Layered Solution: Database configurations
Some of the features mentioned in this document may not be available in the free version. We're using the * symbol to indicate that a feature is available in the Team and Higher licenses.
ABP Studio's Layered Solution Template includes pre-configured database settings. This document explains how to manage database configurations in your solution.
Connection Strings
Connection strings are stored in the appsettings.json file. You can customize them for different environments by modifying the respective appsettings.json files. The *.DbMigrator project and one of the Web Application projects use the Default connection string by default.
To change the connection string for the Default key, update the appsettings.json file in your project. Connection strings are defined under the ConnectionStrings section, as shown below:
{
"ConnectionStrings": {
"Default": "Server=(LocalDb)\\MSSQLLocalDB;Database=Bookstore;Trusted_Connection=True;TrustServerCertificate=true"
}
}
The DbContext Class
In the *.EntityFrameworkCore project, the DbContext class is defined. The DbContext class is derived from the AbpDbContext class, which is a part of the ABP Framework.
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(IIdentityProDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(ISaasDbContext))]
[ConnectionStringName("Default")]
public class BookstoreDbContext :
AbpDbContext<BookstoreDbContext>,
ISaasDbContext,
IIdentityProDbContext
{
#region Entities from the modules
// Identity
public DbSet<IdentityUser> Users { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentityRole> Roles { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentityClaimType> ClaimTypes { get; set; }
public DbSet<OrganizationUnit> OrganizationUnits { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentitySecurityLog> SecurityLogs { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentityLinkUser> LinkUsers { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentityUserDelegation> UserDelegations { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentitySession> Sessions { get; set; }
// SaaS
public DbSet<Tenant> Tenants { get; set; }
public DbSet<Edition> Editions { get; set; }
public DbSet<TenantConnectionString> TenantConnectionStrings { get; set; }
#endregion
public BookstoreDbContext(DbContextOptions<BookstoreDbContext> options)
: base(options)
{
}
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(builder);
builder.ConfigurePermissionManagement();
builder.ConfigureSettingManagement();
builder.ConfigureBackgroundJobs();
builder.ConfigureAuditLogging();
builder.ConfigureFeatureManagement();
builder.ConfigureIdentityPro();
builder.ConfigureOpenIddictPro();
builder.ConfigureLanguageManagement();
builder.ConfigureSaas();
builder.ConfigureTextTemplateManagement();
builder.ConfigureGdpr();
builder.ConfigureCmsKit();
builder.ConfigureCmsKitPro();
builder.ConfigureBlobStoring();
/* Configure your own tables/entities inside here */
//builder.Entity<YourEntity>(b =>
//{
// b.ToTable(BookstoreConsts.DbTablePrefix + "YourEntities", BookstoreConsts.DbSchema);
// b.ConfigureByConvention(); //auto configure for the base class props
// //...
//});
}
}
ConnectionStringName Attribute
We're using the Default connection string in the BookstoreDbContext class. You can change the connection string name by updating the ConnectionStringName attribute.
[ConnectionStringName("Default")]
The ConnectionStringName attribute defines the unique name of the connection string that is being used by that DbContext class. It matches with the connection string defined in the appsettings.json file. That name is also used in database migrations to distinguish different database schemas, and used as the key while storing tenant connection strings for a multi-tenant system.
ReplaceDbContext Attribute
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(IIdentityProDbContext))]
[ReplaceDbContext(typeof(ISaasDbContext))]
The application DbContext utilizes the Identity and Saas * modules and creates a single database that contains these modules database schemas. These modules define their own DbContext class normally. But the ReplaceDbContext attribute tells to ABP to use this (BookstoreDbContext) DbContext class instead of the DbContext classes defined by these modules. Technically, it replaces the given DbContext classes on runtime. We are doing that to ensure that we have a single (merged) database schema, single database migration path and a single database transaction operation when we work these multiple modules. When we replace a DbContext, we should implement its interface as done with the BookstoreDbContext class:
public class BookstoreDbContext :
AbpDbContext<BookstoreDbContext>,
ISaasDbContext,
IIdentityProDbContext
- That class implements
ISaasDbContextandIIdentityProDbContext, so these modules can use it.
As the next part, the BookstoreDbContext class defines the following properties those are forced by the implemented interfaces:
// Identity
public DbSet<IdentityUser> Users { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentityRole> Roles { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentityClaimType> ClaimTypes { get; set; }
public DbSet<OrganizationUnit> OrganizationUnits { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentitySecurityLog> SecurityLogs { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentityLinkUser> LinkUsers { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentityUserDelegation> UserDelegations { get; set; }
public DbSet<IdentitySession> Sessions { get; set; }
// SaaS
public DbSet<Tenant> Tenants { get; set; }
public DbSet<Edition> Editions { get; set; }
public DbSet<TenantConnectionString> TenantConnectionStrings { get; set; }
OnModelCreating Method
The OnModelCreating method is used to configure the database schema. It calls the Configure* methods of the ABP Framework to configure the database schema for the modules. You can also configure your own tables/entities inside this method.
protected override void OnModelCreating(ModelBuilder builder)
{
base.OnModelCreating(builder);
builder.ConfigurePermissionManagement();
builder.ConfigureSettingManagement();
builder.ConfigureBackgroundJobs();
builder.ConfigureAuditLogging();
builder.ConfigureFeatureManagement();
builder.ConfigureIdentityPro();
builder.ConfigureOpenIddictPro();
builder.ConfigureLanguageManagement();
builder.ConfigureSaas();
builder.ConfigureTextTemplateManagement();
builder.ConfigureGdpr();
builder.ConfigureCmsKit();
builder.ConfigureCmsKitPro();
builder.ConfigureBlobStoring();
/* Configure your own tables/entities inside here */
//builder.Entity<YourEntity>(b =>
//{
// b.ToTable(BookstoreConsts.DbTablePrefix + "YourEntities", BookstoreConsts.DbSchema);
// b.ConfigureByConvention(); //auto configure for the base class props
// //...
//});
}
The
Configure*methods are extension methods defined in each module'sEntityFrameworkCoreproject. These methods are used to configure the database schema for their respective modules. At runtime, theDbContextclass is replaced by theBookstoreDbContextclass only for theDbContextclasses that use theReplaceDbContextattribute. For other modules, their own dedicatedDbContextclasses are used without replacement.
The IDesignTimeDbContextFactory Implementation
The IDesignTimeDbContextFactory interface is used to create a DbContext instance at design time. It is used by EF Core tools to create migrations and update the database. The BookstoreDbContextFactory class implements the IDesignTimeDbContextFactory interface to create a BookstoreMigrationsDbContext instance.
public class BookstoreDbContextFactory : IDesignTimeDbContextFactory<BookstoreDbContext>
{
public BookstoreDbContext CreateDbContext(string[] args)
{
var configuration = BuildConfiguration();
BookstoreEfCoreEntityExtensionMappings.Configure();
var builder = new DbContextOptionsBuilder<BookstoreDbContext>()
.UseSqlServer(configuration.GetConnectionString("Default"));
return new BookstoreDbContext(builder.Options);
}
private static IConfigurationRoot BuildConfiguration()
{
var builder = new ConfigurationBuilder()
.SetBasePath(Path.Combine(Directory.GetCurrentDirectory(), "../Acme.Bookstore.DbMigrator/"))
.AddJsonFile("appsettings.json", optional: false);
return builder.Build();
}
}
Configuration
In the *.EntityFrameworkCore project, the BookstoreEntityFrameworkCoreModule class is used to configure the database context.
public override void ConfigureServices(ServiceConfigurationContext context)
{
context.Services.AddAbpDbContext<BookstoreDbContext>(options =>
{
/* Remove "includeAllEntities: true" to create
* default repositories only for aggregate roots */
options.AddDefaultRepositories(includeAllEntities: true);
});
Configure<AbpDbContextOptions>(options =>
{
/* The main point to change your DBMS.
* See also BookstoreDbContextFactory for EF Core tooling. */
options.UseSqlServer();
});
}
We are basically setting the SQL Server as the default DBMS for this application. and registering the BookstoreDbContext class to the dependency injection system.
SaaS Module: The Tenant Management UI *
SaaS module provides the necessary UI to set and change connection string for tenants and trigger the database migrations.
The Connection String Management Modal
You can click to the Database Connection Strings command in the Actions dropdown button for a tenant in the Tenants page of the SaaS module:
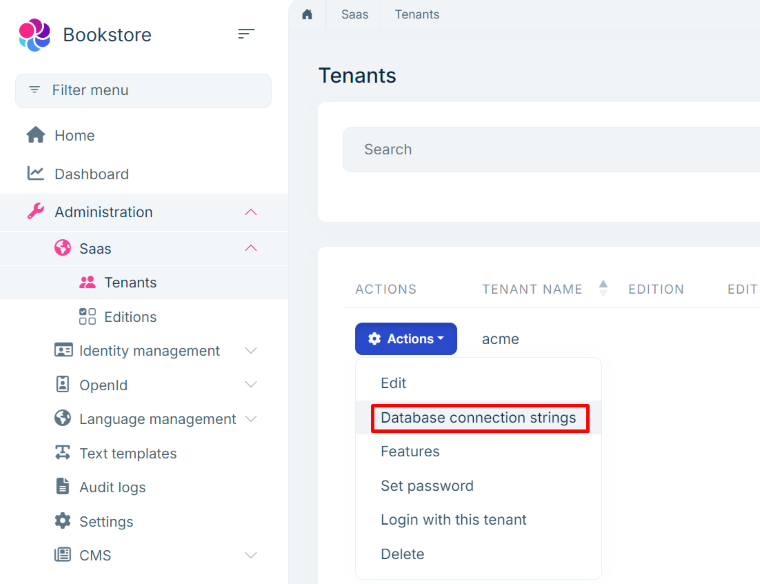
It opens the Database Connection Strings modal as shown below:
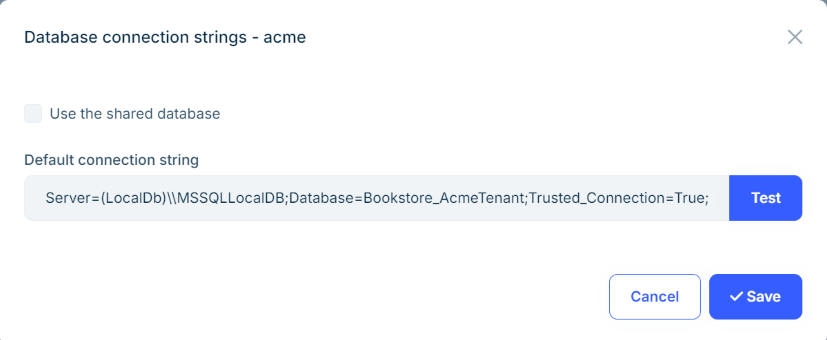
Here, we can set a Default connection string for the tenant.
When you make the changes and save the dialog, the database is automatically created and migrated. If you later update the connection string (for example if you change the database name), it will also trigger the database migration process again.
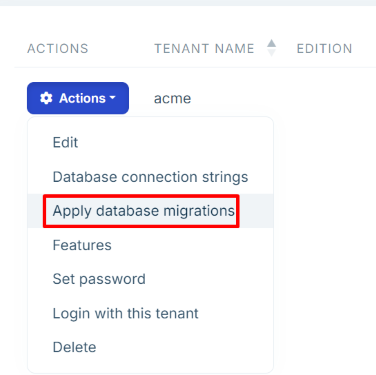
Manually Applying the Database Migrations
If you need to manually trigger the database migrations for a specific tenant, click the Actions dropdown for the related tenant and select the Apply Database Migrations command on the Tenant Management page of the SaaS module: