Microservice Tutorial Part 02: Creating the initial Catalog service
In this tutorial, you will create a new Catalog service and integrate it to the solution.
Creating the Catalog Service
Right-click the services folder in the Solution Explorer panel, select the Add -> New Module -> Microservice command:
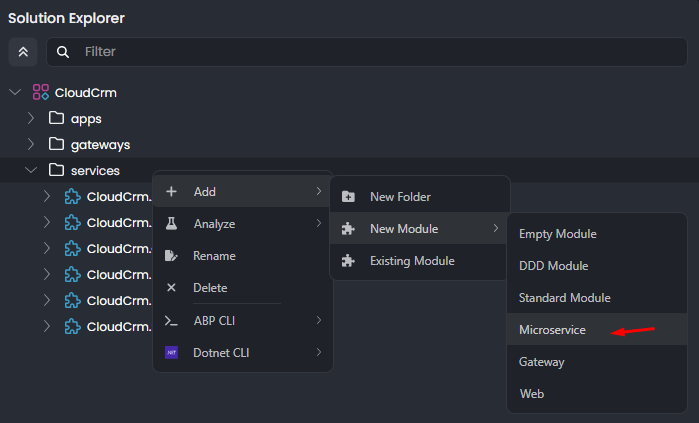
This command opens a new dialog to define the properties of the new microservice. You can use the following values to create a new microservice named CatalogService:
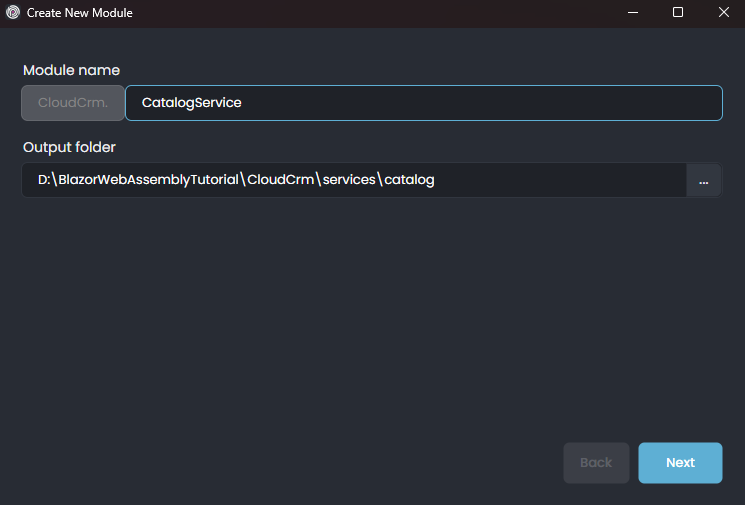
When you click the Next button, you are redirected to the database provider selection step.
Selecting the Database Type
Here, you can select the database provider to be used by the new microservice:
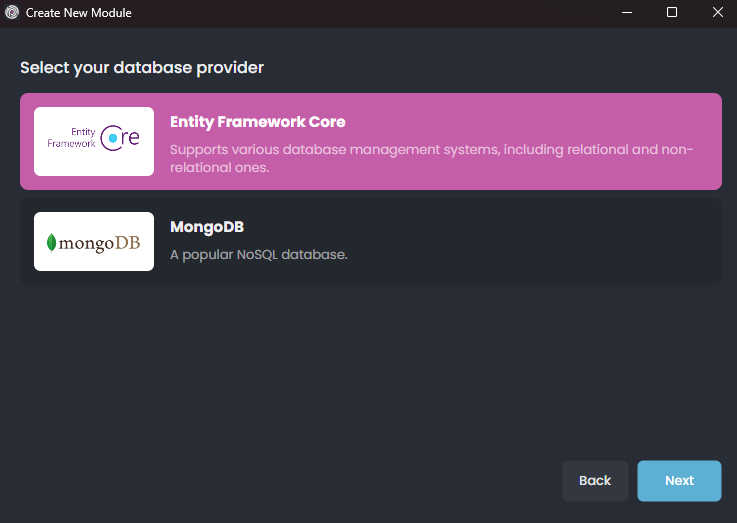
Select Entity Framework Core option and proceed the Next step.
Selecting Database Management System
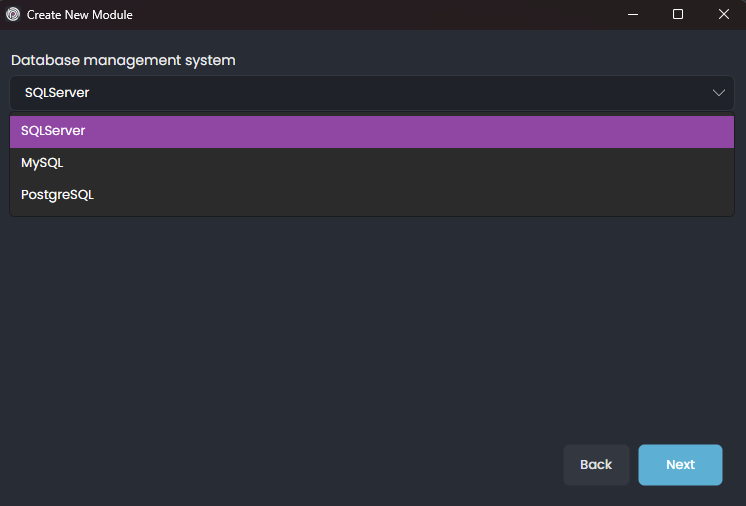
Select the desired option and proceed to the next step.
Additional Options
In this step, you can select additional options for the new microservice. You can leave them as default and click the Create button.
That's all, ABP Studio creates the new microservice and arranges all the integration and configuration for you.
Integrating to the Solution
In this step, we can select the options for integrating the new microservice to the rest of the solution components:
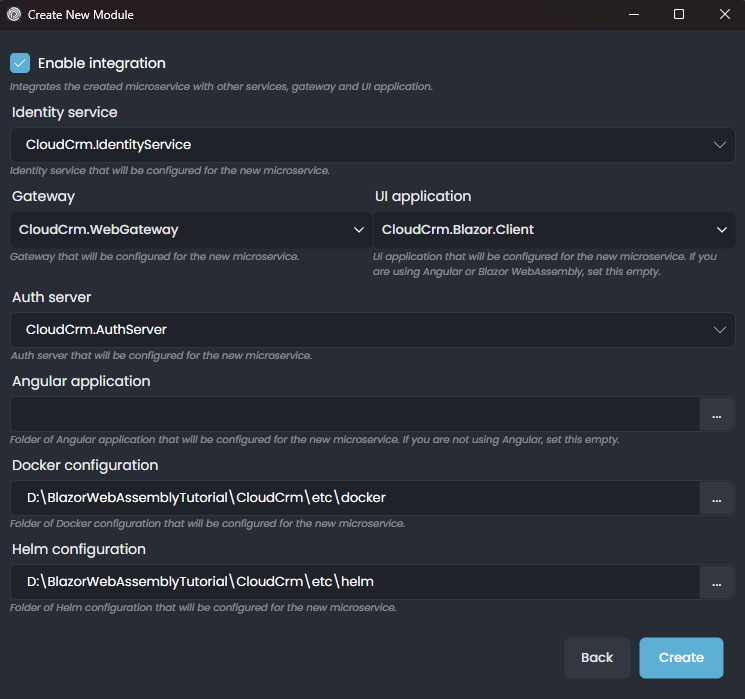
ABP Studio intelligently selects the right values for you, but you should still check them carefully since they directly affect what we will do in the next parts of this tutorial.
Ensure the options are configured the same as in the preceding figure, and click the Next button.
Exploring the New Catalog Microservice
In this section, we will investigate the new microservice in overall.
Understanding the Packages of The Service
The new microservice is added under the services folder in the CloudCrm ABP Studio solution:
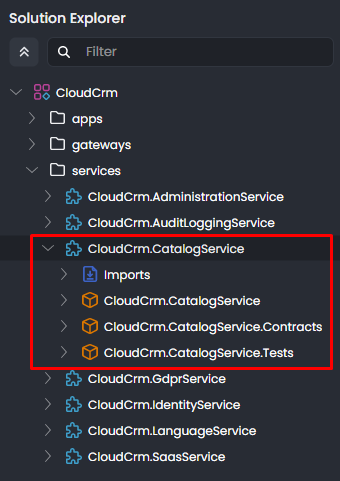
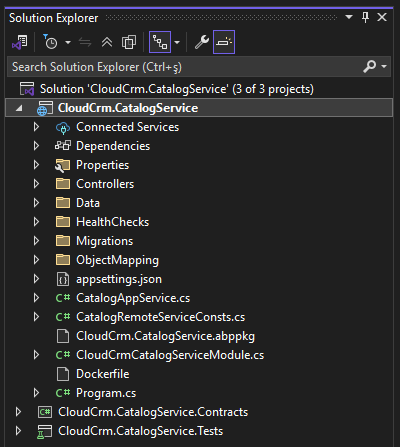
The new microservice has its own separate .NET solution that includes three packages (.NET projects):
CloudCrm.CatalogServiceis the main project that you will implement your service. It typically contains your entities, repositories, application services, API controllers, etc.CloudCrm.CatalogService.Contractsproject can be shared with the other services and applications. It typically contains interfaces of your application services, data transfer objects, and some other types you may want to share with the clients of this microservice.CloudCrm.CatalogService.Testsis for building your unit and integration tests for this microservice.
Opening the Service in an IDE
You can open the new microservice in your favorite IDE for development. As a shortcut, you can right-click it in ABP Studio, select the Open with -> Visual Studio command for example:
Here is the CloudCrm.CatalogService .NET solution in Visual Studio:
Running the New Service
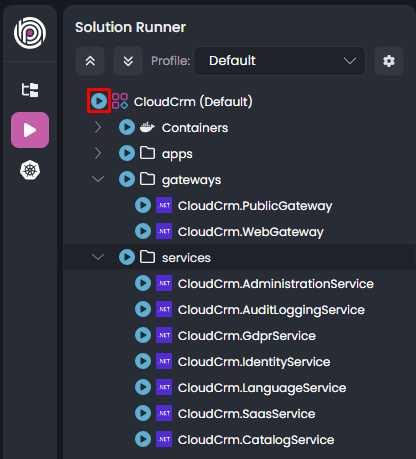
You can run the solution using ABP Studio's Solution Runner. It will also run the new Catalog service as a part of the solution.
Before running the solution, ensure that all the applications are built. If you are not sure, right-click the root item (
CloudCrm) in the Solution Explorer panel and select the Build -> Graph Build command.
Click the Play button near to the solution root:
Browsing the Catalog Service
Once all of the applications have started, right-click the Catalog service and select the Browse command:
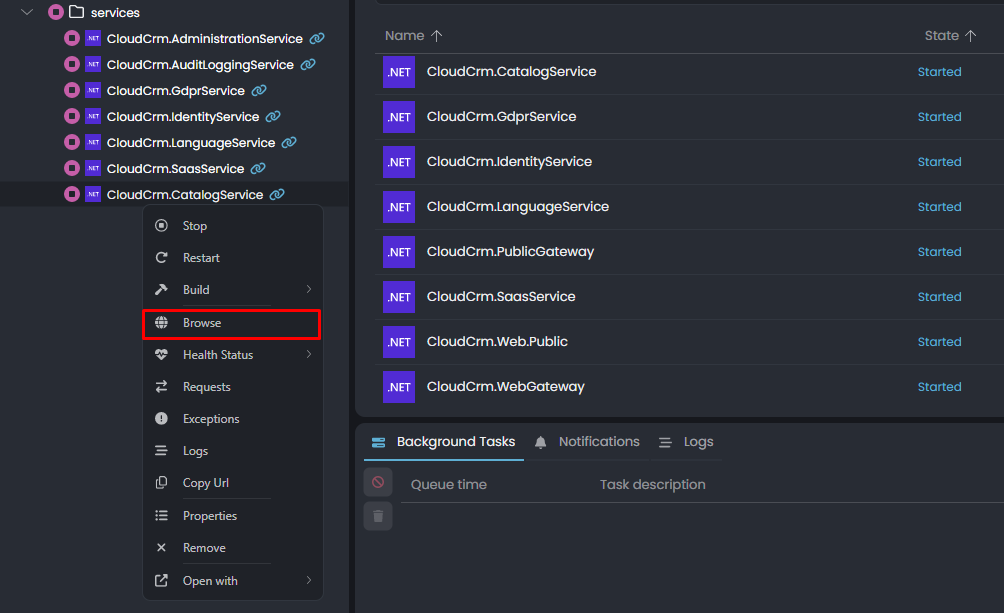
It will open the built-in browser and you will see the Swagger UI for the Catalog service:
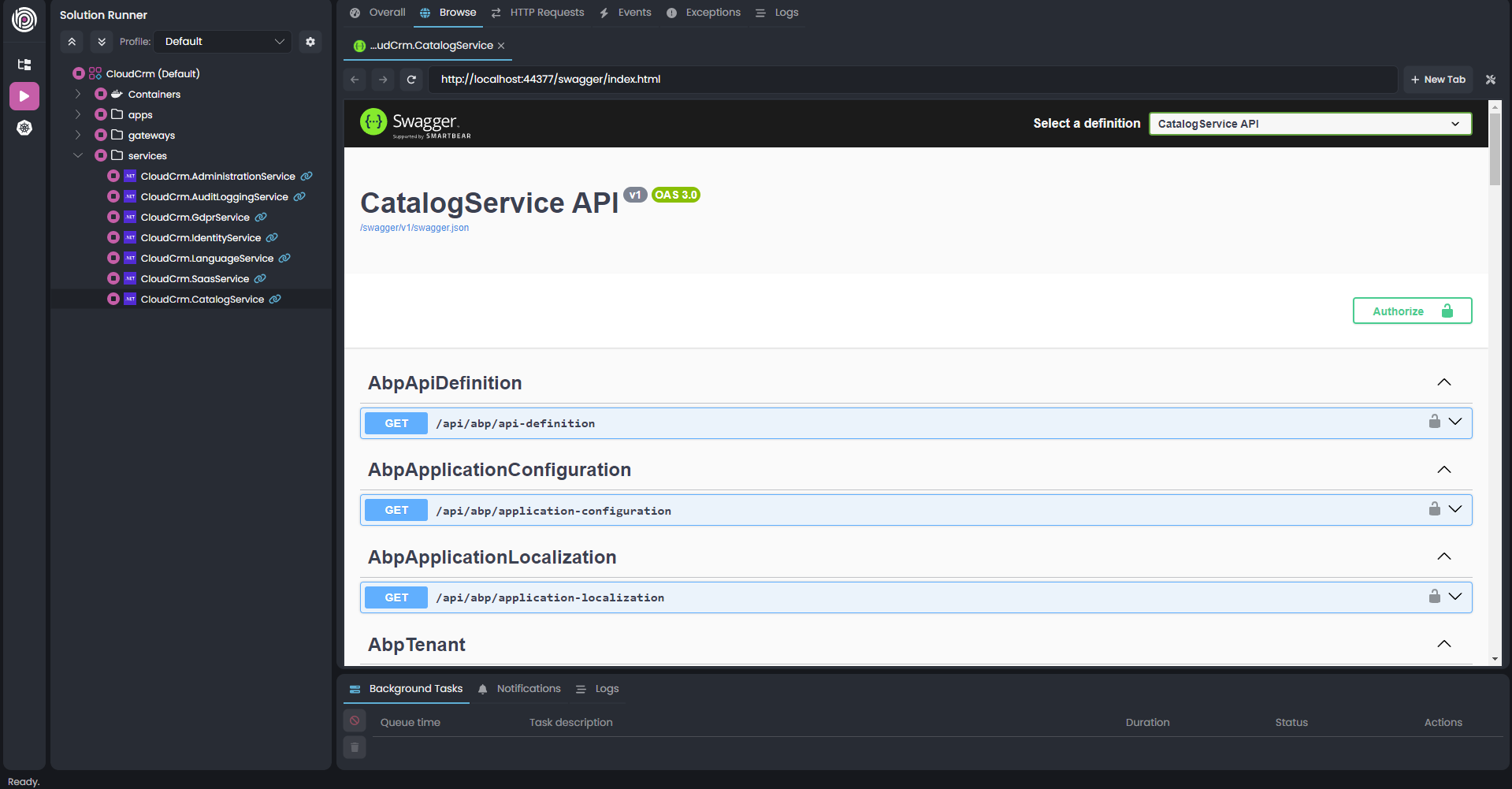
You can test the APIs on the Swagger UI to see if the new microservice is properly working.
Opening the Catalog Database
The new Catalog microservice has its own database. That database is created automatically by the microservice application, when you run the microservice. Also, Entity Framework's database migrations are automatically applied by the microservice when it runs. So, you don't care about the database schema changes every time you deploy the microservice.
Assuming you've selected SQL Server as your DBMS, you can open the SQL Server Management Studio to see its databases:
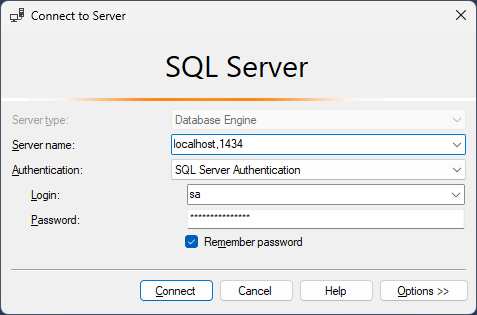
Use localhost,1434 as the Server name, select the SQL Server Authentication as the Authentication type, use sa as the Login name and myPassw@rd as the Password value. You can find these values in the appsettings.json file in the CloudCrm.CatalogService project of the .NET solution of the Catalog microservice.
Once you click the Connect button, you can see all the databases and explore their data:
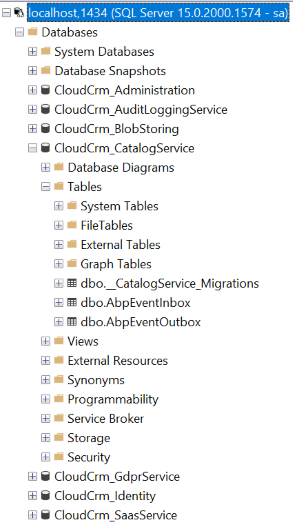
The Catalog service's database has only three initial table. The first one is for Entity Framework Core's migration system, and the others are for ABP's distributed event bus to properly apply transactional events using the outbox and inbox patterns. You don't need to care about these tables since they are created and managed by Entity Framework Core and ABP.
Summary
In this part of the Microservice Development Tutorial, we added a new Catalog microservice to the solution, explored its code structure and database, and browse its APIs using the Swagger UI. In the next part, we will create functionality in that new microservice.
































































