Asynchronous Communication between Microservices
This documentation introduces guidance for event based communication between microservices.
The below sample demonstrates event based communication between ProductService and OrderService. See Adding New Microservice Guide to understand how to add a new microservice project (OrderService) to your solution.
Message Broker
Microservices may interact through a central event bus. This is achieved by publishing event to event bus and subscribed microservice's handling the events. Apart from communicating with gRPC/HTTP; publisher doesn't need to know about consumer hence reducing the coupling between microservices.
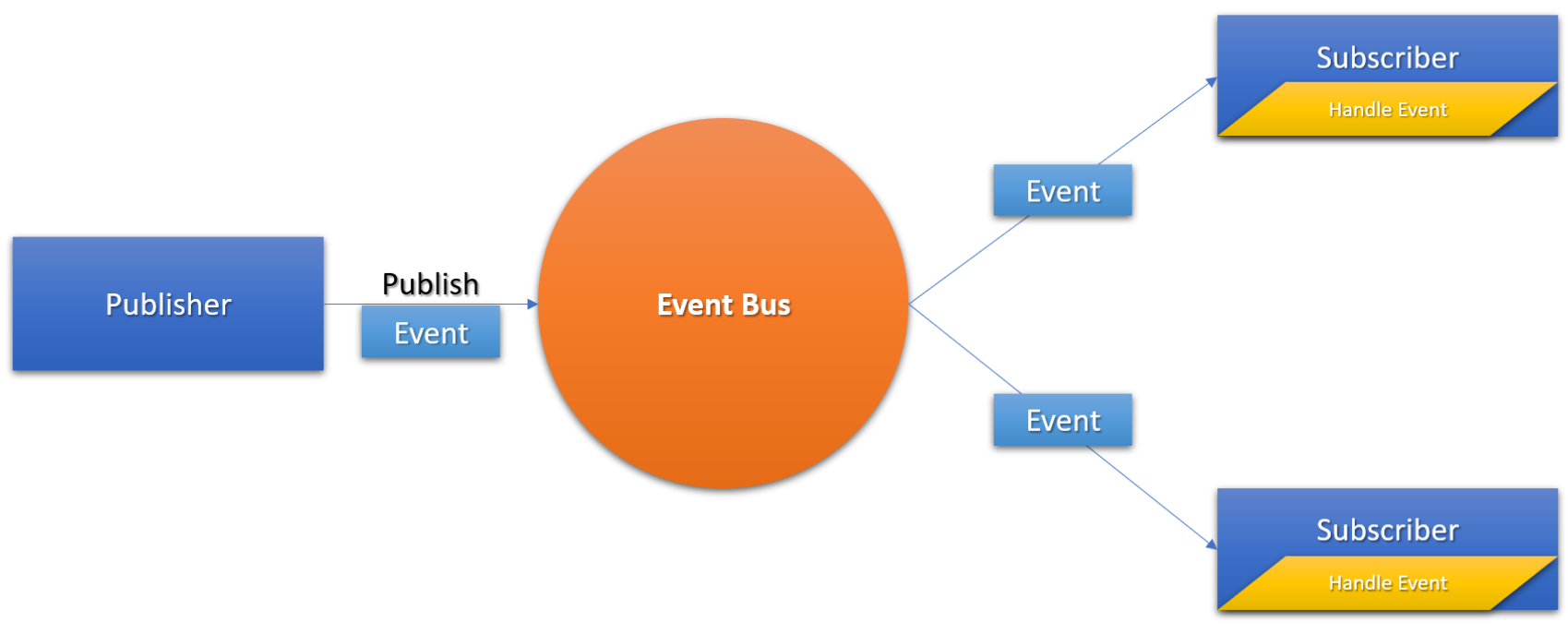
This is also crucial when Data Consistency is important and data duplication between services.
Sample Scenario
Consider ProductService publishes a distributed event whenever product price is updated. ProductAppService has the following updated method and the Event Transfer Object:
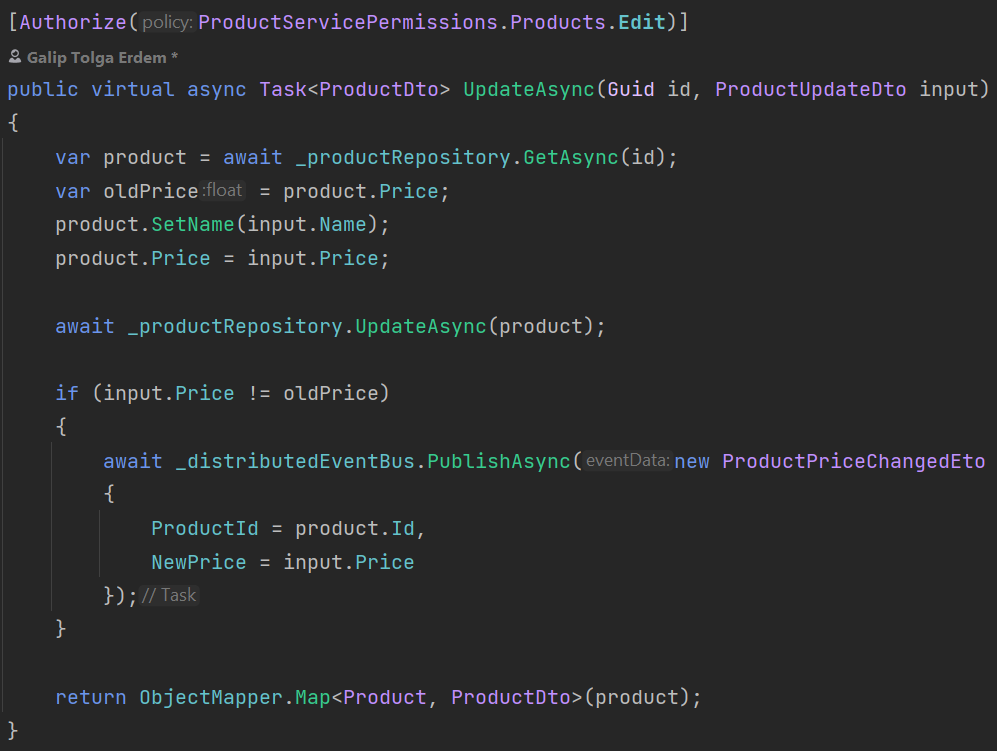
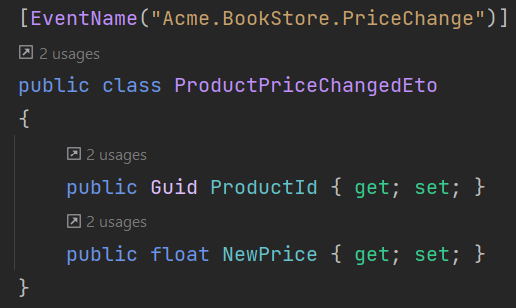
OrderService is one of the subscriber to this event and makes discount if the criteria are met.
Note that there can be many other subscriber microservices listening to the same event.
Updating OrderService Application Contracts
In order to make ProductPriceChangedEto available for OrderService application, you need to add the project reference of ProductService.Application.Contracts to OrderService.Application.Contracts.
Add csproj reference:
Open Acme.BookStore.OrderService.Application.Contracts.csproj and add the following project reference
<ProjectReference Include="..\..\..\product\src\Acme.BookStore.ProductService.Application.Contracts\Acme.BookStore.ProductService.Application.Contracts.csproj" />
Add DependsOn attribute:
Open OrderServiceApplicationContractsModule.cs class and add the following module dependency
typeof(ProductServiceApplicationContractsModule)
Handling the Distributed Event
Create a handler class that inherits IDistributedEventHandler<ProductPriceChangedEto> under Acme.BookStore.OrderService.BookStore.Application project.
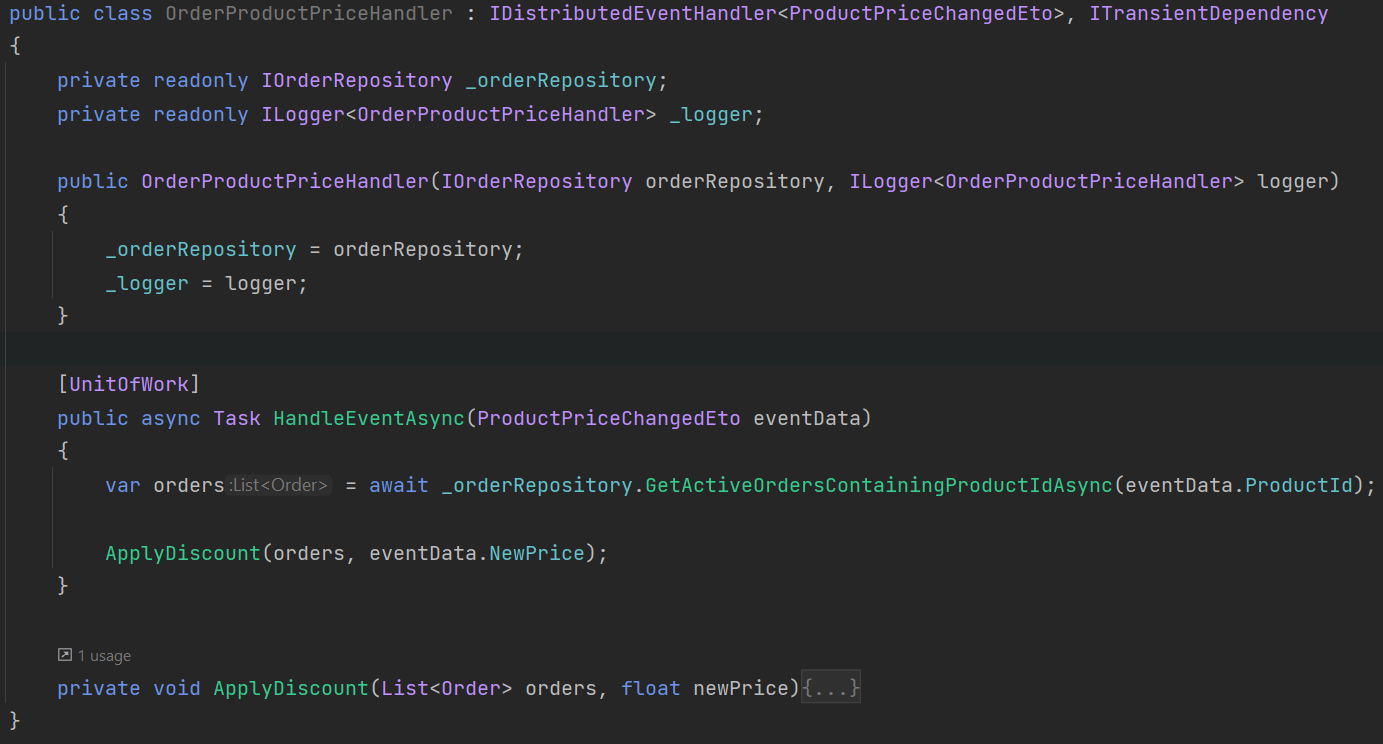
Note that you can also handle multiple events in the same handler.
Auto Events
You can also subscribe to pre-defined events. ABP publishes events for create, update and delete operations for an entity once you configure it. Consider you want to update your order whenever a user information is changed.
IdentityService using Identity Module auto publishes UserEto. To reference UserEto,
Add package reference:
Open Acme.BookStore.OrderService.Application.csproj and add the following project reference
<PackageReference Include="Volo.Abp.Users.Abstractions" Version="4.4.2" />
Create Handler:
Create a handler class that inherits IDistributedEventHandler<EntityUpdatedEto<UserEto>> under Acme.BookStore.OrderService.BookStore.Application project as below:
public class OrderUserUpdateHandler : IDistributedEventHandler<EntityUpdatedEto<UserEto>>,ITransientDependency
{
private readonly ILogger<OrderProductPriceHandler> _logger;
public OrderUserUpdateHandler(ILogger<OrderProductPriceHandler> logger)
{
_logger = logger;
}
[UnitOfWork]
public async Task HandleEventAsync(EntityUpdatedEto<UserEto> eventData)
{
_logger.LogInformation($"\n{JsonConvert.SerializeObject(eventData.Entity)}");
}
}
Note: You can also use pre-defined ETO classes like
IdentityUserCreatedEto. Check the Pre-Defined Events documentations for more.
































































