Chat module
This module implements real time messaging between users for an application.
See the module description page for an overview of the module features.
To download the source-code of the Chat module, you can use ABP Suite or you can use the ABP CLI with the following command:
abp get-source Volo.Chat
How to Install
Chat module is not installed in the startup templates. So, it needs to be installed manually. There are two ways of installing a module into your application.
Installation
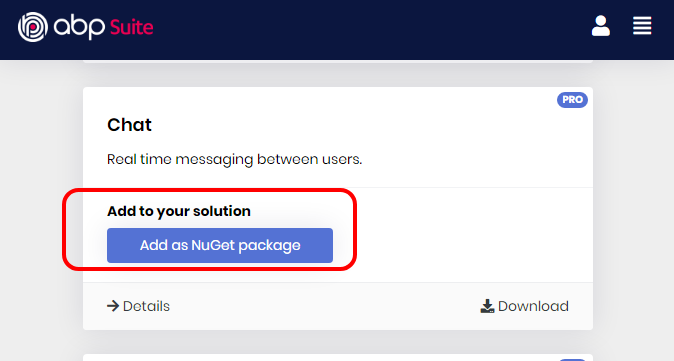
1. Using ABP Suite
ABP Suite allows adding a module to a solution using Add to your solution option in modules list.
2. Manual Installation
If you modified your solution structure, adding module using ABP Suite might not work for you. In such cases, chat module can be added to a solution manually.
In order to do that, add packages listed below to matching project on your solution. For example, Volo.Chat.Application package to your {ProjectName}.Application.csproj like below;
<PackageReference Include="Volo.Chat.Application" Version="x.x.x" />
After adding the package reference, open the module class of the project (eg: {ProjectName}ApplicationModule) and add the below code to the DependsOn attribute.
[DependsOn(
//...
typeof(ChatApplicationModule)
)]
The Volo.Chat.SignalR package must be added according to your project structure:
- Mvc
- Non-Tiered: {ProjectName}.Web project.
- Tiered: {ProjectName}.Web project.
- Blazor Server : {ProjectName}.Blazor.Server.
- Angular
- Unified Backend: {ProjectName}.HttpApi.Host project.
- Separated Auth Server: {ProjectName}.HttpApi.Host project.
If database provider of your project is EntityFrameworkCore, use modelBuilder.ConfigureChat() to configure database tables in your project's DbContext.
Configuration
SignalR Access Token Configuration for Angular Projects
See Microsoft SignalR Authentication and Authorization and Microsoft SignalR Security documentations.
In standard web APIs, bearer tokens are sent in an HTTP header. However, SignalR is unable to set these headers in browsers when using some transports. When using WebSockets and Server-Sent Events, the token is transmitted as a query string parameter. To support this on the server, additional configuration is required.
Here is a sample configuration for this:
app.Use(async (httpContext, next) =>
{
var accessToken = httpContext.Request.Query["access_token"];
var path = httpContext.Request.Path;
if (!string.IsNullOrEmpty(accessToken) &&
(path.StartsWithSegments("/signalr-hubs/chat")))
{
httpContext.Request.Headers["Authorization"] = "Bearer " + accessToken;
}
await next();
});
Adding Distributed Event Bus for distributed architecture projects
When Web & API tiers are separated, it is impossible to directly send a server-to-client message from the HTTP API. This is also true for a microservice architected application. Chat Module uses the distributed event bus to deliver the message from API application to the web application, then to the client.
If your project has such an architecture (example: MVC + tiered option), then you need a Distributed Event Bus. See related ABP documentation to understand Distributed Event Bus system in ABP framework. Also see RabbitMQ Integration documentation if your choice is to use RabbitMQ.
Packages
This module follows the module development best practices guide and consists of several NuGet and NPM packages. See the guide if you want to understand the packages and relations between them.
You can visit Chat module package list page to see list of packages related with this module.
User interface
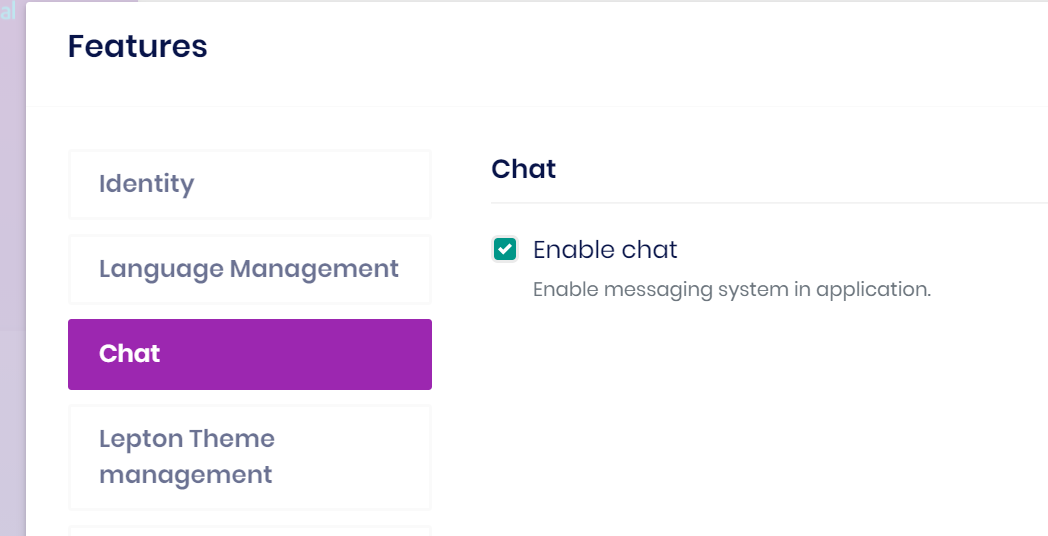
Manage chat feature
Chat module defines the chat feature, you need to enable the chat feature to use chat.
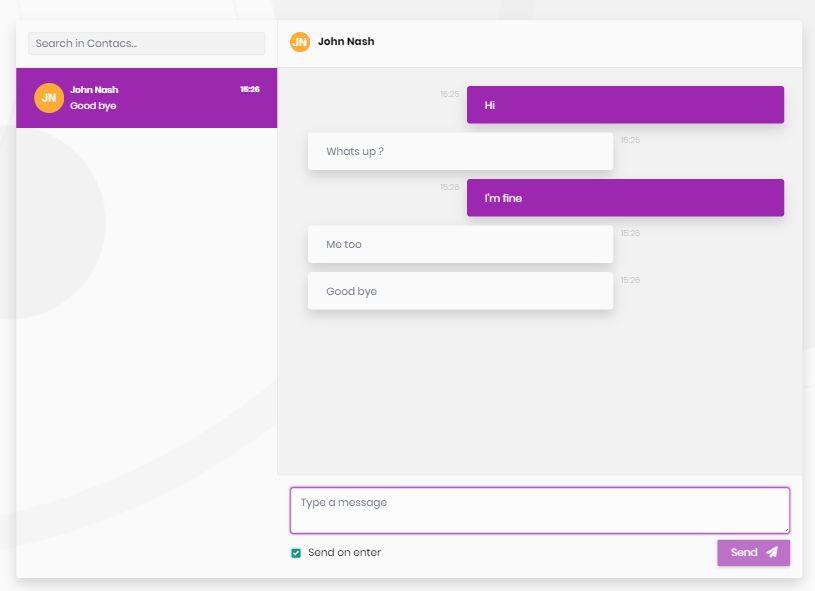
Chat page
This is the page that users send messages to each other.
Chat icon on navigation bar
An icon that shows unread message count of the user and leads to chat page when clicked is added to navigation menu.
![]()
Internals
Domain layer
Entities and aggregate roots
Message(aggregate root): Represents a chat message. ImplementsIMultiTenant.Text: Message content.IsAllRead: Message read information.ReadTime: Message read time information.
ChatUser(aggregate root): Represents a chat user. ImplementsIUserandIUpdateUserDatainterfaces.UserMessage: is created for each side (sender and receiver) of a message. ImplementsIMultiTenantandIAggregateRootinterfaces.ChatMessageId: Id of relatedMessage.UserId: Id of relatedChatUser.TargetUserId: Id of other relatedChatUser.Side: States that if it is a send message or received message.IsRead: Read information.ReadTime: Read time information.
Conversation: is created for each side of a conversation between users. ImplementsIMultiTenantandIAggregateRootinterfaces.UserId: Id of relatedChatUser.TargetUserId: Id of other relatedChatUser.LastMessageSide: States the side of the latest message (send or received).LastMessage: Content of the last message in the conversation.LastMessageDate: Date of the last message in the conversation.UnreadMessageCount: Count of unread messages in the conversation.
Repositories
This module follows the Repository Best Practices & Conventions guide.
Following custom repositories are defined for this module:
IConversationRepositoryIUserMessageRepositoryIChatUserRepositoryIMessageRepository
Domain Services
MessagingManager
Application layer
Application services
ConversationAppService(implementsIConversationAppService): Used to send messages, get conversation between users and mark a conversation as read.SettingsAppService(implementsISettingsAppService): Used to save chat settings.ContactAppService(implementsIContactAppService): Used to get list of contacts and total unread message count of a user.DistributedEventBusRealTimeChatMessageSender(implementsIRealTimeChatMessageSender): Used to publish chat messages to distributed event bus.SignalRRealTimeChatMessageSender(implementsIRealTimeChatMessageSender): Used to send messages to targetSignalRclient.
Database providers
Common
Table / collection prefix & schema
All tables/collections use the Chat prefix by default. Set static properties on the ChatDbProperties class if you need to change the table prefix or set a schema name (if supported by your database provider).
Connection string
This module uses Chat for the connection string name. If you don't define a connection string with this name, it fallbacks to the Default connection string.
See the connection strings documentation for details.
Entity Framework Core
Tables
- ChatUsers
- ChatMessages
- ChatUserMessages
- ChatConversations
MongoDB
Collections
- ChatUsers
- ChatMessages
- ChatUserMessages
- ChatConversations
Angular UI
Installation
In order to configure the application to use the ChatModule, you first need to import ChatConfigModule from @volo/abp.ng.chat/config to root module. ChatConfigModule has a static forRoot method which you should call for a proper configuration.
// app.module.ts
import { ChatConfigModule } from '@volo/abp.ng.chat/config';
@NgModule({
imports: [
// other imports
ChatConfigModule.forRoot(),
// other imports
],
// ...
})
export class AppModule {}
The ChatModule should be imported and lazy-loaded in your routing module. It has a static forLazy method for configuration. It is available for import from @volo/abp.ng.chat.
// app-routing.module.ts
const routes: Routes = [
// other route definitions
{
path: 'chat',
loadChildren: () =>
import('@volo/abp.ng.chat').then(m => m.ChatModule.forLazy(/* options here */)),
},
];
@NgModule(/* AppRoutingModule metadata */)
export class AppRoutingModule {}
Services / Models
Chat module services and models are generated via generate-proxy command of the ABP CLI. If you need the module's proxies, you can run the following command in the Angular project directory:
abp generate-proxy --module chat
Remote Endpoint URL
The Chat module remote endpoint URLs can be configured in the environment files.
export const environment = {
// other configurations
apis: {
default: {
url: 'default url here',
},
Chat: {
url: 'Chat remote url here',
signalRUrl: 'Chat signalR remote url here',
},
// other api configurations
},
};
The Chat module remote URL configurations shown above are optional.
If you don't set the
signalRUrl,Chat.urlwill be used as fallback. If you don't set theChatproperty, thedefault.urlwill be used as fallback.
Distributed Events
This module defines an event for messaging. It is published when a new message is sent from a user to another user, with an Event Transfer Object type of ChatMessageEto. See the standard distributed events for more information about distributed events.
































































