OpenIddict Deployment
OpenIddict is the default OpenId Provider library used by ABP templates through the OpenIddict Module. It is hosted by the AuthServer project in the tiered/seperate-authserver application templates. For non-tiered applications, it is hosted by the Web (MVC/Razor), BlazorServer or the HttpApi.Host project for Blazor and Angular applications.
Update Cors Origins
Cors origins configuration for gateways, microservices swagger authorization, and Angular/Blazor (web assembly) must be updated for deployment. This can be found under the App configuration in appsettings.json
"CorsOrigins": "https://*.MyProjectName.com,http://localhost:4200,https://localhost:44307,https://localhost:44325,https://localhost:44353,https://localhost:44367,https://localhost:44388,https://localhost:44381,https://localhost:44361",
Update Redirect Allowed URLs
If Angular or Blazor (Web Assembly) is used as a back-office web application, this configuration must be done. It is found under App configuration in appsettings.json.
"RedirectAllowedUrls": "http://localhost:4200,https://localhost:44307"
Update DbMigrator
OpenIddictDataSeedContributor uses OpenIddict.Applications section of appsettings.json for ClientId, RedirectUri, PostLogoutRedirectUri and CorsOrigins.
Update DbMigrator project appsettings.json OpenIddict.Applications.RootUrls with production values or override them:
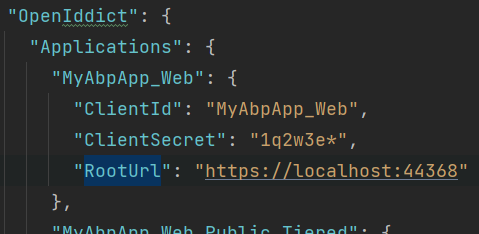
If you are using microservice template self-migration and not using DbMigrator project, update IdentityService appsettings.
Eventually, you shouldn't have any localhost related data.
Update AuthServer
In the development environment, OpenIddict uses a development encryption and signing certificate. In the production environment, this must be disabled. OpenIddict needs a real certificate for signing and encrypting the tokens.
Signing and Encryption Certificate
The default development environment uses developer signing certificates option. Using developer signing certificates may cause IDX10501: Signature validation failed error on production.
Update AuthServerModule by using a real certificate on OpenIddictBuilder pre-configuration.
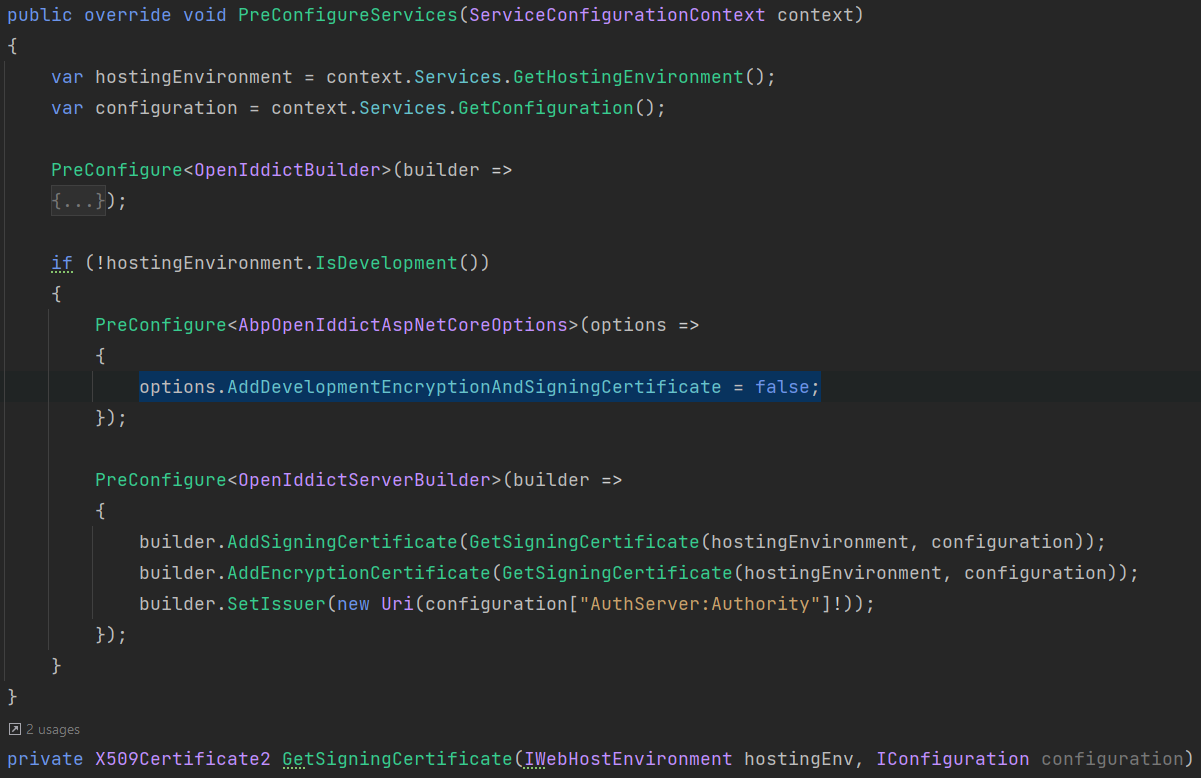
When you create a new application from the application template, ABP CLI automatically generates a new self-signed certificate with the name openiddict.pfx and a random password. This file and the password are provided in the GetSigningCertificate method.
Note: If you are receiving errors about not being able to reach the
openiddict.pfxfile on the server, make sure you have the necessary permissions.
The best place to store your certificates will depend on your host:
- For IIS applications, storing the certificates in the machine store is the recommended option.
- On Azure, certificates can be uploaded and exposed to Azure App Service applications using the special
WEBSITE_LOAD_CERTIFICATESflag. For more information, visit the Use a TLS/SSL certificate in your code in Azure App Service document.
Please check OpenIddict documentation for more information and using different types of signing/encryption keys.
Using or Disabling the HTTPS
AuthServer that hosts the OpenIddict openid-provider library uses the SSL/TLS binding of the ASP.NET Core middleware. If you host it on HTTPS, the Issuer will be hosted on HTTPS.
In some deployment scenarios, you may come across an error:
error: invalid_request
error_description: This server only accepts HTTPS requests.
error_uri: https//documnentation.openiddict.com/errors/ID2083
You can easily disable the HTTPS requirement from the appsettings.json:
"AuthServer": {
"Authority": "https://localhost:44369",
"RequireHttpsMetadata": "false"
},
This configuration can be found under the ConfigureServices method of the AuthServer project:
if (!Convert.ToBoolean(configuration["AuthServer:RequireHttpsMetadata"]))
{
Configure<OpenIddictServerAspNetCoreOptions>(options =>
{
options.DisableTransportSecurityRequirement = true;
});
}
Behind Load Balancer
You may need to forward the headers if you are using Nginx or Kubernetes Nginx Ingress.
Configure the options in the ConfigureServices method of AuthServerModule:
Configure<ForwardedHeadersOptions>(options =>
{
options.ForwardedHeaders = ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedFor | ForwardedHeaders.XForwardedProto;
});
And use the middleware in the OnApplicationInitialization method of AuthServerModule:
if (env.IsDevelopment())
{
app.UseDeveloperExceptionPage();
}
app.UseForwardedHeaders();
...
Sometimes, including forwarded headers in requests proxied to the application may be impossible.
If the proxy enforces that all public external requests are HTTPS, the scheme can be manually set before using any middleware.
Configure it under the OnApplicationInitialization method of AuthServerModule:
app.Use((httpContext, next) =>
{
httpContext.Request.Scheme = "https";
return next();
});
FAQ
- I see
Server Error 502!- Check your application logs under the Logs folder. A misconfiguration can prevent your application from starting up, and the easiest way is to pinpoint the problem by checking the logs.
System.IO.FileNotFoundException: Signing Certificate couldn't found!:- Ensure you have the .pfx file in the related location. The .pfx file should be marked as an embedded resource, and it should be in the publish directory when you publish your application.
- I can't see the login page! It shows an
HTTP 400error.- This is related to the generated URL from the application that tries to authenticate against the AuthServer. Check the AuthServer logs and make sure you have valid redirect_uri seeded from the OpenIddictDataSeedContributor and the application that redirects to AuthServer has the same configuration.






























































