Microservice Solution: Adding New API Gateways
You must have an ABP Business or a higher license to be able to create a microservice solution.
API gateways are the entry points of your microservice system. They are responsible for routing the incoming requests to the correct microservices. In a microservice system, you can have multiple API gateways to serve different purposes. For example, you can have a public API gateway for your customers and a private API gateway for your internal services. In the solution template, there is a folder named gateways that includes the API gateway projects. You can add new API gateways to this folder.
Additionally, there is a folder named _templates in the root directory. This folder contains templates you can use to create new microservices, API gateways, and applications. These templates can be customized according to your needs.
Adding a New API Gateway
To add a new gateway application to the solution, you can use the gateway template. This template creates a new ASP.NET Core application with the necessary configurations and dependencies. Follow the steps below to add a new web application:
In ABP Studio Solution Explorer, right-click on the gateways folder and select Add -> New Module -> Gateway.
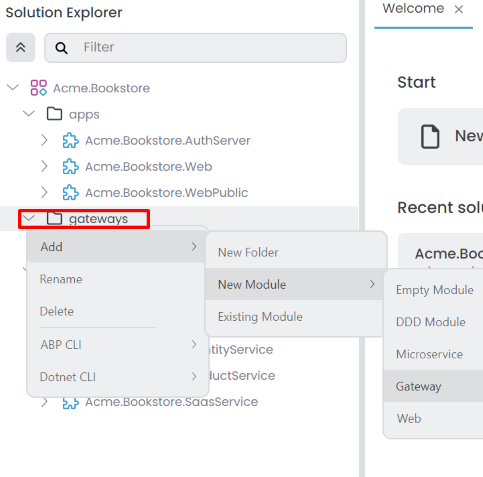
It opens the Create New Module dialog. Enter the name of the new gateway application, specify the output directory if needed, and click the Create button. There is a naming convention: the Module name should include the solution name as a prefix, and the use of the dot (.) character in the Module name is not allowed.
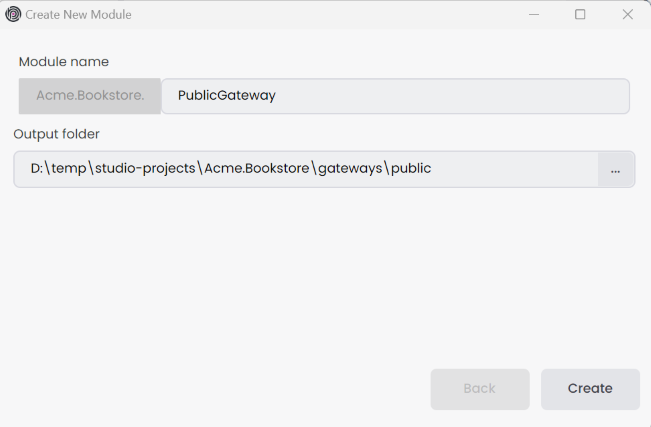
The new gateway is created and added to the solution. You can see the new application in the gateways folder.

Configuring the appsettings.json
The new gateway application is use the YARP as a reverse proxy. You can configure the appsettings.json file to define the routes and endpoints. The ReverseProxy section in the appsettings.json file includes the configuration for the reverse proxy. You can add new routes and endpoints to this section.
{
"ReverseProxy": {
"Routes": {
"AbpApi": {
"ClusterId": "Administration",
"Match": {
"Path": "/api/abp/{**catch-all}"
}
},
"AdministrationSwagger": {
"ClusterId": "Administration",
"Match": {
"Path": "/swagger-json/Administration/swagger/v1/swagger.json"
},
"Transforms": [
{ "PathRemovePrefix": "/swagger-json/Administration" }
]
},
"ProductService": {
"ClusterId": "ProductService",
"Match": {
"Path": "/api/productservice/{**catch-all}"
}
},
"ProductServiceSwagger": {
"ClusterId": "ProductService",
"Match": {
"Path": "/swagger-json/ProductService/swagger/v1/swagger.json"
},
"Transforms": [
{ "PathRemovePrefix": "/swagger-json/ProductService" }
]
}
},
"Clusters": {
"Administration": {
"Destinations": {
"Administration": {
"Address": "http://localhost:44393/"
}
}
},
"ProductService": {
"Destinations": {
"ProductService": {
"Address": "http://localhost:44350/"
}
}
}
}
}
}
Configuring the OpenId Options
We should configure the OpenId options by modifying the OpenIddictDataSeeder in the Identity service. Below is an example of the OpenIddictDataSeeder options for the PublicGateway application.
Add the created gateway URL to the redirectUris parameter in the CreateSwaggerClientAsync method in the OpenIddictDataSeeder class.
private async Task CreateSwaggerClientAsync(string clientId, string[] scopes)
{
var webGatewaySwaggerRootUrl = _configuration["OpenIddict:Applications:WebGateway:RootUrl"]!.TrimEnd('/');
//PublicGateway Url
var publicGatewaySwaggerRootUrl = _configuration["OpenIddict:Applications:PublicGateway:RootUrl"]!.TrimEnd('/');
...
await CreateOrUpdateApplicationAsync(
name: clientId,
type: OpenIddictConstants.ClientTypes.Public,
consentType: OpenIddictConstants.ConsentTypes.Implicit,
displayName: "Swagger Test Client",
secret: null,
grantTypes: new List<string>
{
OpenIddictConstants.GrantTypes.AuthorizationCode,
},
scopes: commonScopes.Union(scopes).ToList(),
redirectUris: new List<string> {
$"{webGatewaySwaggerRootUrl}/swagger/oauth2-redirect.html",
$"{publicGatewaySwaggerRootUrl}/swagger/oauth2-redirect.html", // PublicGateway redirect uri
...
},
clientUri: webGatewaySwaggerRootUrl,
logoUri: "/images/clients/swagger.svg"
);
}
Add the new gateway URL to the appsettings.json file in the Identity service.
{
"OpenIddict": {
"Applications": {
...
"PublicGateway": {
"RootUrl": "http://localhost:44382"
}
}
}
}
Configuring the AuthServer
We should configure the AuthServer for CORS and RedirectAllowedUrls.
"App": {
"SelfUrl": "http://localhost:***",
"CorsOrigins": "...... ,http://localhost:44382",
"EnablePII": false,
"RedirectAllowedUrls": "...... ,http://localhost:44382"
}
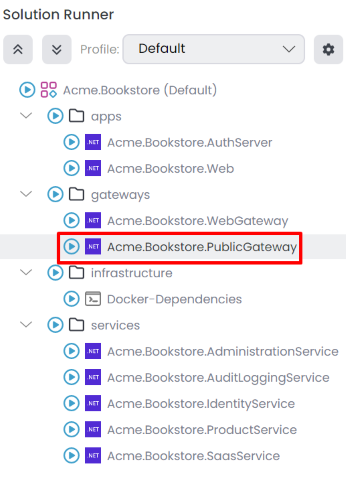
Add the New Gateway to the Solution Runner
We should add the new gateway to the solution runner profile for running applications in the ABP Studio. You can follow the steps explained in the Solution Runner document to add the new gateway to the solution runner profile. Afterwards, you can start the new gateway by selecting it in the solution runner.
Creating Helm Chart for the New Gateway
If you want to deploy the new gateway to Kubernetes, you should create a Helm chart for the new application.
First, add the new gateway to the build-all-images.ps1 script in the etc/helm folder. You can copy the configurations from the existing applications and modify them according to the new application. Below is an example of the build-all-images.ps1 script for the PublicGateway application.
./build-image.ps1 -ProjectPath "../../gateways/public/Acme.Bookstore.PublicGateway/Acme.Bookstore.PublicGateway.csproj" -ImageName bookstore/publicgateway
Since we want to expose our gateway outside the cluster, we should add the host URL to the values.projectname-local.yaml file in the etc/helm/projectname folder. Below is an example of the values.bookstore-local.yaml file for the PublicGateway application.
global:
...
hosts:
...
publicgateway: "[RELEASE_NAME]-publicgateway"
For development purposes, we should also create TLS certificates for the new gateway. You can edit the create-tls-certificate.ps1 script in the etc/helm folder to generate TLS certificates for the new gateway. Below is an example of the create-tls-certificate.ps1 script for the PublicGateway application.
mkcert --cert-file bookstore-local.pem --key-file bookstore-local-key.pem "bookstore-local" ... "bookstore-local-publicgateway"
kubectl create namespace bookstore-local
kubectl create secret tls -n bookstore-local bookstore-local-tls --cert=./bookstore-local.pem --key=./bookstore-local-key.pem
Lastly, we should define the new application in the _helpers.tpl file in the etc/helm/projectname/templates folder. You can copy the configurations from the existing applications and modify them according to the new application. Below is an example of the _helpers.tpl file for the PublicGateway application.
{{- define "bookstore.hosts.publicgateway" -}}
{{- print "https://" (.Values.global.hosts.publicgateway | replace "[RELEASE_NAME]" .Release.Name) -}}
{{- end -}}
Afterwards, we need to create a new Helm chart for the new gateway. You can copy the configurations from the existing applications and modify them according to the new gateway. Below is an example of the publicgateway Helm chart for the PublicGateway application.
# values.yaml
image:
repository: "bookstore/publicgateway"
tag: "latest"
pullPolicy: "IfNotPresent"
swagger:
isEnabled: "true"
# Chart.yaml
apiVersion: v2
name: publicgateway
appVersion: "1.0"
description: Bookstore Public API Gateway
version: 1.0.0
type: application
# publicapigateway.yaml
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
spec:
containers:
- image: "{{ .Values.image.repository }}:{{ .Values.image.tag }}"
imagePullPolicy: "{{ .Values.image.pullPolicy }}"
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
ports:
- name: "http"
containerPort: 80
env:
- name: "DOTNET_ENVIRONMENT"
value: "{{ .Values.global.dotnetEnvironment }}"
- name: "ElasticSearch__IsLoggingEnabled"
value: "{{ .Values.global.elasticSearch.isLoggingEnabled }}"
- name: "ElasticSearch__Url"
value: "http://{{ .Release.Name }}-elasticsearch:{{ .Values.global.elasticSearch.port }}"
- name: "Swagger__IsEnabled"
value: "{{ .Values.swagger.isEnabled }}"
- name: "AbpStudioClient__StudioUrl"
value: "{{ .Values.global.abpStudioClient.studioUrl }}"
- name: "AbpStudioClient__IsLinkEnabled"
value: "{{ .Values.global.abpStudioClient.isLinkEnabled }}"
- name: "ReverseProxy__Clusters__Administration__Destinations__Administration__Address"
value: "http://{{ .Release.Name }}-administration"
- name: "ReverseProxy__Clusters__ProductService__Destinations__ProductService__Address"
value: "http://{{ .Release.Name }}-productservice"
# publicapigateway-service.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
labels:
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
spec:
ports:
- name: "80"
port: 80
selector:
app: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
# publicapigateway-ingress.yaml
apiVersion: networking.k8s.io/v1
kind: Ingress
metadata:
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/rewrite-target: "/"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/force-ssl-redirect: "true"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffer-size: "32k"
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/proxy-buffers-number: "8"
cert-manager.io/cluster-issuer: "letsencrypt"
spec:
ingressClassName: "nginx"
tls:
- hosts:
- "{{ (include "bookstore.hosts.publicgateway" .) | trimPrefix "https://" }}"
secretName: "{{ .Values.global.tlsSecret }}"
rules:
- host: "{{ (include "bookstore.hosts.publicgateway" .) | trimPrefix "https://" }}"
http:
paths:
- path: /
pathType: "Prefix"
backend:
service:
name: "{{ .Release.Name }}-{{ .Chart.Name }}"
port:
number: 80
After creating the Helm chart, you can Refresh Sub Charts in the ABP Studio.
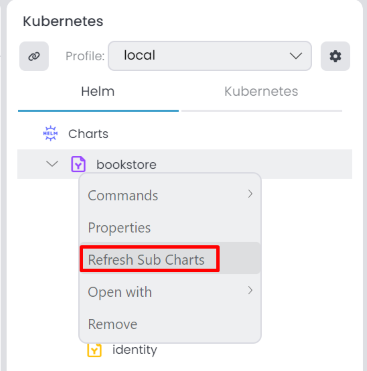
Then, update Metadata information right-click the gateway sub-chart, select Properties it open Chart Properties window. You can edit in the Metadata tab.
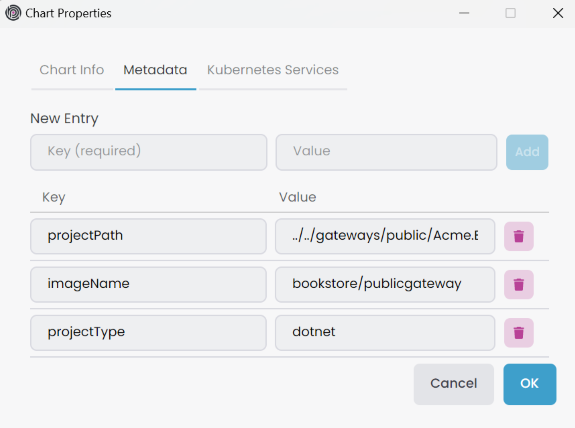
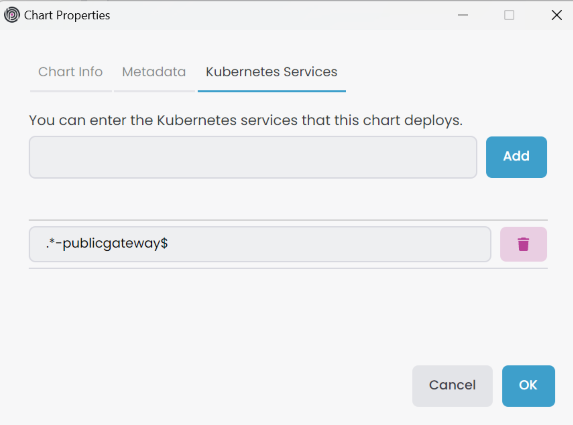
Add the service name Regex pattern Kubernetes Services in the Chart Properties -> Kubernetes Services tab.
Last but not least, we need to configure the helm chart environments for identity microservice and auth-server application.
# identity.yaml
# Add this line to the "env:" section
- name: "OpenIddict__Applications__PublicGateway__RootUrl"
value: "{{ include "bookstore.hosts.publicgateway" . }}"
# authserver.yaml
# Concat the following lines for "App__CorsOrigins" section
- name: "App__CorsOrigins"
value: "...,http://{{ .Release.Name }}-administration,{{ include "bookstore.hosts.publicgateway" . }}"
































































