ASP.NET Core MVC / Razor Pages: Forms & Validation
ABP Framework provides infrastructure and conventions to make easier to create forms, localize display names for the form elements and handle server & client side validation;
- abp-dynamic-form tag helper automates creating a complete form from a C# model class: Creates the input elements, handles localization and client side validation.
- ABP Form tag helpers (
abp-input,abp-select,abp-radio...) render a single form element with handling localization and client side validation. - ABP Framework automatically localizes the display name of a form element without needing to add a
[DisplayName]attribute. - Validation errors are automatically localized based on the user culture.
This document is for the client side validation and it doesn't cover the server side validation. Check the validation document for server side validation infrastructure.
The Classic Way
In a typical Bootstrap based ASP.NET Core MVC / Razor Pages UI, you need to write such a boilerplate code to create a simple form element:
<div class="form-group">
<label asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="control-label"></label>
<input asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="form-control" />
<span asp-validation-for="Movie.ReleaseDate" class="text-danger"></span>
</div>
You can continue to use this approach if you need or prefer it. However, ABP Form tag helpers can produce the same output with a minimal code.
ABP Dynamic Forms
abp-dynamic-form tag helper completely automates the form creation. Take this model class as an example:
using System;
using System.ComponentModel.DataAnnotations;
using Volo.Abp.AspNetCore.Mvc.UI.Bootstrap.TagHelpers.Form;
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages
{
public class MovieViewModel
{
[Required]
[StringLength(256)]
public string Name { get; set; }
[Required]
[DataType(DataType.Date)]
public DateTime ReleaseDate { get; set; }
[Required]
[TextArea]
[StringLength(1000)]
public string Description { get; set; }
public Genre Genre { get; set; }
public float? Price { get; set; }
public bool PreOrder { get; set; }
}
}
It uses the data annotation attributes to define validation rules and UI styles for the properties. Genre, is an enum in this example:
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages
{
public enum Genre
{
Classic,
Action,
Fiction,
Fantasy,
Animation
}
}
In order to create the form in a razor page, create a property in your PageModel class:
using System.Threading.Tasks;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc;
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Mvc.RazorPages;
namespace MyProject.Web.Pages
{
public class CreateMovieModel : PageModel
{
[BindProperty]
public MovieViewModel Movie { get; set; }
public void OnGet()
{
Movie = new MovieViewModel();
}
public async Task OnPostAsync()
{
if (ModelState.IsValid)
{
//TODO: Save the Movie
}
}
}
}
Then you can render the form in the .cshtml file:
@page
@model MyProject.Web.Pages.CreateMovieModel
<h2>Create a new Movie</h2>
<abp-dynamic-form abp-model="Movie" submit-button="true" />
The result is shown below:
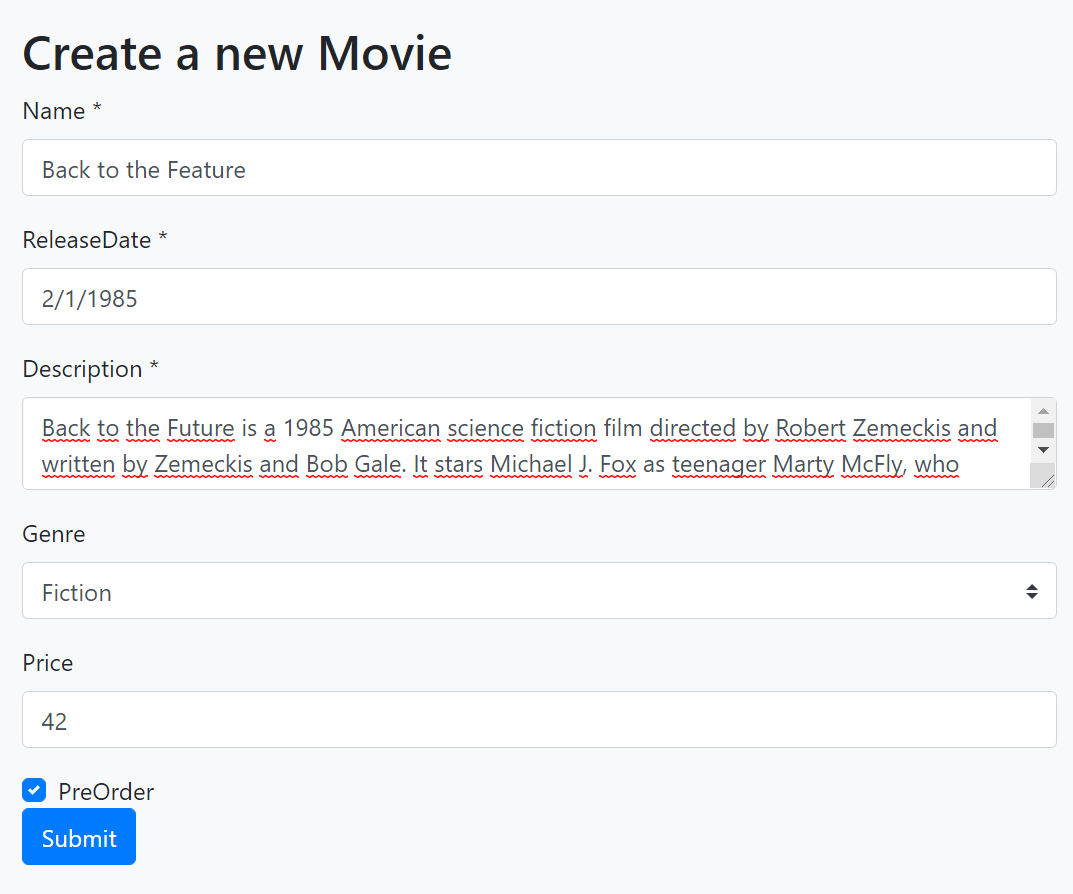
See the Localization & Validation section below to localize the field display names and see how the validation works.
See its own document for all options of the
abp-dynamic-formtag helper.
ABP Form Tag Helpers
abp-dynamic-form covers most of the scenarios and allows you to control and customize the form using the attributes.
However, if you want to render the form body yourself (for example, you may want to fully control the form layout), you can directly use the ABP Form Tag Helpers. The same auto-generated form above can be created using the ABP Form Tag Helpers as shown below:
@page
@model MyProject.Web.Pages.CreateMovieModel
<h2>Create a new Movie</h2>
<form method="post">
<abp-input asp-for="Movie.Name"/>
<abp-input asp-for="Movie.ReleaseDate"/>
<abp-input asp-for="Movie.Description"/>
<abp-select asp-for="Movie.Genre"/>
<abp-input asp-for="Movie.Price"/>
<abp-input asp-for="Movie.PreOrder"/>
<abp-button button-type="Primary" type="submit">Save</abp-button>
</form>
See the ABP Form Tag Helpers document for details of these tag helpers and their options.
Validation & Localization
Both of the Dynamic Form and the Form Tag Helpers automatically validate the input based on the data annotation attributes and shows validation error messages on the user interface. Error messages are automatically localized based on the current culture.
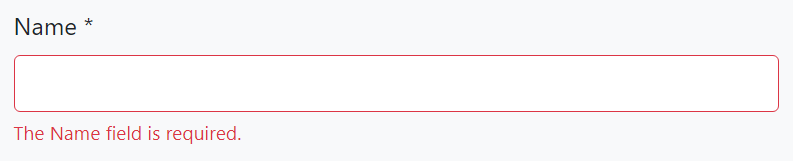
Example: User leaves empty a required string property
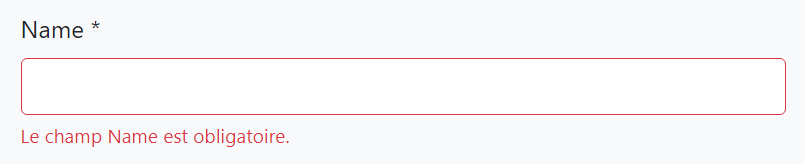
The error message below is shown if the language is French:
Validation errors are already translated a lot of languages. You can contribute to the translation for your own language or override the texts for your own application by following the localization documentation.
Display Name Localization
ABP Framework uses the property name as the field name on the user interface. You typically want to localize this name based on the current culture.
ABP Framework can conventionally localize the fields on the UI when you add the localization keys to the localization JSON files.
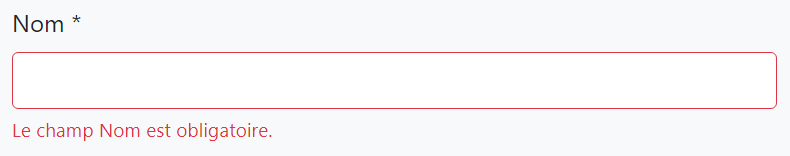
Example: French localization for the Name property (add into the fr.json in the application):
"Name": "Nom"
Then the UI will use the given name for French language:
Using the DisplayName: Prefix
Directly using the property name as the localization key may be a problem if you need to use the property name for other purpose, which a different translation value. In this case, use the DisplayName: prefix for the localization key:
"DisplayName:Name": "Nom"
ABP prefers to use the DisplayName:Name key over the Name key if it does exists.
Using a Custom Localization Key
If you need, you can use the [DisplayName] attribute to specify the localization key for a specific property:
[DisplayName("MyNameKey")]
public string Name { get; set; }
In this case, you can add an entry to the localization file using the key MyNameKey.
If you use the
[DisplayName]but not add a corresponding entity to the localization file, then ABP Framework shows the given key as the field name,MyNameKeyfor this case. So, it provides a way to specify a hard coded display name even if you don't need to use the localization system.
Enum Localization
Enum members are also automatically localized wherever possible. For example, when we added <abp-select asp-for="Movie.Genre"/> to the form (like we did in the ABP Form Tag Helpers section), ABP can automatically fill the localized names of Enum members. To enabled it, you should define the localized values in your localization JSON file. Example entries for the Genre Enum defined in the ABP Form Tag Helpers section:
"Enum:Genre.0": "Classic movie",
"Enum:Genre.1": "Action movie",
"Enum:Genre.2": "Fiction",
"Enum:Genre.3": "Fantasy",
"Enum:Genre.4": "Animation/Cartoon"
You can use one of the following syntaxes for the localization keys:
Enum:<enum-type-name>.<enum-value><enum-type-name>.<enum-value>
Remember that if you don't specify values for your Enum, the values will be ordered, starting from
0.
MVC tag helpers also support using Enum member names instead of values (so, you can define
"Enum:Genre.Action"instead of"Enum:Genre.1", for example), but it is not suggested. Because, when you serialize Enum properties to JSON and send to clients, default serializer uses Enum values instead of Enum names. So, the Enum name won't be available to clients, and it will be a problem if you want to use the same localization values on the client side.






























































