Web Application Development Tutorial - Part 5: Authorization
About This Tutorial
In this tutorial series, you will build an ABP based web application named Acme.BookStore. This application is used to manage a list of books and their authors. It is developed using the following technologies:
- Entity Framework Core as the database provider.
- Blazor WebAssembly as the UI Framework.
This tutorial is organized as the following parts;
- Part 1: Creating the project and book list page
- Part 2: The book list page
- Part 3: Creating, updating and deleting books
- Part 4: Integration tests
- Part 5: Authorization (this part)
- Part 6: Authors: Domain layer
- Part 7: Authors: Database Integration
- Part 8: Authors: Application Layer
- Part 9: Authors: User Interface
- Part 10: Book to Author Relation
Download the Source Code
This tutorial has multiple versions based on your UI and Database preferences. We've prepared a few combinations of the source code to be downloaded:
If you encounter the "filename too long" or "unzip" error on Windows, please see this guide.
Permissions
ABP Framework provides an authorization system based on the ASP.NET Core's authorization infrastructure. One major feature added on top of the standard authorization infrastructure is the permission system which allows to define permissions and enable/disable per role, user or client.
Permission Names
A permission must have a unique name (a string). The best way is to define it as a const, so we can reuse the permission name.
Open the BookStorePermissions class inside the Acme.BookStore.Application.Contracts project (in the Permissions folder) and change the content as shown below:
namespace Acme.BookStore.Permissions;
public static class BookStorePermissions
{
public const string GroupName = "BookStore";
public static class Dashboard
{
public const string DashboardGroup = GroupName + ".Dashboard";
public const string Host = DashboardGroup + ".Host";
public const string Tenant = GroupName + ".Tenant";
}
// Added items
public static class Books
{
public const string Default = GroupName + ".Books";
public const string Create = Default + ".Create";
public const string Edit = Default + ".Edit";
public const string Delete = Default + ".Delete";
}
}
This is a hierarchical way of defining permission names. For example, "create book" permission name was defined as BookStore.Books.Create. ABP doesn't force you to a structure, but we find this way useful.
Permission Definitions
You should define permissions before using them.
Open the BookStorePermissionDefinitionProvider class inside the Acme.BookStore.Application.Contracts project (in the Permissions folder) and change the content as shown below:
using Acme.BookStore.Localization;
using Volo.Abp.Authorization.Permissions;
using Volo.Abp.Localization;
using Volo.Abp.MultiTenancy;
namespace Acme.BookStore.Permissions;
public class BookStorePermissionDefinitionProvider : PermissionDefinitionProvider
{
public override void Define(IPermissionDefinitionContext context)
{
var bookStoreGroup = context.AddGroup(BookStorePermissions.GroupName, L("Permission:BookStore"));
bookStoreGroup.AddPermission(BookStorePermissions.Dashboard.Host, L("Permission:Dashboard"), MultiTenancySides.Host);
bookStoreGroup.AddPermission(BookStorePermissions.Dashboard.Tenant, L("Permission:Dashboard"), MultiTenancySides.Tenant);
var booksPermission = bookStoreGroup.AddPermission(BookStorePermissions.Books.Default, L("Permission:Books"));
booksPermission.AddChild(BookStorePermissions.Books.Create, L("Permission:Books.Create"));
booksPermission.AddChild(BookStorePermissions.Books.Edit, L("Permission:Books.Edit"));
booksPermission.AddChild(BookStorePermissions.Books.Delete, L("Permission:Books.Delete"));
}
private static LocalizableString L(string name)
{
return LocalizableString.Create<BookStoreResource>(name);
}
}
This class defines a permission group (to group permissions on the UI, will be seen below) and 4 permissions inside this group. Also, Create, Edit and Delete are children of the BookStorePermissions.Books.Default permission. A child permission can be selected only if the parent was selected.
Finally, edit the localization file (en.json under the Localization/BookStore folder of the Acme.BookStore.Domain.Shared project) to define the localization keys used above:
"Permission:BookStore": "Book Store",
"Permission:Books": "Book Management",
"Permission:Books.Create": "Creating new books",
"Permission:Books.Edit": "Editing the books",
"Permission:Books.Delete": "Deleting the books"
Localization key names are arbitrary and there is no forcing rule. But we prefer the convention used above.
Permission Management UI
Once you define the permissions, you can see them on the permission management modal.
Go to the Administration -> Identity Management -> Roles page, select Permissions action for the admin role to open the permission management modal:
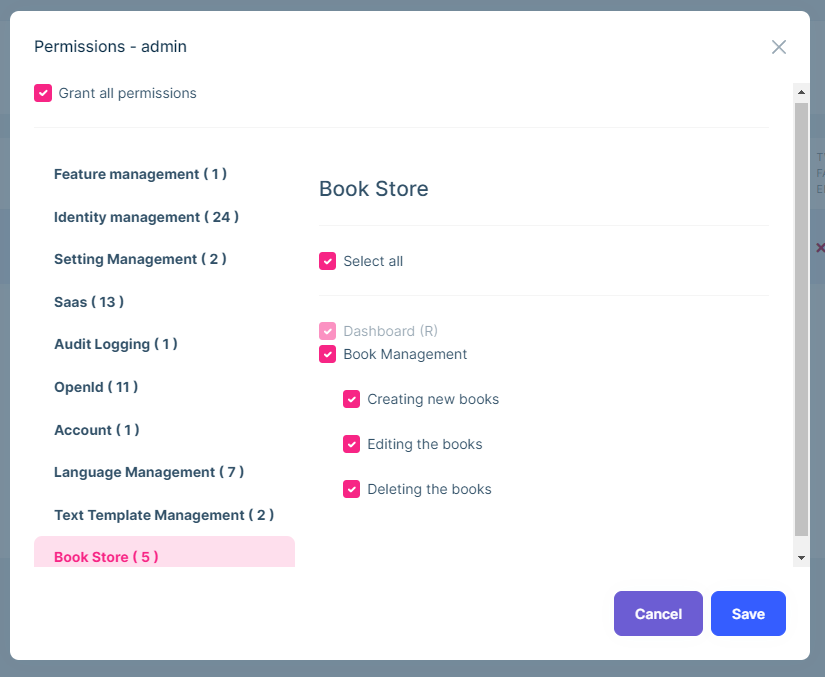
Grant the permissions you want and save the modal.
Tip: New permissions are automatically granted to the admin role if you run the
Acme.BookStore.DbMigratorapplication.
Authorization
Now, you can use the permissions to authorize the book management.
Application Layer & HTTP API
Open the BookAppService class and add set the policy names as the permission names defined above:
using Acme.BookStore.Permissions; //-> add this namespace
using System;
using Volo.Abp.Application.Dtos;
using Volo.Abp.Application.Services;
using Volo.Abp.Domain.Repositories;
namespace Acme.BookStore.Books;
public class BookAppService :
CrudAppService<
Book, //The Book entity
BookDto, //Used to show books
Guid, //Primary key of the book entity
PagedAndSortedResultRequestDto, //Used for paging/sorting
CreateUpdateBookDto>, //Used to create/update a book
IBookAppService //implement the IBookAppService
{
public BookAppService(IRepository<Book, Guid> repository)
: base(repository)
{
GetPolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Default;
GetListPolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Default;
CreatePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Create;
UpdatePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Edit;
DeletePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Delete;
}
}
Added code to the constructor. Base CrudAppService automatically uses these permissions on the CRUD operations. This makes the application service secure, but also makes the HTTP API secure since this service is automatically used as an HTTP API as explained before (see auto API controllers).
You will see the declarative authorization, using the
[Authorize(...)]attribute, later while developing the author management functionality.
Authorize the Razor Component
Open the /Pages/Books.razor file in the Acme.BookStore.Blazor project and add an Authorize attribute just after the @page directive and the following namespace imports (@using lines), as shown below:
@page "/books"
@attribute [Authorize(BookStorePermissions.Books.Default)]
@using Acme.BookStore.Permissions
@using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Authorization
...
Adding this attribute prevents to enter this page if the current hasn't logged in or hasn't granted for the given permission. In case of attempt, the user is redirected to the login page.
Show/Hide the Actions
The book management page has a New Book button and Edit and Delete actions for each book. We should hide these buttons/actions if the current user has not granted for the related permissions.
The base AbpCrudPageBase class already has the necessary functionality for these kind of operations.
Set the Policy (Permission) Names
Add the following constructor to the Books.razor.cs file:
public Books()
{
CreatePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Create;
UpdatePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Edit;
DeletePolicyName = BookStorePermissions.Books.Delete;
}
The base AbpCrudPageBase class automatically checks these permissions on the related operations. It also defines the given properties for us if we need to check them manually:
HasCreatePermission: True, if the current user has permission to create the entity.HasUpdatePermission: True, if the current user has permission to edit/update the entity.HasDeletePermission: True, if the current user has permission to delete the entity.
Hide the New Book Button
Add the requiredPolicyName parameter to button configuration as shown below:
Toolbar.AddButton(L["NewBook"],
OpenCreateModalAsync,
IconName.Add,
requiredPolicyName: CreatePolicyName);
Hide the Edit/Delete Actions
EntityAction component defines Visible attribute (parameter) to conditionally show the action.
Update the EntityActions section as shown below:
<EntityActions TItem="BookDto" EntityActionsColumn="@EntityActionsColumn">
<EntityAction TItem="BookDto"
Text="@L["Edit"]"
Visible=HasUpdatePermission
Clicked="() => OpenEditModalAsync(context)" />
<EntityAction TItem="BookDto"
Text="@L["Delete"]"
Visible=HasDeletePermission
Clicked="() => DeleteEntityAsync(context)"
ConfirmationMessage="()=>GetDeleteConfirmationMessage(context)" />
</EntityActions>
About the Permission Caching
You can run and test the permissions. Remove a book related permission from the admin role to see the related button/action disappears from the UI.
ABP Framework caches the permissions of the current user in the client side. So, when you change a permission for yourself, you need to manually refresh the page to take the effect. If you don't refresh and try to use the prohibited action you get an HTTP 403 (forbidden) response from the server.
Changing a permission for a role or user immediately available on the server side. So, this cache system doesn't cause any security problem.
Menu Item
Even we have secured all the layers of the book management page, it is still visible on the main menu of the application. We should hide the menu item if the current user has no permission.
Open the BookStoreMenuContributor class in the Acme.BookStore.Blazor project, find the code block below:
var bookStoreMenu = new ApplicationMenuItem(
"BooksStore",
l["Menu:BookStore"],
icon: "fa fa-book"
);
bookStoreMenu.AddItem(
new ApplicationMenuItem(
"BooksStore.Books",
l["Menu:Books"],
url: "/books"
)
)
context.Menu.AddItem(bookStoreMenu);
And use the RequirePermissions method as shown below:
var bookStoreMenu = new ApplicationMenuItem(
"BooksStore",
l["Menu:BookStore"],
icon: "fa fa-book"
);
bookStoreMenu.AddItem(
new ApplicationMenuItem(
"BooksStore.Books",
l["Menu:Books"],
url: "/books"
).RequirePermissions(BookStorePermissions.Books.Default)
)
context.Menu.AddItem(bookStoreMenu);
The final ConfigureMainMenuAsync method should be the following:
private Task ConfigureMainMenuAsync(MenuConfigurationContext context)
{
var l = context.GetLocalizer<BookStoreResource>();
context.Menu.AddItem(new ApplicationMenuItem(
BookStoreMenus.Home,
l["Menu:Home"],
"/",
icon: "fas fa-home",
order: 1
));
var bookStoreMenu = new ApplicationMenuItem(
"BooksStore",
l["Menu:BookStore"],
icon: "fa fa-book"
);
bookStoreMenu.AddItem(
new ApplicationMenuItem(
"BooksStore.Books",
l["Menu:Books"],
url: "/books"
).RequirePermissions(BookStorePermissions.Books.Default)
)
context.Menu.AddItem(bookStoreMenu);
//HostDashboard
context.Menu.AddItem(
new ApplicationMenuItem(
BookStoreMenus.HostDashboard,
l["Menu:Dashboard"],
"/HostDashboard",
icon: "fa fa-chart-line",
order: 2
).RequirePermissions(BookStorePermissions.Dashboard.Host)
);
//TenantDashboard
context.Menu.AddItem(
new ApplicationMenuItem(
BookStoreMenus.TenantDashboard,
l["Menu:Dashboard"],
"/Dashboard",
icon: "fa fa-chart-line",
order: 2
).RequirePermissions(BookStorePermissions.Dashboard.Tenant)
);
context.Menu.SetSubItemOrder(SaasHostMenus.GroupName, 3);
//Administration
var administration = context.Menu.GetAdministration();
administration.Order = 3;
//Administration->Identity
administration.SetSubItemOrder(IdentityProMenus.GroupName, 1);
//Administration->OpenId
administration.SetSubItemOrder(OpenIddictProMenus.GroupName, 2);
//Administration->Language Management
administration.SetSubItemOrder(LanguageManagementMenus.GroupName, 3);
//Administration->Text Template Management
administration.SetSubItemOrder(TextTemplateManagementMenus.GroupName, 4);
//Administration->Audit Logs
administration.SetSubItemOrder(AbpAuditLoggingMenus.GroupName, 5);
//Administration->Settings
administration.SetSubItemOrder(SettingManagementMenus.GroupName, 6);
return Task.CompletedTask;
}






























































