Setting Management Module
Setting Management Module implements the ISettingStore (see the setting system) to store the setting values in a database and provides the ISettingManager to manage (change) the setting values in the database.
Setting Management module is already installed and configured for the startup templates. So, most of the times you don't need to manually add this module to your application.
ISettingManager
ISettingManager is used to get and set the values for the settings. Examples:
using System;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Volo.Abp.DependencyInjection;
using Volo.Abp.SettingManagement;
namespace Demo
{
public class MyService : ITransientDependency
{
private readonly ISettingManager _settingManager;
//Inject ISettingManager service
public MyService(ISettingManager settingManager)
{
_settingManager = settingManager;
}
public async Task FooAsync()
{
Guid user1Id = ...;
Guid tenant1Id = ...;
//Get/set a setting value for the current user or the specified user
string layoutType1 =
await _settingManager.GetOrNullForCurrentUserAsync("App.UI.LayoutType");
string layoutType2 =
await _settingManager.GetOrNullForUserAsync("App.UI.LayoutType", user1Id);
await _settingManager.SetForCurrentUserAsync("App.UI.LayoutType", "LeftMenu");
await _settingManager.SetForUserAsync(user1Id, "App.UI.LayoutType", "LeftMenu");
//Get/set a setting value for the current tenant or the specified tenant
string layoutType3 =
await _settingManager.GetOrNullForCurrentTenantAsync("App.UI.LayoutType");
string layoutType4 =
await _settingManager.GetOrNullForTenantAsync("App.UI.LayoutType", tenant1Id);
await _settingManager.SetForCurrentTenantAsync("App.UI.LayoutType", "LeftMenu");
await _settingManager.SetForTenantAsync(tenant1Id, "App.UI.LayoutType", "LeftMenu");
//Get/set a global and default setting value
string layoutType5 =
await _settingManager.GetOrNullGlobalAsync("App.UI.LayoutType");
string layoutType6 =
await _settingManager.GetOrNullDefaultAsync("App.UI.LayoutType");
await _settingManager.SetGlobalAsync("App.UI.LayoutType", "TopMenu");
}
}
}
So, you can get or set a setting value for different setting value providers (Default, Global, User, Tenant... etc).
Use the
ISettingProviderinstead of theISettingManagerif you only need to read the setting values, because it implements caching and supports all deployment scenarios. You can use theISettingManagerif you are creating a setting management UI.
Setting Cache
Setting values are cached using the distributed cache system. Always use the ISettingManager to change the setting values which manages the cache for you.
Setting Management Providers
Setting Management module is extensible, just like the setting system. You can extend it by defining setting management providers. There are 5 pre-built setting management providers registered it the following order:
DefaultValueSettingManagementProvider: Gets the value from the default value of the setting definition. It can not set the default value since default values are hard-coded on the setting definition.ConfigurationSettingManagementProvider: Gets the value from the IConfiguration service. It can not set the configuration value because it is not possible to change the configuration values on runtime.GlobalSettingManagementProvider: Gets or sets the global (system-wide) value for a setting.TenantSettingManagementProvider: Gets or sets the setting value for a tenant.UserSettingManagementProvider: Gets the setting value for a user.
ISettingManager uses the setting management providers on get/set methods. Typically, every setting management provider defines extension methods on the ISettingManagement service (like SetForUserAsync defined by the user setting management provider).
If you want to create your own provider, implement the ISettingManagementProvider interface or inherit from the SettingManagementProvider base class:
public class CustomSettingProvider : SettingManagementProvider, ITransientDependency
{
public override string Name => "Custom";
public CustomSettingProvider(ISettingManagementStore store)
: base(store)
{
}
}
SettingManagementProvider base class makes the default implementation (using the ISettingManagementStore) for you. You can override base methods as you need. Every provider must have a unique name, which is Custom in this example (keep it short since it is saved to database for each setting value record).
Once you create your provider class, you should register it using the SettingManagementOptions options class:
Configure<SettingManagementOptions>(options =>
{
options.Providers.Add<CustomSettingProvider>();
});
The order of the providers are important. Providers are executed in the reverse order. That means the CustomSettingProvider is executed first for this example. You can insert your provider in any order in the Providers list.
See Also
Setting Management UI
Setting Mangement module provided the email setting UI by default, and it is extensible; You can add your tabs to this page for your application settings.
MVC UI
Create a setting View Component
Create MySettingGroup folder under the Components folder. Add a new view component. Name it as MySettingGroupViewComponent:
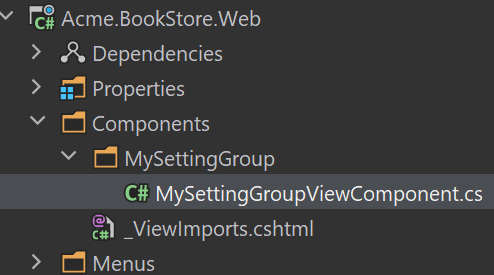
Open the MySettingGroupViewComponent.cs and change the whole content as shown below:
public class MySettingGroupViewComponent : AbpViewComponent
{
public virtual IViewComponentResult Invoke()
{
return View("~/Components/MySettingGroup/Default.cshtml");
}
}
You can also use the
InvokeAsyncmethod, In this example, we use theInvokemethod.
Default.cshtml
Create a Default.cshtml file under the MySettingGroup folder.
Open the Default.cshtml and change the whole content as shown below:
<div>
<p>My setting group page</p>
</div>
BookStoreSettingPageContributor
Create a BookStoreSettingPageContributor.cs file under the Settings folder:
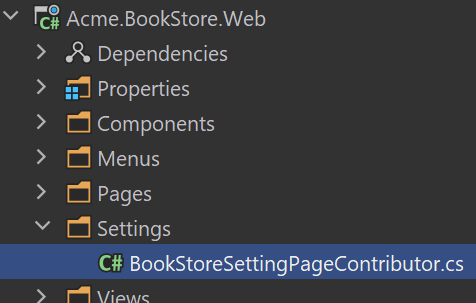
The content of the file is shown below:
public class BookStoreSettingPageContributor : ISettingPageContributor
{
public Task ConfigureAsync(SettingPageCreationContext context)
{
context.Groups.Add(
new SettingPageGroup(
"Volo.Abp.MySettingGroup",
"MySettingGroup",
typeof(MySettingGroupViewComponent)
)
);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
public Task<bool> CheckPermissionsAsync(SettingPageCreationContext context)
{
// You can check the permissions here
return Task.FromResult(true);
}
}
Open the BookStoreWebModule.cs file and add the following code:
Configure<SettingManagementPageOptions>(options =>
{
options.Contributors.Add(new BookStoreSettingPageContributor());
});
Run the Application
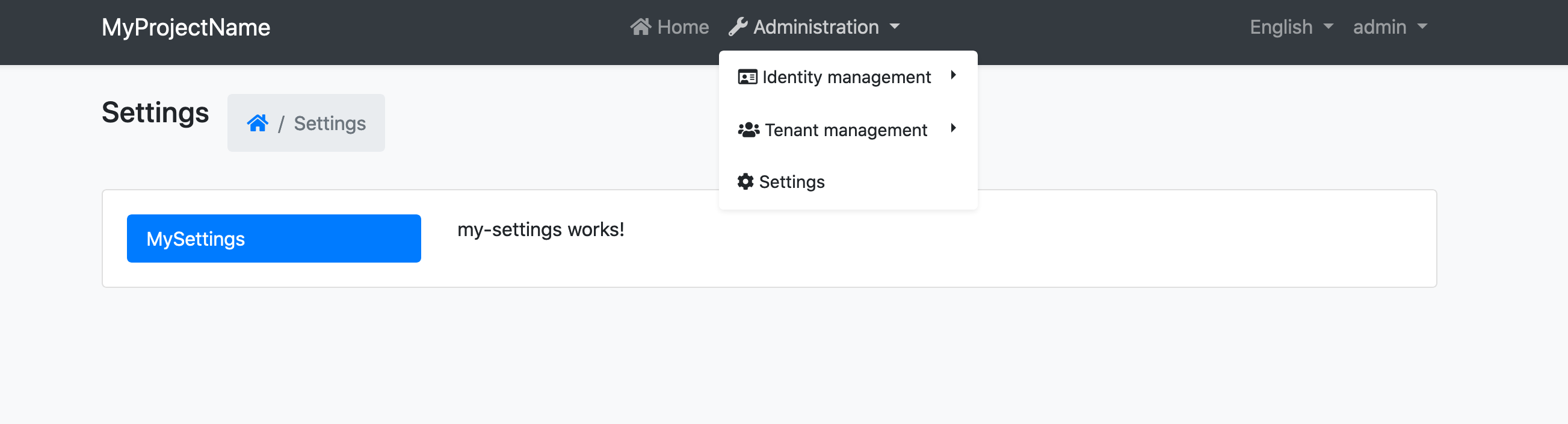
Navigate to /SettingManagement route to see the changes:
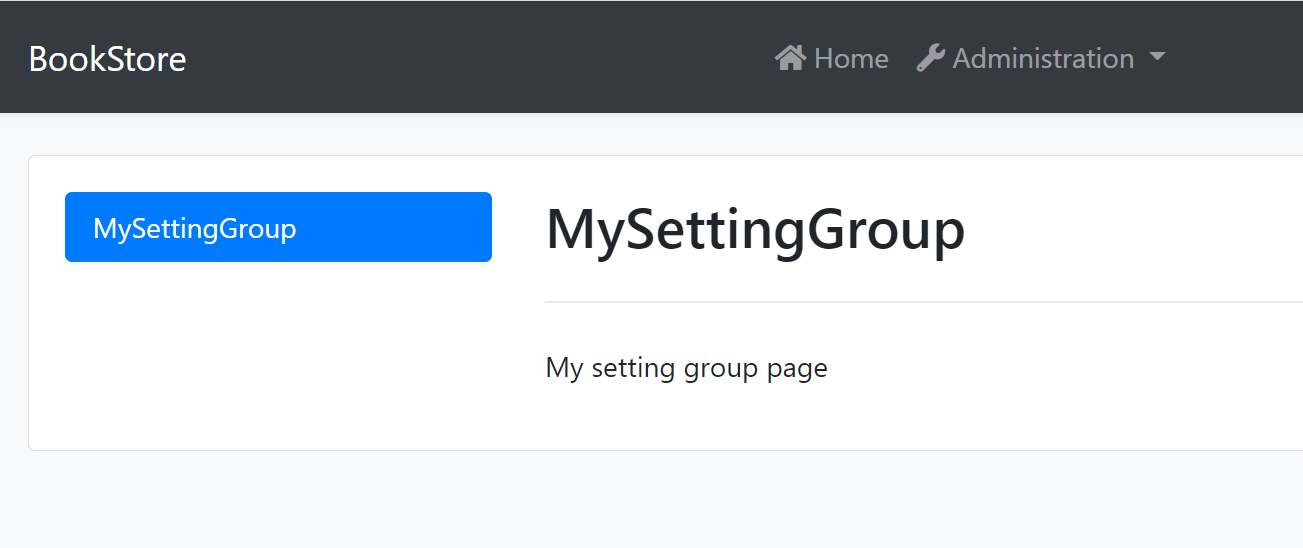
Blazor UI
Create a Razor Component
Create MySettingGroup folder under the Pages folder. Add a new razor component. Name it as MySettingGroupComponent:
Open the MySettingGroupComponent.razor and change the whole content as shown below:
<Row>
<p>my setting group</p>
</Row>
BookStoreSettingComponentContributor
Create a BookStoreSettingComponentContributor.cs file under the Settings folder:
The content of the file is shown below:
public class BookStoreSettingComponentContributor : ISettingComponentContributor
{
public Task ConfigureAsync(SettingComponentCreationContext context)
{
context.Groups.Add(
new SettingComponentGroup(
"Volo.Abp.MySettingGroup",
"MySettingGroup",
typeof(MySettingGroupComponent)
)
);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}
public Task<bool> CheckPermissionsAsync(SettingComponentCreationContext context)
{
// You can check the permissions here
return Task.FromResult(true);
}
}
Open the BookStoreBlazorModule.cs file and add the following code:
Configure<SettingManagementComponentOptions>(options =>
{
options.Contributors.Add(new BookStoreSettingComponentContributor());
});
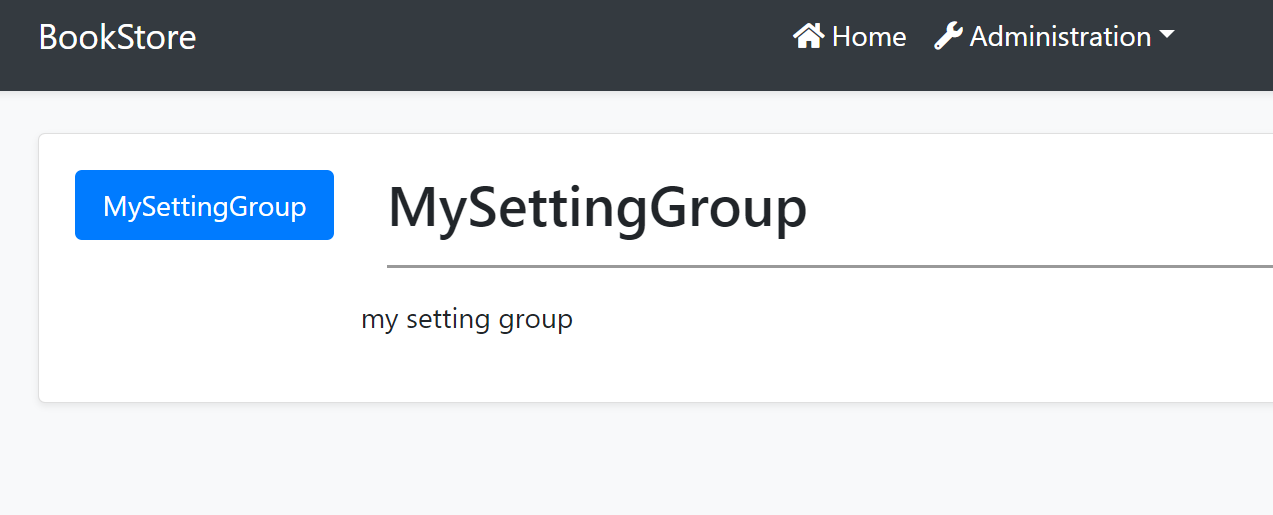
Run the Application
Navigate to /setting-management route to see the changes:
Angular UI
Create a Component
Create a component with the following command:
yarn ng generate component my-settings
Open the app.component.ts and modify the file as shown below:
import { Component } from '@angular/core';
import { SettingTabsService } from '@abp/ng.setting-management/config'; // imported SettingTabsService
import { MySettingsComponent } from './my-settings/my-settings.component'; // imported MySettingsComponent
@Component(/* component metadata */)
export class AppComponent {
constructor(private settingTabs: SettingTabsService) // injected MySettingsComponent
{
// added below
settingTabs.add([
{
name: 'MySettings',
order: 1,
requiredPolicy: 'policy key here',
component: MySettingsComponent,
},
]);
}
}
Run the Application
Navigate to /setting-management route to see the changes: