Layered Solution: BLOB Storing
Some of the features mentioned in this document may not be available in the free version. We're using the * symbol to indicate that a feature is available in the Team and Higher licenses.
This document explains how to store BLOBs (Binary Large Objects) in a layered solution. It is common to store files, images, videos, and other large objects in a distributed system. You can learn more about BLOB storage in the BLOB Storing System documentation.
In the layered solution template, the Database Provider is used to store BLOBs in the database. The Volo.Abp.BlobStoring.Database.EntityFrameworkCore or Volo.Abp.BlobStoring.Database.MongoDB package provides the necessary implementations to store and retrieve BLOBs in the database. This setup is integrated into the layered solution template and is used in all related projects. You can change the database configuration in the appsettings.json file of the related project.
You can use the IBlobContainer or IBlobContainer<T> service to store and retrieve BLOBs. Here is an example of storing a BLOB:
public class MyService : ITransientDependency
{
private readonly IBlobContainer _blobContainer;
public MyService(IBlobContainer blobContainer)
{
_blobContainer = blobContainer;
}
public async Task SaveBytesAsync(byte[] bytes)
{
await _blobContainer.SaveAsync("my-blob-1", bytes);
}
public async Task<byte[]> GetBytesAsync()
{
return await _blobContainer.GetAllBytesOrNullAsync("my-blob-1");
}
}
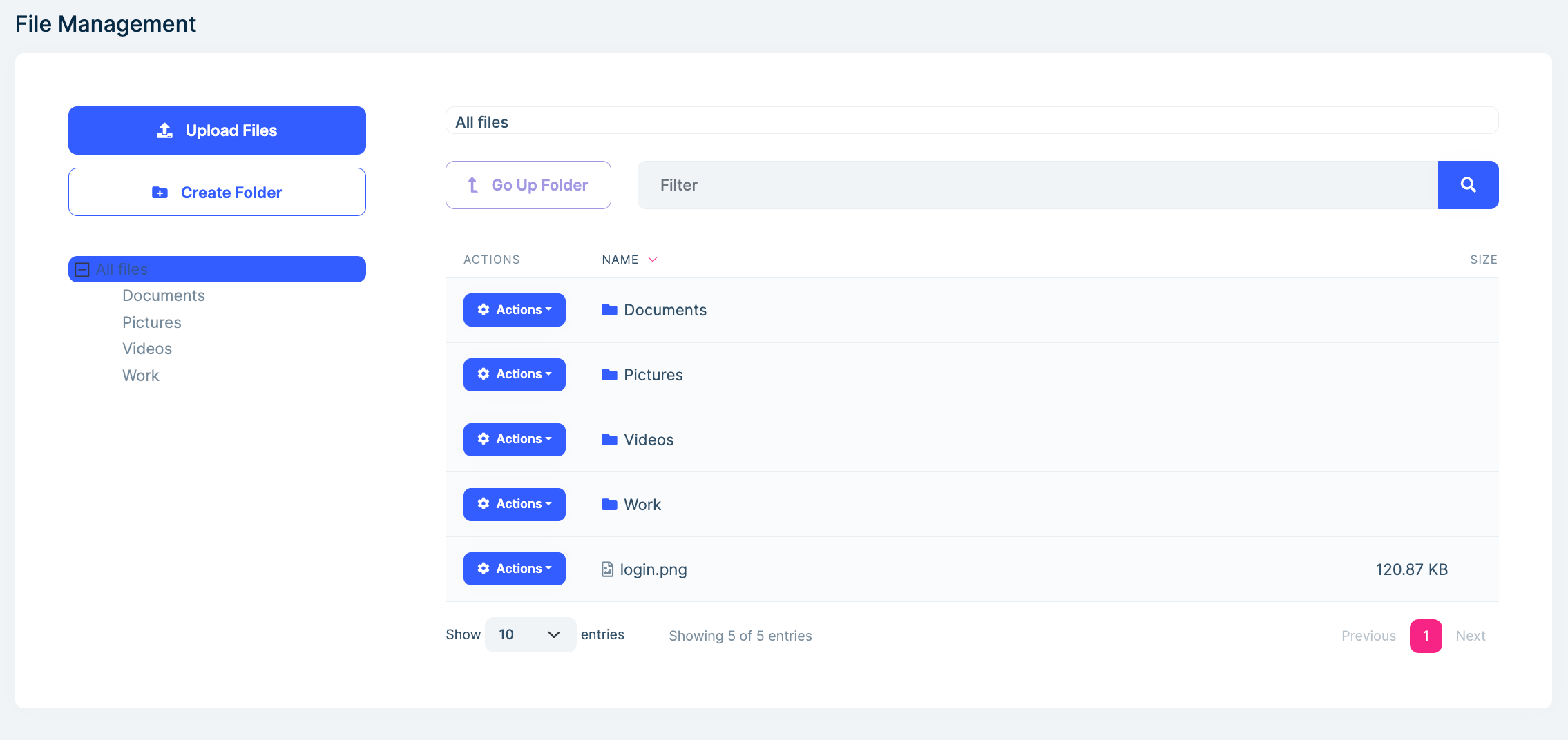
File Management Module
The File Management module is optional and can be added to the solution during the creation process. It provides a user interface to manage folders and files. You can learn more about the module in the File Management * document.