Microservice Startup Template: Microservices
There are four microservices are included in the microservice startup template;
- IdentityService is located under the services/identity folder. This service is an infrastructural microservice and hosts
IdentityandOpenIddictrelated functionality and data store. - AdministrationService is located under the services/administration folder. This service is an infrastructural microservice and hosts administrative functionality such as
permission-management,setting-management,language-management,audit-loggingand such. - SaasService is located under the services/saas folder. This service is an infrastructural microservice and hosts multi-tenancy related functionality and data store.
- ProductService is located the under services/product folder. This is a sample microservice to examine and take as a reference for your services.
The infrastructural microservices typically use pre-built modules.
The microservices are highlighted in the overall solution diagram below:
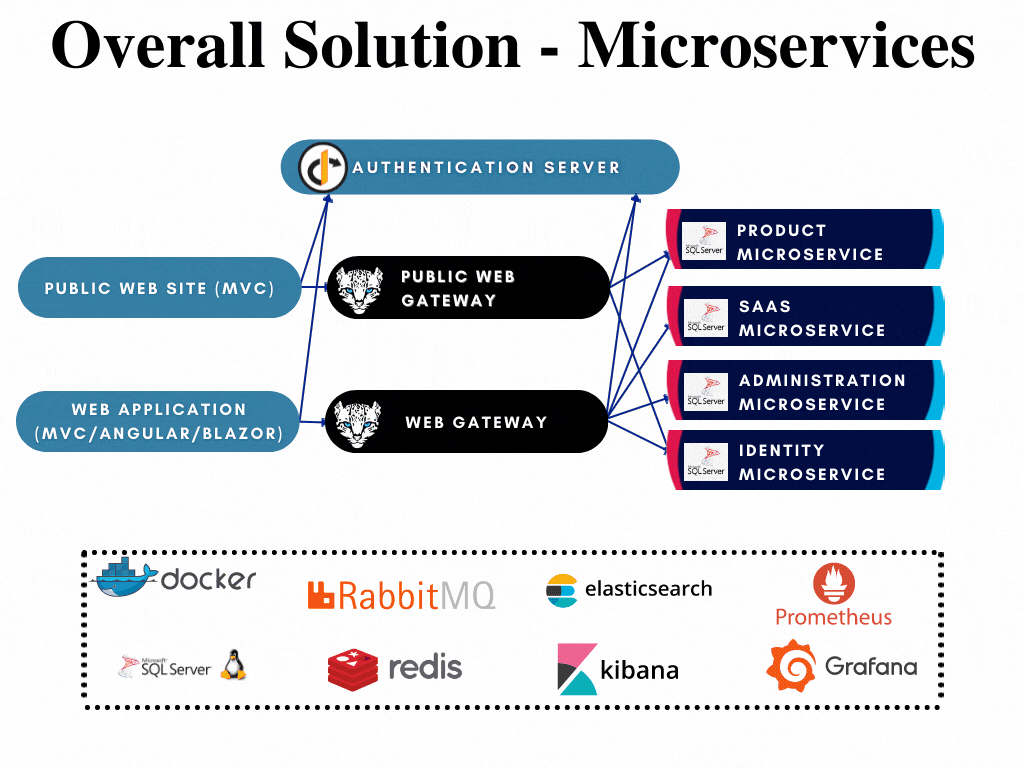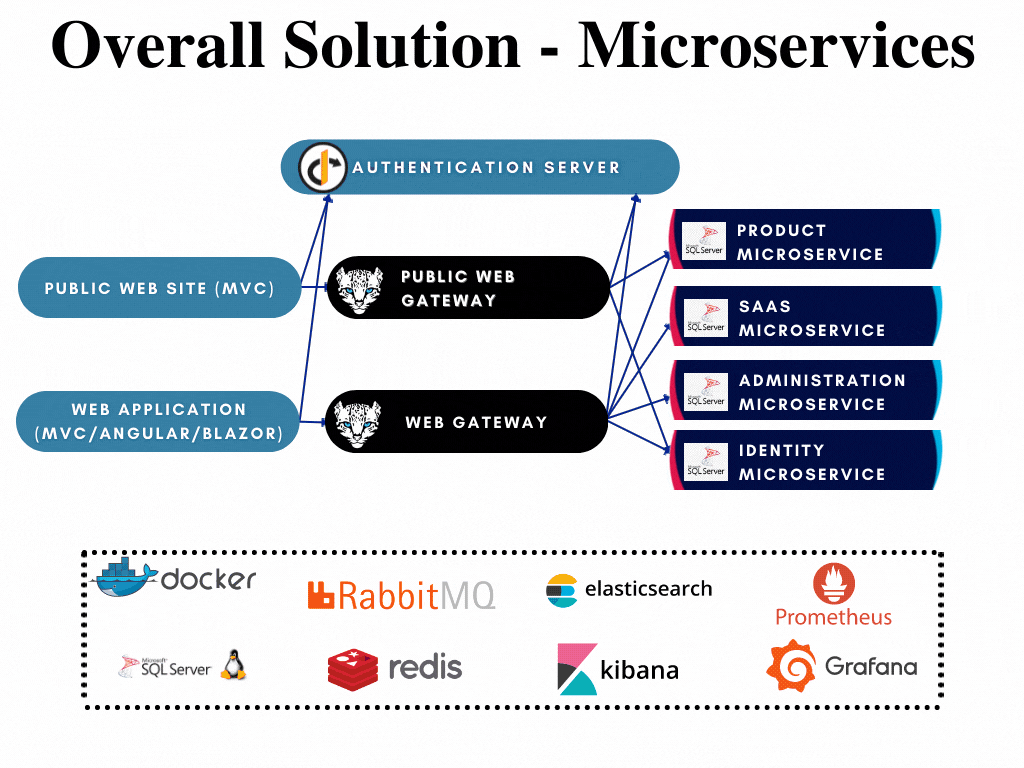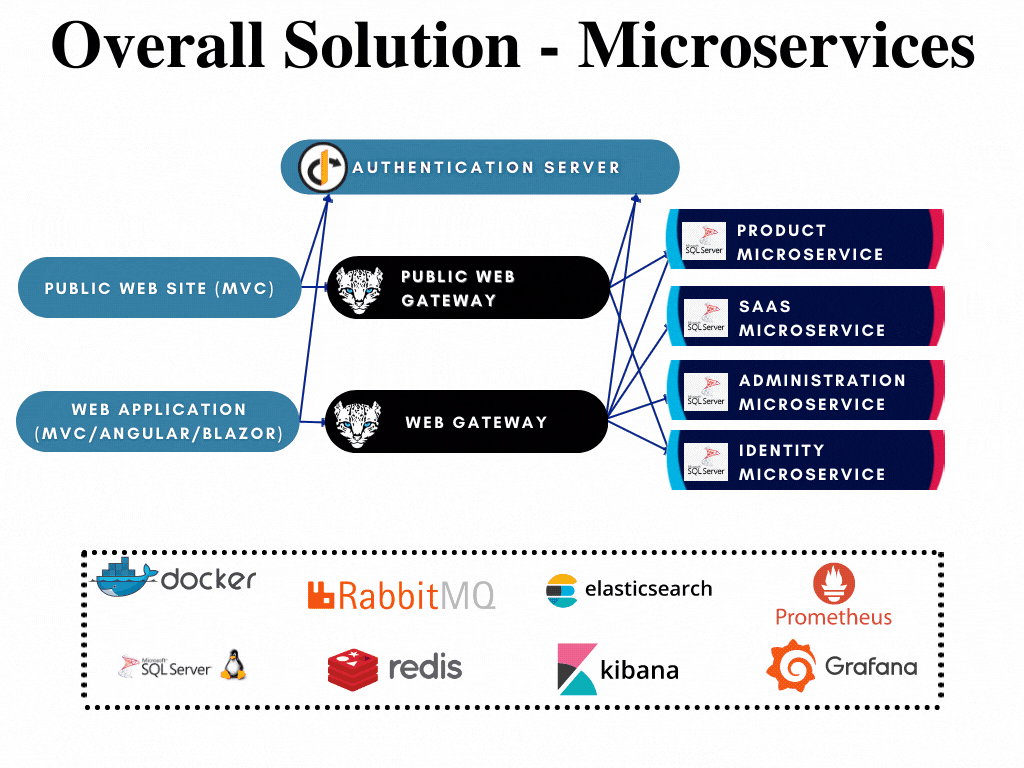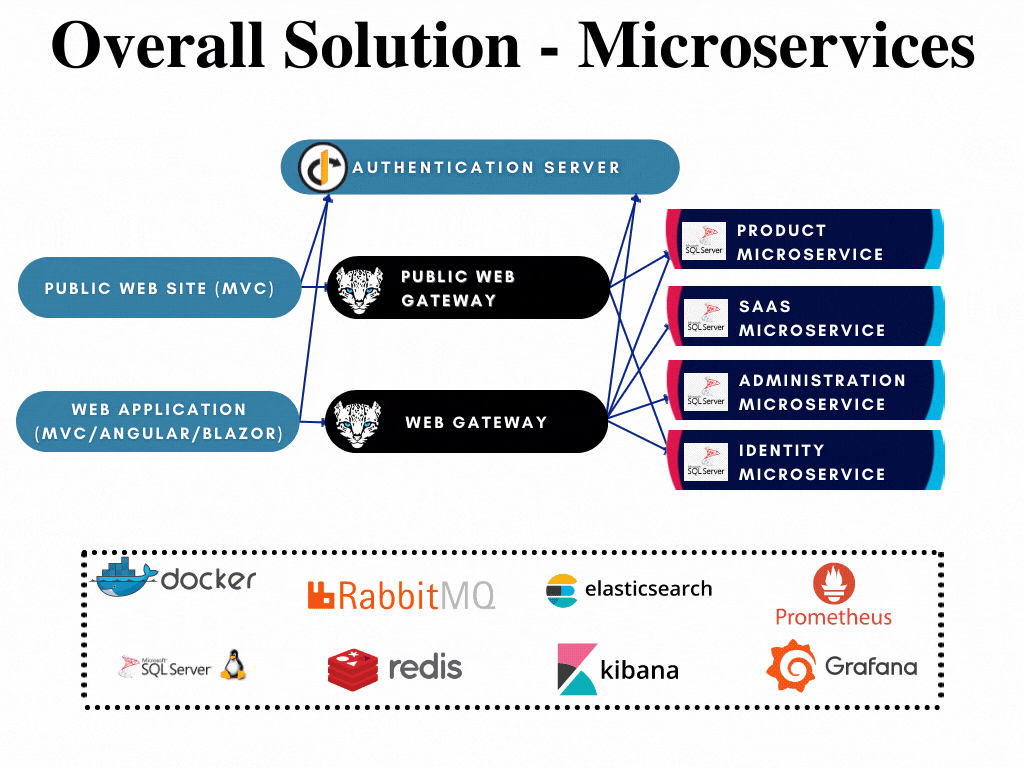
All microservices;
- Have their own solutions (
.slnfiles) including test projects under their respected folders.
- Depend on
SharedHostingMicroservicesModulewhich contains configuration helpers for JwtBearer authorization, Swagger and DbMigrations, - Contains configurations for AuthServer, Redis, RabbitMQ, ElasticSearch in appsettings.json file,
- Are capable of on-the-fly database migration; have
DbMigrationsfolder that containsMigrationCheckerandMigrationEventHandler. This allows microservices migrate and seed their databases using distributed event bus as an alternative usage to shared DbMigrator, - Use Sql Server, containing
.EntityFrameworkCorelayer. This layer contains related database contexts, database context factories and migrations along with related module DB configurations
If you want to switch your database provider to MongoDb instead of EntityFrameworkCore for any of the microservice, you need to create
.MongoDbproject instead of.EntityFrameworkCore. Afterwards, add related modules MongoDb packages dependencies along with similar configurations made in EntityFrameworkCore layer like DB context replacement and such. For more, check MongoDB integration.
IdentityService
IdentityService is an infrastructural microservice that provides a modular solution by combining the Identity and OpenIddict modules. All the related layers reference the respective layers of these modules.
AuthServer Authorization
IdentityService is defined as an API scope with the name IdentityService in OpenIddictDataSeeder.
private async Task CreateApiScopesAsync()
{
await CreateScopesAsync("AccountService");
await CreateScopesAsync("IdentityService");
await CreateScopesAsync("AdministrationService");
await CreateScopesAsync("SaasService");
await CreateScopesAsync("ProductService");
}
See IdentityService Data Seeding for seeding options.
In order to make authorized requests to IdentityService by applications/microservices, IdentityService scope must have been granted for that client.
Web application (Mvc/Angular/Blazor) clients are allowed to request IdentityService scope when created:
private async Task CreateClientsAsync()
{
...
scopes: commonScopes.Union(new[]
{
"AccountService",
"IdentityService",
"AdministrationService",
"SaasService",
"ProductService"
}),
...
}
Web Gateway Swagger application is allowed for all the scopes and each gateway and microservice uses this client for swagger authorization:
private async Task CreateWebGatewaySwaggerClientsAsync()
{
await CreateSwaggerClientAsync("WebGateway",
new[] { "AccountService", "IdentityService", "AdministrationService", "SaasService", "ProductService" });
}
AdministrationService client is allowed to request IdentityService scope when created:
private async Task CreateApplicationAsync()
{
...
//Administration Service Client
await CreateClientAsync(
name: "MyProjectName_AdministrationService",
type: OpenIddictConstants.ClientTypes.Confidential,
consentType: OpenIddictConstants.ConsentTypes.Implicit,
displayName: "Administration Service Client",
secret: "1q2w3e*",
grantTypes: new List<string>
{
OpenIddictConstants.GrantTypes.ClientCredentials
},
scopes: commonScopes.Union(new[] { "IdentityService" }).ToList(),
permissions: new List<string> { IdentityPermissions.Users.Default }
);
}
Database Configuration
IdentityServiceDbContext implements
IIdentityDbContextIOpenIddictDbContext
in order to use these module DB contexts as combined single DB context. However, DI container must also dynamically inject IdentityServiceDbContext whenever IIdentityDbContext or IOpenIddictDbContext is requested. The configuration under ConfigureServices provides the runtime database replacement:
context.Services.AddAbpDbContext<IdentityServiceDbContext>(options =>
{
options.ReplaceDbContext<IIdentityDbContext>();
options.ReplaceDbContext<IOpenIddictDbContext>();
...
});
There is also a SQL configuration for changing the migration table name to separate each service migration history table:
Configure<AbpDbContextOptions>(options =>
{
options.Configure<IdentityServiceDbContext>(c =>
{
c.UseSqlServer(b =>
{
b.MigrationsHistoryTable("__IdentityService_Migrations");
});
});
});
SwaggerConfiguration
IdentityService uses WebGateway_Swagger client for swagger authorization and it uses authorization_code flow with the default IdentityService scope:
SwaggerConfigurationHelper.ConfigureWithOidc(
context: context,
authority: configuration["AuthServer:Authority"]!,
scopes: new[] { "IdentityService" },
flows: new[] { "authorization_code" },
discoveryEndpoint: configuration["AuthServer:MetadataAddress"],
apiTitle: "Identity Service API"
);
AdministrationService
AdministrationService is an infrastructural microservice that hosts Permission Management Module, Feature Management Module, Setting Management Module, Audit Logging, Language Management Module, Text Template Management Module, Lepton Theme Module and functions as a combination of these modules. All the related layers reference the respected layers of these modules.
AuthServer Authorization
By default; Web application (Mvc/Angular/Blazor), Public Web application, and Web Gateway Swagger applications are granted to make requests to AdministrationService scope. The definition of this API scope is done in OpenIddictDataSeeder.
AdministrationService has synched interservice-communication with IdentityService and should be able to make synched HTTP requests to IdentityService in order to function properly. This is done by adding this service as a client using client_credentials grant type with the name MyProjectName_AdministrationService requesting IdentityService with IdentityPermissions.Users.Default permission. This is used for administration service requesting the user list in administration pages.
//Administration Service Client
await CreateApplicationAsync(
name: "MyProjectName_AdministrationService",
type: OpenIddictConstants.ClientTypes.Confidential,
consentType: OpenIddictConstants.ConsentTypes.Implicit,
displayName: "Administration Service Client",
secret: "1q2w3e*",
grantTypes: new List<string>
{
OpenIddictConstants.GrantTypes.ClientCredentials
},
scopes: commonScopes.Union(new[] { "IdentityService" }).ToList(),
permissions: new List<string> { IdentityPermissions.Users.Default }
);
To make the client_credential requests, IdentityModel configuration is done under the IdentityClients section of appsettings along with RemoteServices configuration which points to AbpIdentity to locate the IdentityService endpoint. This is done by using [Static C# Client Proxies](https://github.com/abpframework/abp/blob/dev/docs/en/Blog-Posts/2021-11-18 v5_0_Preview/POST.md#static-generated-client-proxies-for-c-and-javascript).
If you need to make requests from AdministrationService to other microservices, you need to add their scope to client creation with the required permission as in the IdentityService user list request.
Database Configuration
AdministrationServiceDbContext implements
IPermissionManagementDbContextISettingManagementDbContextIFeatureManagementDbContextIAuditLoggingDbContextILanguageManagementDbContextITextTemplateManagementDbContextIBlobStoringDbContext
in order to use these module DB contexts as combined single DB context. DI container dynamically injects AdministrationServiceDbContext whenever one of the used modules dbcontext is requested. The configuration under ConfigureServices provides the runtime database replacement
context.Services.AddAbpDbContext<AdministrationServiceDbContext>(options =>
{
options.ReplaceDbContext<IPermissionManagementDbContext>();
options.ReplaceDbContext<ISettingManagementDbContext>();
options.ReplaceDbContext<IFeatureManagementDbContext>();
options.ReplaceDbContext<IAuditLoggingDbContext>();
options.ReplaceDbContext<ILanguageManagementDbContext>();
options.ReplaceDbContext<ITextTemplateManagementDbContext>();
options.ReplaceDbContext<IBlobStoringDbContext>();
...
});
There is also a SQL configuration for changing the migration table name to separate each service migration history table
Configure<AbpDbContextOptions>(options =>
{
options.Configure<AdministrationServiceDbContext>(c =>
{
c.UseSqlServer(b =>
{
b.MigrationsHistoryTable("__AdministrationService_Migrations");
});
});
});
SwaggerConfiguration
AdministrationService uses WebGateway_Swagger client for swagger authorization and it uses authorization_code flow with the default AdministrationService scope:
SwaggerConfigurationHelper.ConfigureWithOidc(
context: context,
authority: configuration["AuthServer:Authority"]!,
scopes: new[] { "AdministrationService" },
flows: new[] { "authorization_code" },
discoveryEndpoint: configuration["AuthServer:MetadataAddress"],
apiTitle: "Administration Service API"
);
SaasService
SaasService is an infrastructural microservice that for multi-tenancy functionality and data store.
AuthServer Authorization
In order to make authorized requests to SaasService by applications/microservices, SaasService scope must have been granted for that client.
By default; Web applications (Mvc/Angular/Blazor) and Web Gateway Swagger applications are granted to make requests to SaasService scope. The definition of this API scope is done in OpenIddictDataSeeder.
Database Configuration
SaasServiceDbContext implements
ISaasDbContext
in order to use this module DB context. DI container dynamically injects SaasServiceDbContext whenever the Saas module DB context is requested. The configuration under ConfigureServices provides the runtime database replacement
context.Services.AddAbpDbContext<SaasServiceDbContext>(options =>
{
options.ReplaceDbContext<ISaasDbContext>();
...
});
There is also a SQL configuration for changing the migration table name to separate each service migration history table
Configure<AbpDbContextOptions>(options =>
{
options.Configure<SaasServiceDbContext>(c =>
{
c.UseSqlServer(b =>
{
b.MigrationsHistoryTable("__SaasService_Migrations");
});
});
});
SwaggerConfiguration
SaasService uses WebGateway_Swagger client for swagger authorization and it uses authorization_code flow with the default SaasService scope:
SwaggerConfigurationHelper.ConfigureWithOidc(
context: context,
authority: configuration["AuthServer:Authority"]!,
scopes: new[] { "SaasService" },
flows: new[] { "authorization_code" },
discoveryEndpoint: configuration["AuthServer:MetadataAddress"],
apiTitle: "Saas Service API"
);
ProductService
ProductService is a sample microservice for examination, created with using Module Development Best Practices & Conventions. Since the Microservice template solution is created with modularity in mind, it is pretty straightforward to integrate modules as microservices into the solution.
ProductService solution structure contains .Web layer as a library instead of a traditional running project which provides modular UI development. When you develop the UI of your application inside the module, it will be rendered in your host application.
AuthServer Authorization
By default, Web applications (Mvc/Angular/Blazor), Public Web applications, and Web Gateway Swagger applications are granted to make requests to ProductService scope. The definition of this API scope is done in OpenIddictDataSeeder.
Database Configuration
ProductService.EntityFrameworkCore project contains ProductServiceDbContext, ProductServiceDbContextFactory, EfCoreEntityExtensionsMapping, Migrations, EfCore configuration and ProductRepository implementation. ProductServiceDbContext implements
IProductServiceDbContext
which contains ProductService specific DbSets. Moreover, there is no need for runtime DB context replacement hence there is no configuration related to it.
There is a SQL configuration for changing the migration table name to separate each service migration history table
Configure<AbpDbContextOptions>(options =>
{
options.Configure<ProductServiceDbContext>(c =>
{
c.UseSqlServer(b =>
{
b.MigrationsHistoryTable("__ProductService_Migrations");
});
});
});
SwaggerConfiguration
ProductService uses WebGateway_Swagger client for swagger authorization and it uses authorization_code flow with the default ProductService scope:
SwaggerConfigurationHelper.ConfigureWithOidc(
context: context,
authority: configuration["AuthServer:Authority"]!,
scopes: new[] { "ProductService" },
flows: new[] { "authorization_code" },
discoveryEndpoint: configuration["AuthServer:MetadataAddress"],
apiTitle: "Product Service API"
);
































































