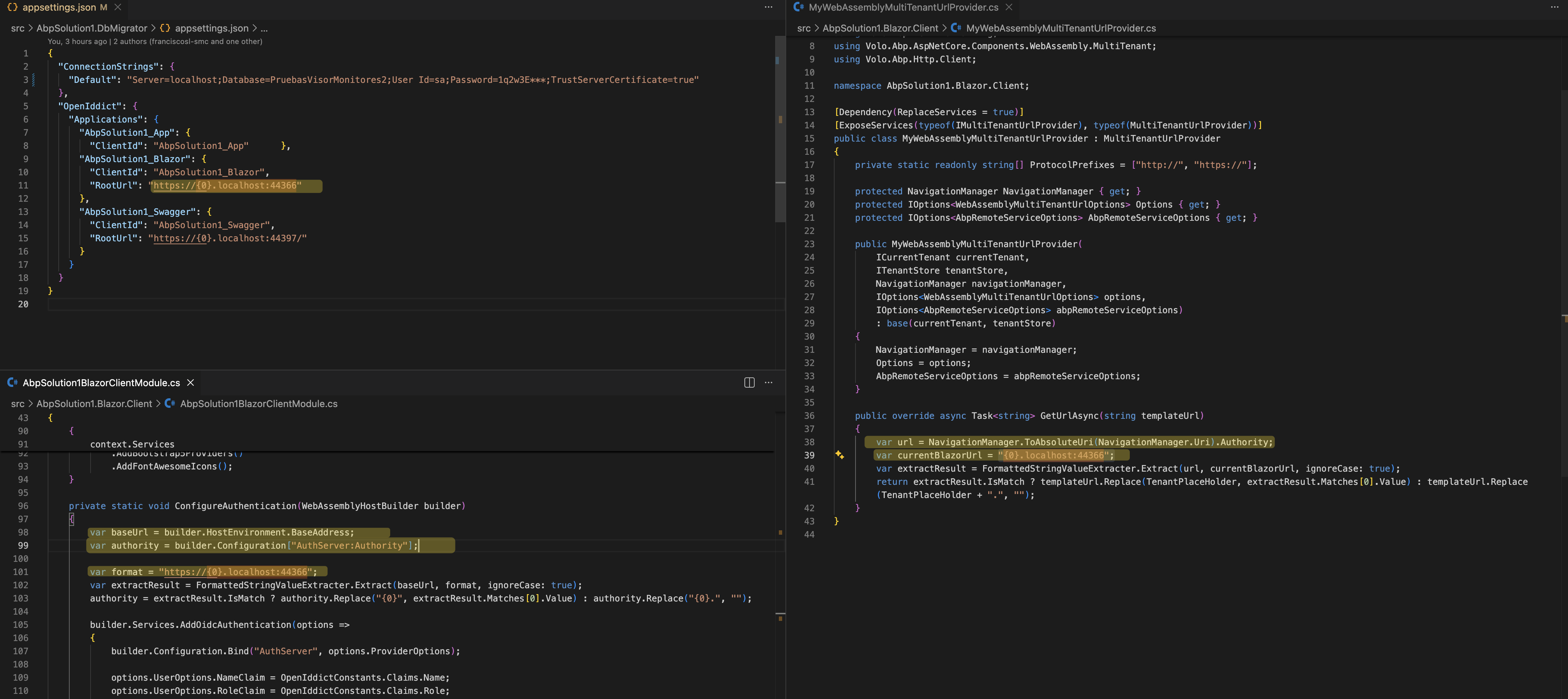
See https://github.com/maliming/abp-app-domain-based/blob/42f7a49b33e8a27e729fc86cea6287d6239081c5/src/AbpSolution1.Blazor.Client/MyWebAssemblyMultiTenantUrlProvider.cs
And use
TokenWildcardIssuerValidator.IssuerValidatorhttps://github.com/maliming//Owl.TokenWildcardIssuerValidator
Please remove
x.TokenValidationParameters.ValidateIssuer = false;, It's test code.Thanks.
-
0
Thank you. I am currently migrating the code to my production application, so I haven't been able to test it yet.
Reviewing the Nuget dependencies that I add to my application, I see that the Nuget
Owl.TokenWildcardIssuerValidatoris added, which comes from your personal repository,Shouldn't this code be inside the abp code?
-
0
This usage scenario is very rare, so it is a standalone package.
It is free and open source.
Thanks.
-
0
When I take it to the production application, I am getting an error in this call: https://{0}.localhost:44393/.well-known/openid-configuration
The ports are different because it is another solution. What could be the reason for this?
-
0
-
0
-
0
hi
Can you share the debug logs of 44393 website?
Thanks
-
0
Hi,
I have uploaded the log to the repository. You can find it here https://github.com/franciscosl-fnet/abp-app-domain-based/blob/main/Logs20251217.txt
-
0
[maliming] said: hi
Can you share the debug logs of 44393 website?
Thanks
If you wish, I can give you access to the source code where I am implementing it, so you can run the application yourself and see what happens. Please contact me by email, francisco.sierra@semicrol.com
-
0
hi
I changed some code in https://github.com/franciscosl-fnet/abp-app-domain-based/pull/2
Can you apply them to your project and reproduce the error and share the API logs.txt to liming.ma@volosoft.com
Thanks.