Web Application Development Tutorial - Part 2: The Book List Page
Localization
Before starting the UI development, we first want to prepare the localization texts (you normally do this when needed while developing your application).
Localization texts are located under the Localization/BookStore folder of the Acme.BookStore.Domain.Shared project:
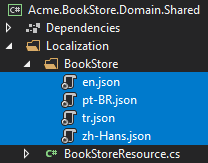
Open the en.json (the English translations) file and change the content as shown below:
{
"Culture": "en",
"Texts": {
"Menu:Home": "Home",
"Welcome": "Welcome",
"LongWelcomeMessage": "Welcome to the application. This is a startup project based on the ABP. For more information, visit abp.io.",
"Menu:BookStore": "Book Store",
"Menu:Books": "Books",
"Actions": "Actions",
"Close": "Close",
"Delete": "Delete",
"Edit": "Edit",
"PublishDate": "Publish date",
"NewBook": "New book",
"Name": "Name",
"Type": "Type",
"Price": "Price",
"CreationTime": "Creation time",
"AreYouSure": "Are you sure?",
"AreYouSureToDelete": "Are you sure you want to delete this item?",
"Enum:BookType.0": "Undefined",
"Enum:BookType.1": "Adventure",
"Enum:BookType.2": "Biography",
"Enum:BookType.3": "Dystopia",
"Enum:BookType.4": "Fantastic",
"Enum:BookType.5": "Horror",
"Enum:BookType.6": "Science",
"Enum:BookType.7": "Science fiction",
"Enum:BookType.8": "Poetry"
}
}
- Localization key names are arbitrary. You can set any name. We prefer some conventions for specific text types;
- Add
Menu:prefix for menu items. - Use
Enum:<enum-type>.<enum-value>or<enum-type>.<enum-value>naming convention to localize the enum members. When you do it like that, ABP can automatically localize the enums in some proper cases.
- Add
If a text is not defined in the localization file, it falls back to the localization key (as ASP.NET Core's standard behavior).
ABP's localization system is built on the ASP.NET Core's standard localization system and extends it in many ways. Check the localization document for details.
Install NPM packages
Notice: This tutorial is based on the ABP v3.1.0+ If your project version is older, then please upgrade your solution. Check the migration guide if you are upgrading an existing project with v2.x.
If you haven't done it before, open a new command line interface (terminal window) and go to your angular folder and then run the yarn command to install the NPM packages:
yarn
Create a Books Page
It's time to create something visible and usable! There are some tools that we will use when developing the Angular frontend application:
- Ng Bootstrap will be used as the UI component library.
- Ngx-Datatable will be used as the datatable library.
Run the following command line to create a new module, named BookModule in the root folder of the angular application:
yarn ng generate module book --module app --routing --route books
This command should produce the following output:
> yarn ng generate module book --module app --routing --route books
yarn run v1.19.1
$ ng generate module book --module app --routing --route books
CREATE src/app/book/book-routing.module.ts (336 bytes)
CREATE src/app/book/book.module.ts (335 bytes)
CREATE src/app/book/book.component.html (19 bytes)
CREATE src/app/book/book.component.spec.ts (614 bytes)
CREATE src/app/book/book.component.ts (268 bytes)
CREATE src/app/book/book.component.scss (0 bytes)
UPDATE src/app/app-routing.module.ts (1289 bytes)
Done in 3.88s.
BookModule
Open the /src/app/book/book.module.ts and replace the content as shown below:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { SharedModule } from '../shared/shared.module';
import { BookRoutingModule } from './book-routing.module';
import { BookComponent } from './book.component';
@NgModule({
declarations: [BookComponent],
imports: [
BookRoutingModule,
SharedModule
]
})
export class BookModule { }
- Added the
SharedModule.SharedModuleexports some common modules needed to create user interfaces. SharedModulealready exports theCommonModule, so we've removed theCommonModule.
Routing
The generated code places the new route definition to the src/app/app-routing.module.ts file as shown below:
const routes: Routes = [
// other route definitions...
{ path: 'books', loadChildren: () => import('./book/book.module').then(m => m.BookModule) },
];
Now, open the src/app/route.provider.ts file and replace the configureRoutes function declaration as shown below:
function configureRoutes(routes: RoutesService) {
return () => {
routes.add([
{
path: '/',
name: '::Menu:Home',
iconClass: 'fas fa-home',
order: 1,
layout: eLayoutType.application,
},
{
path: '/book-store',
name: '::Menu:BookStore',
iconClass: 'fas fa-book',
order: 2,
layout: eLayoutType.application,
},
{
path: '/books',
name: '::Menu:Books',
parentName: '::Menu:BookStore',
layout: eLayoutType.application,
},
]);
};
}
RoutesService is a service provided by the ABP to configure the main menu and the routes.
pathis the URL of the route.nameis the localized menu item name (check the localization document for details).iconClassis the icon of the menu item (you can use Font Awesome icons by default).orderis the order of the menu item.layoutis the layout of the BooksModule's routes (there are three types of pre-defined layouts:eLayoutType.application,eLayoutType.accountoreLayoutType.empty).
For more information, check the RoutesService document.
Service Proxy Generation
ABP CLI provides a generate-proxy command that generates client proxies for your HTTP APIs to make your HTTP APIs easy to consume by the client side. Before running the generate-proxy command, your host must be up and running.
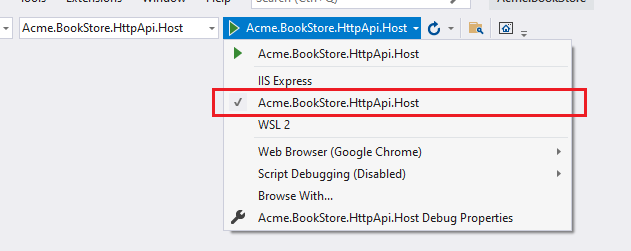
Warning: There is a problem with IIS Express; it doesn't allow connecting to the application from another process. If you are using Visual Studio, select the
Acme.BookStore.HttpApi.Hostinstead of IIS Express in the run button drop-down list, as shown in the figure below:
Once the host application is running, execute the following command in the angular folder:
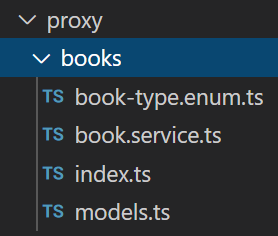
abp generate-proxy -t ng
This command will create the following files under the /src/app/proxy/books folder:
BookComponent
Open the /src/app/book/book.component.ts file and replace the content as below:
import { ListService, PagedResultDto } from '@abp/ng.core';
import { Component, OnInit } from '@angular/core';
import { BookService, BookDto } from '@proxy/books';
@Component({
selector: 'app-book',
templateUrl: './book.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./book.component.scss'],
providers: [ListService],
})
export class BookComponent implements OnInit {
book = { items: [], totalCount: 0 } as PagedResultDto<BookDto>;
constructor(public readonly list: ListService, private bookService: BookService) {}
ngOnInit() {
const bookStreamCreator = (query) => this.bookService.getList(query);
this.list.hookToQuery(bookStreamCreator).subscribe((response) => {
this.book = response;
});
}
}
- We imported and injected the generated
BookService. - We are using the ListService, a utility service from the ABP which provides easy pagination, sorting and searching.
Open the /src/app/book/book.component.html and replace the content as shown below:
<div class="card">
<div class="card-header">
<div class="row">
<div class="col col-md-6">
<h5 class="card-title">
{{ '::Menu:Books' | abpLocalization }}
</h5>
</div>
<div class="text-end col col-md-6"></div>
</div>
</div>
<div class="card-body">
<ngx-datatable [rows]="book.items" [count]="book.totalCount" [list]="list" default>
<ngx-datatable-column [name]="'::Name' | abpLocalization" prop="name"></ngx-datatable-column>
<ngx-datatable-column [name]="'::Type' | abpLocalization" prop="type">
<ng-template let-row="row" ngx-datatable-cell-template>
{{ '::Enum:BookType.' + row.type | abpLocalization }}
</ng-template>
</ngx-datatable-column>
<ngx-datatable-column [name]="'::PublishDate' | abpLocalization" prop="publishDate">
<ng-template let-row="row" ngx-datatable-cell-template>
{{ row.publishDate | date }}
</ng-template>
</ngx-datatable-column>
<ngx-datatable-column [name]="'::Price' | abpLocalization" prop="price">
<ng-template let-row="row" ngx-datatable-cell-template>
{{ row.price | currency }}
</ng-template>
</ngx-datatable-column>
</ngx-datatable>
</div>
</div>
Now you can see the final result on your browser:































































