Localization
Before exploring the localization pipe and the localization service, you should go over the localization keys.
The localization key format consists of two sections which are Resource Name and Key.
ResourceName::Key
If you do not specify the resource name, the
defaultResourceNamewhich is declared inenvironment.tswill be considered as default.
const environment = {
// ...
localization: {
defaultResourceName: "MyProjectName",
},
};
So, these two will give the same results:
<h1>{{ '::Key' | abpLocalization }}</h1>
<h1>{{ 'MyProjectName::Key' | abpLocalization }}</h1>
Using the Localization Pipe
You can use the abpLocalization pipe to get localized text as in this example:
<h1>{{ 'Resource::Key' | abpLocalization }}</h1>
This pipe will replace the key with the localized text.
You can also specify a default value as shown below:
<h1>
{{ { key: 'Resource::Key', defaultValue: 'Default Value' } |
abpLocalization }}
</h1>
In order to use the interpolation, you must give the parameters for the pipe, as an example:
Localization data is stored in key-value pairs:
{
// ...
AbpAccount: { // AbpAccount is the resource name
Key: "Value",
PagerInfo: "Showing {0} to {1} of {2} entries"
}
}
Then, we can use this key like this:
<h1>{{ 'AbpAccount::PagerInfo' | abpLocalization:'20':'30':'50' }}</h1>
<!-- Output: Showing 20 to 30 of 50 entries -->
Using the Localization Service
First of all, you should import the LocalizationService from @abp/ng.core
import { LocalizationService } from '@abp/ng.core';
import { inject } from '@angular/core';
class MyClass {
private localizationService = inject(LocalizationService);
}
After that, you will be able to use the localization service.
You can add interpolation parameters as arguments to
instant()andget()methods.
this.localizationService.instant(
"AbpIdentity::UserDeletionConfirmation",
"John"
);
// with fallback value
this.localizationService.instant(
{
key: "AbpIdentity::UserDeletionConfirmation",
defaultValue: "Default Value",
},
"John"
);
// Output
// User 'John' will be deleted. Do you confirm that?
To get a localized text as Observable use get method instead of instant:
this.localizationService.get("Resource::Key");
// with fallback value
this.localizationService.get({
key: "Resource::Key",
defaultValue: "Default Value",
});
UI Localizations
Localizations can be determined on the backend side. Therefore, Angular UI gets the localization resources from the application-localization API's response then merges these resources with configuration state in ConfigStateService. You can also determine localizations on the UI side.
See an example:
import { provideAbpCore, withOptions } from "@abp/ng.core";
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [
// ...
provideAbpCore(
withOptions({
// ...,
localizations: [
{
culture: "en",
resources: [
{
resourceName: "MyProjectName",
texts: {
Administration: "Administration",
HomePage: "Home",
},
},
],
},
{
culture: "de",
resources: [
{
resourceName: "MyProjectName",
texts: {
Administration: "Verwaltung",
HomePage: "Startseite",
},
},
],
},
],
})
),
],
};
You can also declare the localizations in a feature provider configuration:
// your feature configuration
export function provideFeatureConfiguration(): EnvironmentProviders {
return provideAbpCoreChild({
localizations: [
{
culture: "en",
resources: [
{
resourceName: "MyProjectName",
texts: {
Administration: "Administration",
HomePage: "Home",
},
},
],
},
{
culture: "de-DE",
resources: [
{
resourceName: "MyProjectName",
texts: {
Administration: "Verwaltung",
HomePage: "Startseite",
},
},
],
},
],
});
}
The localizations above can be used like this:
<div>{{ 'MyProjectName::Administration' | abpLocalization }}</div>
<div>{{ 'MyProjectName::HomePage' | abpLocalization }}</div>
Note: If you have specified the same localizations in the UI and backend, the backend localizations override the UI localizations.
RTL Support
As of v2.9 ABP supports RTL. If you are generating a new project with v2.9 and above, everything is set, there is no need to make any changes. If you are migrating your project from an earlier version, please follow the 2 steps below:
Step 1. Create Chunks for Bootstrap LTR and RTL
Find styles configuration in angular.json and make sure the chunks in your project has bootstrap-rtl.min and bootstrap-ltr.min as shown below.
{
"projects": {
"MyProjectName": {
"architect": {
"build": {
"options": {
"styles": [
{
"input": "node_modules/@fortawesome/fontawesome-free/css/all.min.css",
"inject": true,
"bundleName": "fontawesome-all.min"
},
{
"input": "node_modules/@fortawesome/fontawesome-free/css/v4-shims.min.css",
"inject": true,
"bundleName": "fontawesome-v4-shims.min"
},
{
"input": "node_modules/@abp/ng.theme.shared/styles/bootstrap-rtl.min.css",
"inject": false,
"bundleName": "bootstrap-rtl.min"
},
{
"input": "node_modules/bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.min.css",
"inject": true,
"bundleName": "bootstrap-ltr.min"
},
"apps/dev-app/src/styles.scss"
]
}
}
}
}
}
}
Step 2. Clear Lazy Loaded Fontawesome in AppComponent
If you have created and injected chunks for Fontawesome as seen above, you no longer need the lazy loading in the AppComponent which was implemented before v2.9. Simply remove them. The AppComponent in the template of the new version looks like this:
import { Component } from "@angular/core";
@Component({
selector: "app-root",
template: `
<abp-loader-bar />
<router-outlet />
`,
})
export class AppComponent {}
Registering a New Locale
Since ABP has more than one language, Angular locale files load lazily using Webpack's import function to avoid increasing the bundle size and to register the Angular core using the registerLocaleData function. The chunks to be included in the bundle are specified by the Webpack's magic comments as hard-coded. Therefore a registerLocale function that returns Webpack import function must be passed to provideAbpCore(withOptions({...})).
registerLocaleFn
The registerLocale function, exported from the @abp/ng.core/locale package, is a higher-order function.
It accepts the following parameters:
cultureNameLocaleFileMap– an object that maps culture names to their corresponding locale files.errorHandlerFn– a function that handles any errors that occur during locale loading.
It returns a Webpack import function.
You should use registerLocale within the withOptions function of provideAbpCore, as shown in the example below:
import { provideAbpCore, withOptions } from "@abp/ng.core";
import { registerLocale } from "@abp/ng.core/locale";
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [
// ...
provideAbpCore(
withOptions({
// ...,
registerLocaleFn: registerLocale(
// you can pass the cultureNameLocaleFileMap and errorHandlerFn as optionally
{
cultureNameLocaleFileMap: { "pt-BR": "pt" },
errorHandlerFn: ({ resolve, reject, locale, error }) => {
// the error can be handled here
},
}
),
})
),
// ...
],
};
Mapping of Culture Name to Angular Locale File Name
Some of the culture names defined in .NET do not match Angular locales. In such cases, the Angular app throws an error like below at runtime:
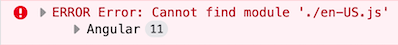
If you see an error like this, you should pass the cultureNameLocaleFileMap property like below to the registerLocale function.
// app.config.ts
import { registerLocale } from "@abp/ng.core/locale";
// if you have commercial license and the language management module, add the below import
// import { registerLocale } from '@volo/abp.ng.language-management/locale';
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [
// ...
provideAbpCore(
withOptions({
// ...,
registerLocaleFn: registerLocale({
cultureNameLocaleFileMap: {
DotnetCultureName: "AngularLocaleFileName",
"pt-BR": "pt", // example
},
}),
})
),
],
};
See all locale files in Angular.
Adding a New Culture
If you want to register a new language, you can add the code below to the app.config.ts by replacing your-locale placeholder with a correct locale name.
//app.config.ts
import { storeLocaleData } from "@abp/ng.core/locale";
import(
/* webpackChunkName: "_locale-your-locale-js"*/
/* webpackMode: "eager" */
"@angular/common/locales/your-locale.js"
).then((m) => storeLocaleData(m.default, "your-locale"));
You can also configure a custom registerLocale function that can be passed to the abp core provider configuration options:
// register-locale.ts
import { differentLocales } from "@abp/ng.core";
export function registerLocale(locale: string) {
return import(
/* webpackChunkName: "_locale-[request]"*/
/* webpackInclude: /[/\\](/docs/latest/framework/ui/angular/en%7Cfr).js/ */
/* webpackExclude: /[/\\]global|extra/ */
`@angular/common/locales/${differentLocales[locale] || locale}.js`
);
}
// app.config.ts
import { registerLocale } from "./register-locale";
export const appConfig: ApplicationConfig = {
providers: [
// ...
provideAbpCore(
withOptions({
// ...,
registerLocaleFn: registerLocale,
})
),
//...
],
};
After adding a custom registerLocale function, only the en and fr locale files will be created as separate chunks.
This happens because only these locales are included in the webpackInclude configuration.

The locale files that you added to the webpackInclude magic comment will be included in the bundle.






























































