HTTP Error Handling
Error Configurations
ABP offers a configurations for errors handling like below
import { ThemeSharedModule } from '@abp/ng.theme.shared';
import { MyCustomRouteErrorComponent } from './my-custom-route.component';
@NgModule({
imports: [
ThemeSharedModule.forRoot({
httpErrorConfig: {
skipHandledErrorCodes: [403],
errorScreen: {
forWhichErrors: [404],
component: CustomErrorComponent,
hideCloseIcon: false
}
}
}),
...
],
})
export class AppModule {}
ErrorScreenErrorCodesthe error codes that you can pass toskipHandledErrorCodesandforWhichErrors.skipHandledErrorCodesthe error codes those you don't want to handle.errorScreenthe screen that you want to show when a route error occurs.componentcomponent that you want to show.forWhichErrorssame asErrorScreenErrorCodeshideCloseIconhides close icon in default ABP component.
Custom HTTP Error Handler
When the RestService is used, all HTTP errors are reported to the HttpErrorReporterService, and then ErrorHandler, a service exposed by the @abp/ng.theme.shared package automatically handles the errors.
Function Method Deprecated
A custom HTTP error handler can be registered to an injection token named HTTP_ERROR_HANDLER. If a custom handler function is registered, the ErrorHandler executes that function.
See an example:
// http-error-handler.ts
import { ContentProjectionService, PROJECTION_STRATEGY } from '@abp/ng.core';
import { ToasterService } from '@abp/ng.theme.shared';
import { HttpErrorResponse } from '@angular/common/http';
import { Injector } from '@angular/core';
import { of, EMPTY } from 'rxjs';
import { Error404Component } from './error404/error404.component';
export function handleHttpErrors(injector: Injector, httpError: HttpErrorResponse) {
if (httpError.status === 400) {
const toaster = injector.get(ToasterService);
toaster.error(httpError.error?.error?.message || 'Bad request!', '400');
return EMPTY;
}
if (httpError.status === 404) {
const contentProjection = injector.get(ContentProjectionService);
contentProjection.projectContent(PROJECTION_STRATEGY.AppendComponentToBody(Error404Component));
return EMPTY;
}
return of(httpError);
}
// app.module.ts
import { Error404Component } from './error404/error404.component';
import { handleHttpErrors } from './http-error-handling';
import { HTTP_ERROR_HANDLER, ... } from '@abp/ng.theme.shared';
@NgModule({
// ...
providers: [
// ...
{ provide: HTTP_ERROR_HANDLER, useValue: handleHttpErrors }
],
declarations: [
//...
Error404Component],
})
export class AppModule {}
In the example above:
Created a function named
handleHttpErrorsand defined as value of theHTTP_ERROR_HANDLERprovider in app.module. After this, the function executes when an HTTP error occurs.400 bad request errors is handled. When a 400 error occurs.
Since
of(httpError)is returned at bottom of thehandleHttpErrors, theErrorHandlerwill handle the HTTP errors except 400 and 404 errors.
Note 1: If you put return EMPTY to next line of handling an error, default error handling will not work for that error. EMPTY can be imported from rxjs.
export function handleHttpErrors(
injector: Injector,
httpError: HttpErrorResponse
) {
if (httpError.status === 403) {
// handle 403 errors here
return EMPTY; // put return EMPTY to skip default error handling
}
}
Note 2: If you put return of(httpError), default error handling will work.
ofis a function. It can be imported fromrxjs.httpErroris the second parameter of the error handler function which is registered to theHTTP_ERROR_HANDLERprovider. Type of thehttpErrorisHttpErrorResponse.
import { of } from "rxjs";
export function handleHttpErrors(
injector: Injector,
httpError: HttpErrorResponse
) {
if (httpError.status === 500) {
// handle 500 errors here
}
// you can return the of(httpError) at bottom of the function to run the default handler of ABP for HTTP errors that you didn't handle above.
return of(httpError);
}
Service Method
You can provide more than one handler with services, a custom HTTP error handler service can be registered with injection token named CUSTOM_ERROR_HANDLERS. ABP has some default error handlers.
How To Add New Handler Service
ABP error handler services are implements the interface of CustomHttpErrorHandlerService.
Interface of CUSTOM_ERROR_HANDLERS
interface CustomHttpErrorHandlerService {
readonly priority: number;
canHandle(error: unknown): boolean;
execute(): void;
}
priorityABP sorts the services according to the number of the priority variable. Higher priority will be checked first.canHandleCheck if the service can handle the error. Returns boolean.executeIf the service can handle the error, then run the execute method.
In Summary
- Services are sorted by their priority number.
- Start from highest priority service and run canHandle() method. Pick the service if can handle the error, if not check next service.
- If the service found, run the execute method of a service. Done.
See an example:
// custom-error-handler.service.ts
import { inject, Injectable } from "@angular/core";
import { HttpErrorResponse } from "@angular/common/http";
import { CustomHttpErrorHandlerService } from "@abp/ng.theme.shared";
import { CUSTOM_HTTP_ERROR_HANDLER_PRIORITY } from "@abp/ng.theme.shared";
import { ToasterService } from "@abp/ng.theme.shared";
@Injectable({ providedIn: "root" })
export class MyCustomErrorHandlerService
implements CustomHttpErrorHandlerService
{
// You can write any number here, ex: 9999
readonly priority = CUSTOM_HTTP_ERROR_HANDLER_PRIORITY.veryHigh;
protected readonly toaster = inject(ToasterService);
private error: HttpErrorResponse | undefined = undefined;
// What kind of error should be handled by this service? You can decide it in this method. If error is suitable to your case then return true; otherwise return false.
canHandle(error: unknown): boolean {
if (error instanceof HttpErrorResponse && error.status === 400) {
this.error = error;
return true;
}
return false;
}
// If this service is picked from ErrorHandler, this execute method will be called.
execute() {
this.toaster.error(
this.error.error?.error?.message || "Bad request!",
"400"
);
}
}
// app.module.ts
import { CUSTOM_ERROR_HANDLERS, ... } from '@abp/ng.theme.shared';
import { MyCustomErrorHandlerService } from './custom-error-handler.service';
@NgModule({
// ...
providers: [
// ...
{
provide: CUSTOM_ERROR_HANDLERS,
useExisting: MyCustomErrorHandlerService,
multi: true,
}
]
})
export class AppModule {}
In the example above:
Created a service named
MyCustomErrorHandlerService, and provided viauseExistingkey because we dont want another instance of it. And setmultikey to true because ABP default error handlers are also provided with CUSTOM_ERROR_HANDLERS injection token.400 errors are handled from custom
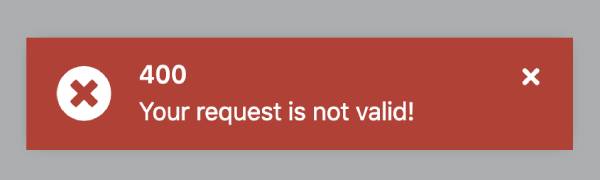
MyCustomErrorHandlerService. When a 400 error occurs, backend error message will be displayed as shown below:
Notes
- If your service cannot handle the error. Then ABP will check the next Error Service.
- If none of the service handle the error. Then basic confirmation message about the error will be shown to the user.
- You can provide more than one service, with CUSTOM_ERROR_HANDLER injection token.
- If you want your custom service to be evaluated (checked) earlier, set the priority variable high.
































































